July 18, 2024
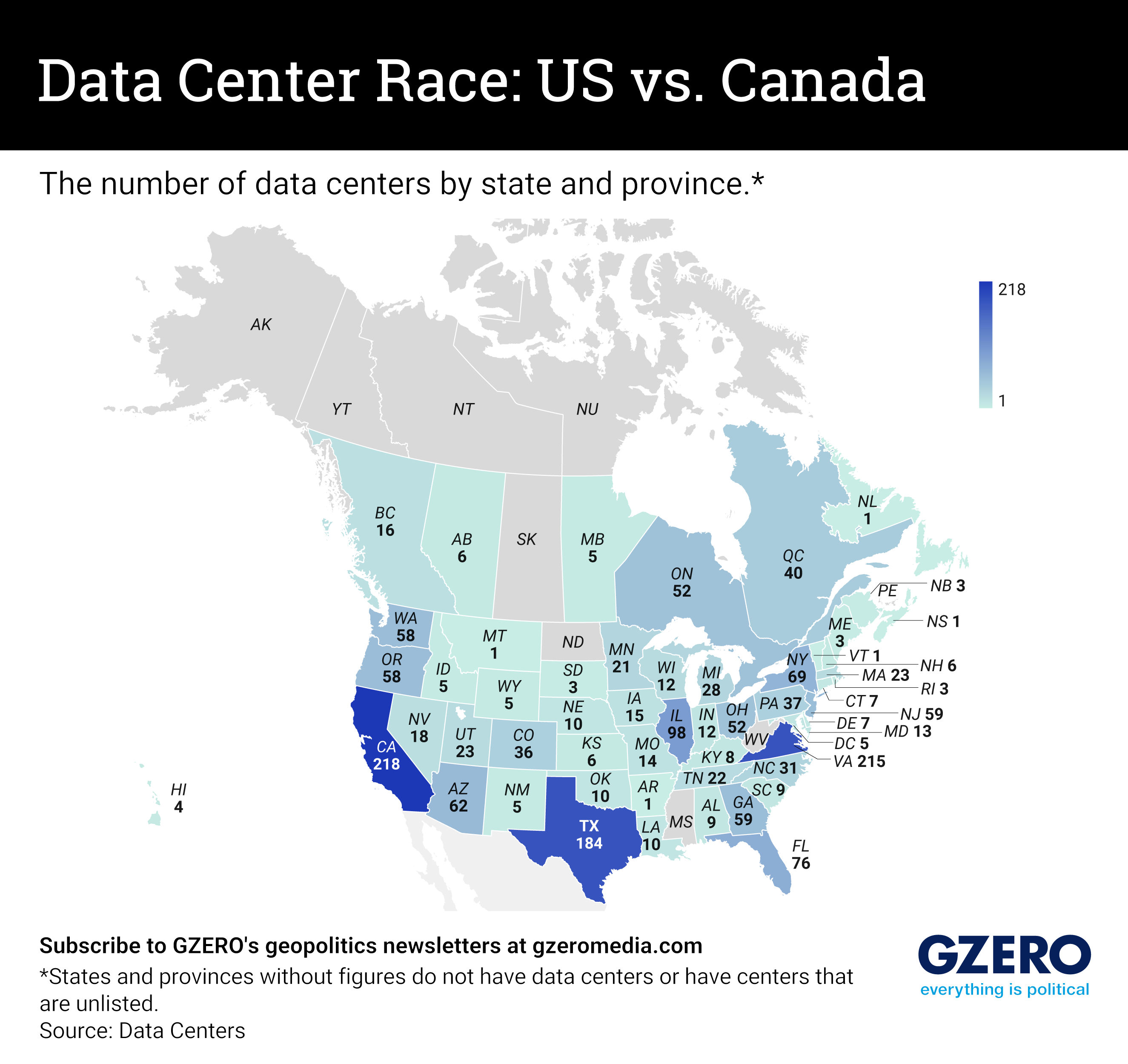
Data center construction was already on the rise, but thanks to the tech world’s new crush on artificial intelligence, there’s been an acceleration worldwide.
Data centers are the digital infrastructure that most of the world has come to depend on – so much so that they now account for over 1% of the world’s electricity use. Governments, businesses, and everyday folks have come to rely on these facilities for data storage, management, security, and so much more.
But everything comes at a cost. And for data centers, it’s the climate. Data centers require a constant and immense inflow of energy to support operations. Their high energy consumption has been linked to increases in greenhouse gas emissions, water usage (for cooling purposes), and exacerbating the energy crisis.
Companies like Microsoft and Google – front-runners in the AI race – have had to step back on energy pledges set before the AI boom and have been redirecting resources into the construction of new data centers to stay competitive. Microsoft, for example, seeks to double its number of data centers (and its carbon footprint).
Double-edged sword. Revolutionary advancements in technology and AI can be attributed to the growing number of data centers, but so can worsening climate conditions.
From Your Site Articles
More For You
Bad Bunny during the Super Bowl LX halftime show press conference at Moscone Center.
Kirby Lee-Imagn Images
100 million: The number of people expected to watch the Super Bowl halftime performance with Bad Bunny, the Puerto Rican superstar and newly minted Album of the Year winner at the Grammys.
Most Popular
Think you know what's going on around the world? Here's your chance to prove it.
- YouTube
An imminent US airstrike on iran is not only possible, it's probable.
Americans are moving less — and renting more. Cooling migration and rising vacancy rates, especially across the Sunbelt, have flattened rent growth and given renters new leverage. For many lower-income households, that relief is beginning to show up in discretionary spending. Explore what's changing in US housing by subscribing to Bank of America Institute.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.