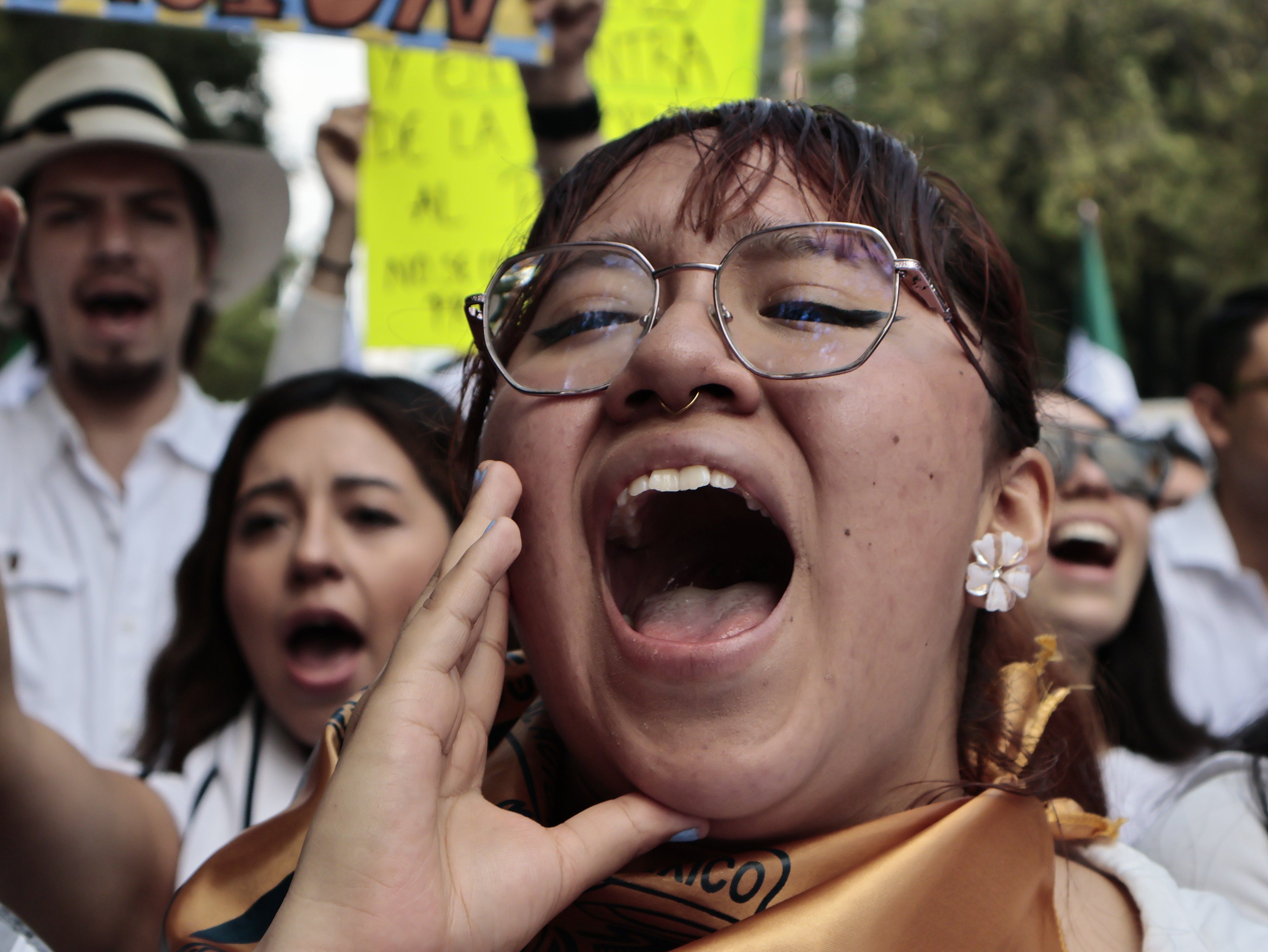On Wednesday, Mexico’s lower house approved a controversial judicial overhaul bill that would force federal judges to seek election. They voted while seated in a sports hall in Mexico City because protesters blocked access to Congress.
A day earlier, the country’s 11 Supreme Court justices voted 8-3 to join an ongoing strike of judges and judicial workers against the overhaul. Demonstrations have been underway for weeks in cities across Mexico.
The bill, which now heads to the Senate, is expected to pass despite all the opposition in the streets, and it will likely become law before President Andrés Manuel Lopez Obrador, aka AMLO, leaves office on Sept. 30.
Markets aren’t happy. Mexico’s peso is trading near two-year lows and has lost nearly 12% of its value since the presidential election in June. Putting judges up for election threatens to politicize decisions around potential investments in Mexico and diminish the country’s economic horizon. However, AMLO and his Morena party frame it as necessary to break the entrenched oligarchy and reduce corruption.
Neighbors aren’t thrilled, either. US Ambassador to Mexico Ken Salazar issued a rare direct criticism of the judicial overhaul, as did his Canadian counterpart Graeme Clark, leading AMLO to “pause” relations. (Important to note: Mexico paused relations with the embassies specifically, not the US and Canadian governments as a whole). The judicial overhaul is certain to become a flashpoint when the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement comes up for renegotiation in 2026.
What does it mean for the new president? AMLO’s incoming successor, Claudia Sheinbaum, will find herself without much of a honeymoon, says Eurasia Group’s Latin America Managing Director Daniel Kerner.
“The judicial overhaul creates problems with the private sector, with the judiciary, and with the US, which constrains how much of the rest of her agenda she can carry out,” he explains. “If this starts negatively impacting her popularity — which I think it will — then she’s gonna have to rely a lot more on Lopez Obrador and Morena.”