June 19, 2023
State Farm, the largest homeowner insurance company in California, recently announced that it’s halting new insurance sales across the Golden State. This is part of a nationwide trend of insurers raising rates, restricting coverage, or pulling out of areas altogether. Why? Because they’re tired of losing money to natural disasters.
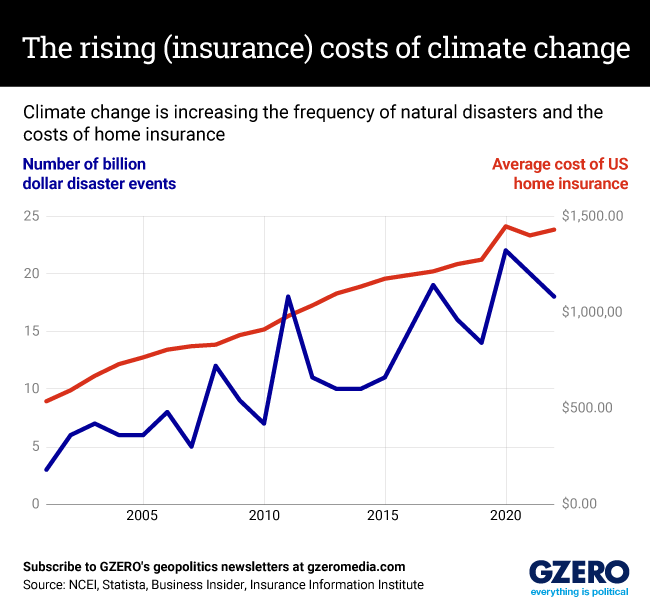
In the 1980s, for example, the US averaged three or four annual disasters with costs in the billions. But those numbers started to tick up significantly after 2010, and in 2021, 18 disasters cost $175.2 billion in damages.
Increasingly frequent natural disasters, in turn, are wreaking havoc on the insurance market and turning it into a system where, in some places, only the most affluent will be able to afford coverage. In 2021, FEMA, which had provided taxpayer-backed flood insurance nationwide, had to start setting rates equal to the flood risk. This change caused the average cost of flood insurance to jump from $888 a year to $1,808, with prices being exponentially higher for those in flood zones.
Florida is on the verge of an insurance crisis thanks to consecutive years of bad storms. Twelve private insurers in Florida have gone out of business since 2020, six in the last year alone, and 30 more are being monitored by state regulators over their risk of insolvency. Meanwhile, severe storms in the Midwest, droughts and wildfires in the Southwest, and flooding in Kentucky and Missouri have priced hundreds of thousands out of the system in the last year alone.
In Louisiana, the insurance market has been buckling since 2005’s Hurricane Katrina. After the last few years of bad storms, the state government has had to borrow $600 million to prop up insurers and rescue homeowners who have been abandoned by the broken system.
The lack of insurance makes extreme weather events even more costly. It slows economic recovery, increases the likelihood of cascading financial consequences, and can leave people in financial ruin, especially in low-income communities, which are increasingly being left at the mercy of Mother Nature as natural disasters become more intense.
Many of these vulnerable communities are being blue-lined, whereby banks or mortgage lenders designate neighborhoods that are more susceptible to climate risk and have less access to affordable insurance premiums.
Earlier in 2023, the Biden administration released a report detailing the economic challenges a warming planet posed to the US. It argued that bailing out homeowners after natural disasters incentivizes them to reside in riskier areas, increasing costs on taxpayers and slowing down climate change adaptation.
While the report is not legislation, it identifies how climate change has upended the nature of risk across the American economy and how the federal government will bear significantly higher costs in the future if it does not correct where it is creating market distortions. Two examples of distortions: paying more for healthcare for victims of heat stroke and paying to rebuild coastal homes flooded by hurricanes.
The government wants climate change risk factored into Americans’ decisions, and insurance companies want it factored into their prices. But inevitably, those paying the biggest price will be low-income Americans with fewer resources to relocate.
From Your Site Articles
More For You
Most Popular
- YouTube
In this Quick Take, Ian Bremmer reacts to President Trump’s State of the Union address, calling it “a rehashing of the greatest hits” with little new policy direction.
Small business hiring surged 7% above the 2024 average in December, led by a surprise rally in retail. But with uncertainty still historically high and mounting concerns over tariffs, can this momentum survive 2026? Explore the data behind the resilience of the US small business sector. Get the latest economic insights from Bank of America Institute.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.