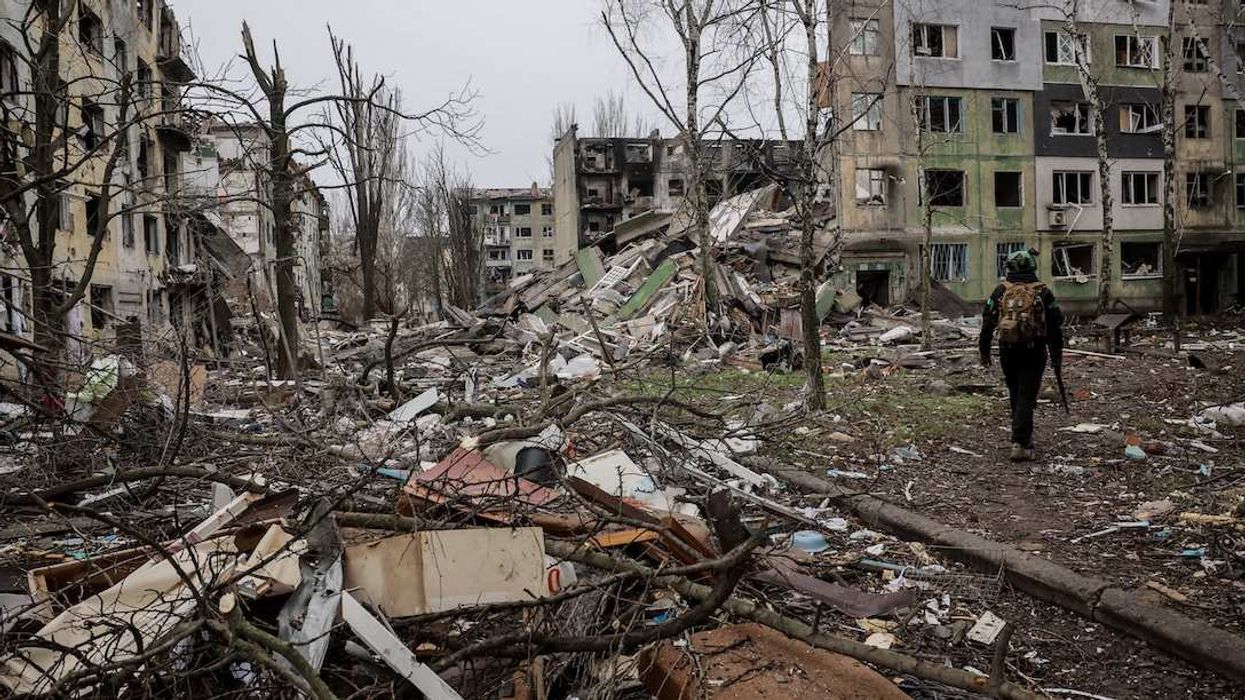
VIDEOSGZERO World with Ian BremmerQuick TakePUPPET REGIMEIan ExplainsGZERO ReportsAsk IanGlobal Stage
Site Navigation
Search
Human content,
AI powered search.
Latest Stories
Start your day right!
Get latest updates and insights delivered to your inbox.
Alex Kliment
Creative Director, Senior Editor/Producer
Alex wears a few different caps and tips them all regularly. He writes for the GZERO Daily, works as a field correspondent for GZERO's nationally syndicated TV show GZERO WORLD WITH IAN BREMMER, and writes/directs/voices GZERO's award-winning puppet satire show PUPPET REGIME. Prior to joining GZERO, Alex worked as an analyst covering Russia and broader Emerging Markets for Eurasia Group. He has also written for the Financial Times from Washington, DC, and Sao Paulo Brazil. In his spare time, he makes short films and composes scores for long ones. He studied history and Slavic literature at Columbia and has a Master's from Johns Hopkins SAIS. He's a native New Yorker, a long-suffering Mets fan, and owns too many bicycles.
Fields of expertise
Global politics, Russia, Latin America
Education
Columbia University, Johns Hopkins (SAIS)
Contact:
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/alexander-kliment-789b4129/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/youngnevsky