November 30, 2023
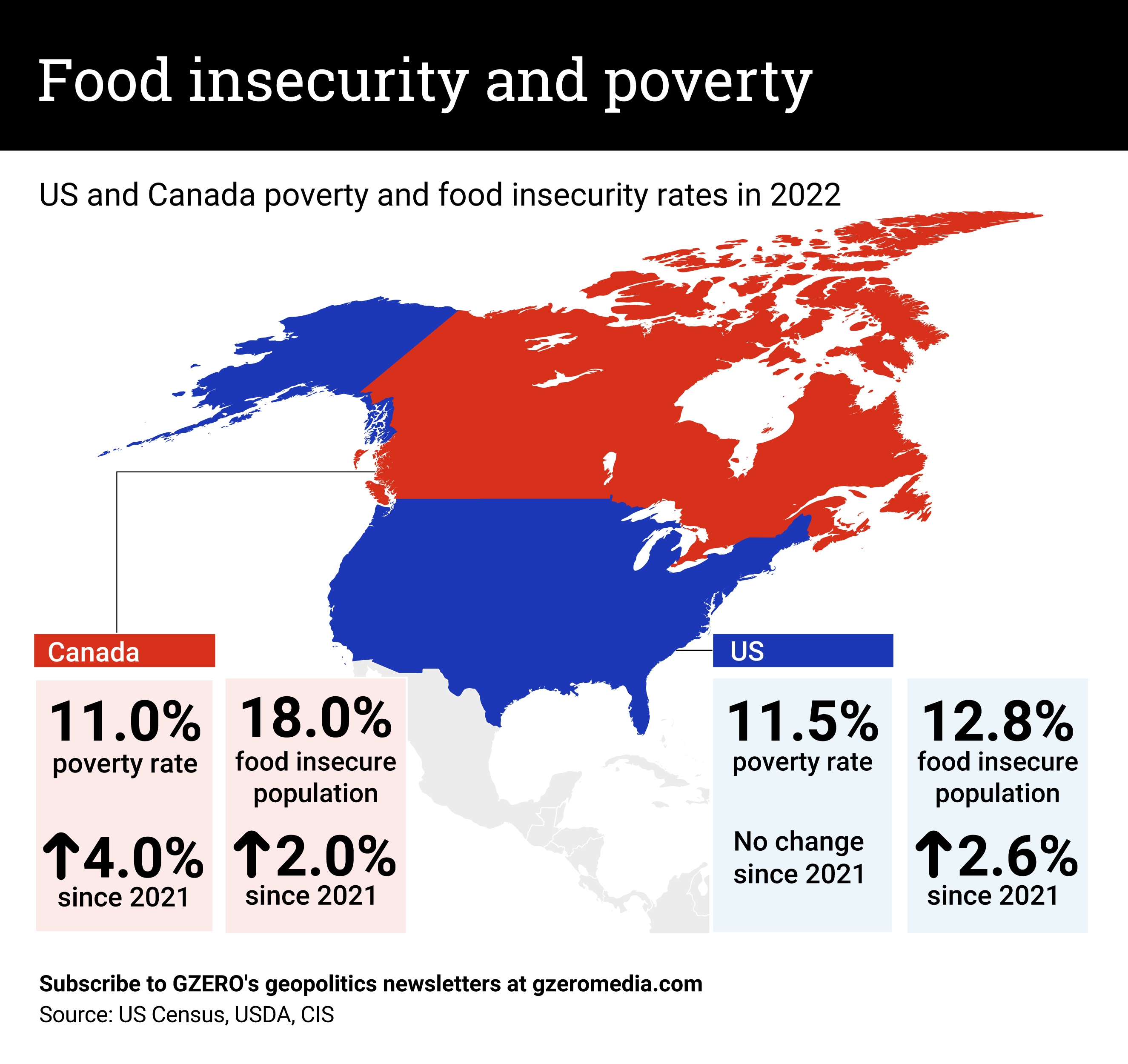
Poverty and food insecurity, exacerbated by COVID and the soaring cost of living, plague both the US and Canada. At the height of the pandemic, school closures in the US deprived many children of their vital food source: free school lunches. This, coupled with job losses and inflation, plunged many into food insecurity. The economic outlook has still not improved for these families, thanks to the high rate of inflation, which is keeping grocery and gas prices elevated.
In Canada, a cost-of-living crisis has seen demand for food banks surge, with the 2023 Hunger Count by Food Banks Canada revealing a 32% rise in year-on-year visits in 2022. Parents made up the largest share of food bank users. Like in the US, they are grappling with exorbitant housing, food, and fuel costs, compounded by childcare expenses. A record 1.9 million Canadians sought assistance from food banks in just March 2023 alone.
How has US food insecurity increased, but not poverty? The poverty line, defined by Lyndon B. Johnson in 1963, hasn't been reassessed since. Back then, poverty was defined as anyone spending a third of their income on a “bare essentials diet.” But thanks to globalization and agricultural advances, an average American now spends only one-eighth of their income on food.
Instead, housing and childcare are the biggest budget busters. An American renter making $30,000 likely allocates over half their income to housing and may struggle with food insecurity. But, given the 1960s “poverty” guidelines, they need to earn nearly three times less, or $12,880, to be considered poor.More For You
Ian Bremmer sits down with former US Ambassador to NATO Ivo Daalder to unpack a historic shift in the transatlantic alliance: Europe is preparing to defend itself without its American safety net.
Most Popular
Think you know what's going on around the world? Here's your chance to prove it.
U.S President Donald Trump, U.S. Vice President JD Vance, and U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio pose for a family photo with other representatives participating in the inaugural Board of Peace meeting, at the U.S. Institute of Peace in Washington, D.C., U.S., February 19, 2026.
REUTERS/Kevin Lamarque
Argentina, Armenia, Belarus, Egypt, Indonesia, Jordan, Pakistan, Paraguay, Vietnam – to name only a few.
A poster featuring Andrew Mountbatten-Windsor, formerly known as Prince Andrew, is installed on a sign leading to the parking area of the Sandringham Estate in Wolferton, as pressure builds on him to give evidence after the U.S. Justice Department released more records tied to the late financier and convicted sex offender Jeffrey Epstein, in Norfolk, Britain, February 5, 2026.
REUTERS/Isabel Infantes
British police arrested former Prince Andrew Mountbatten-Windsor today over allegations that in 2010, when he was a UK trade envoy, he shared confidential government documents with convicted sex offender Jeffrey Epstein.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.