March 06, 2022
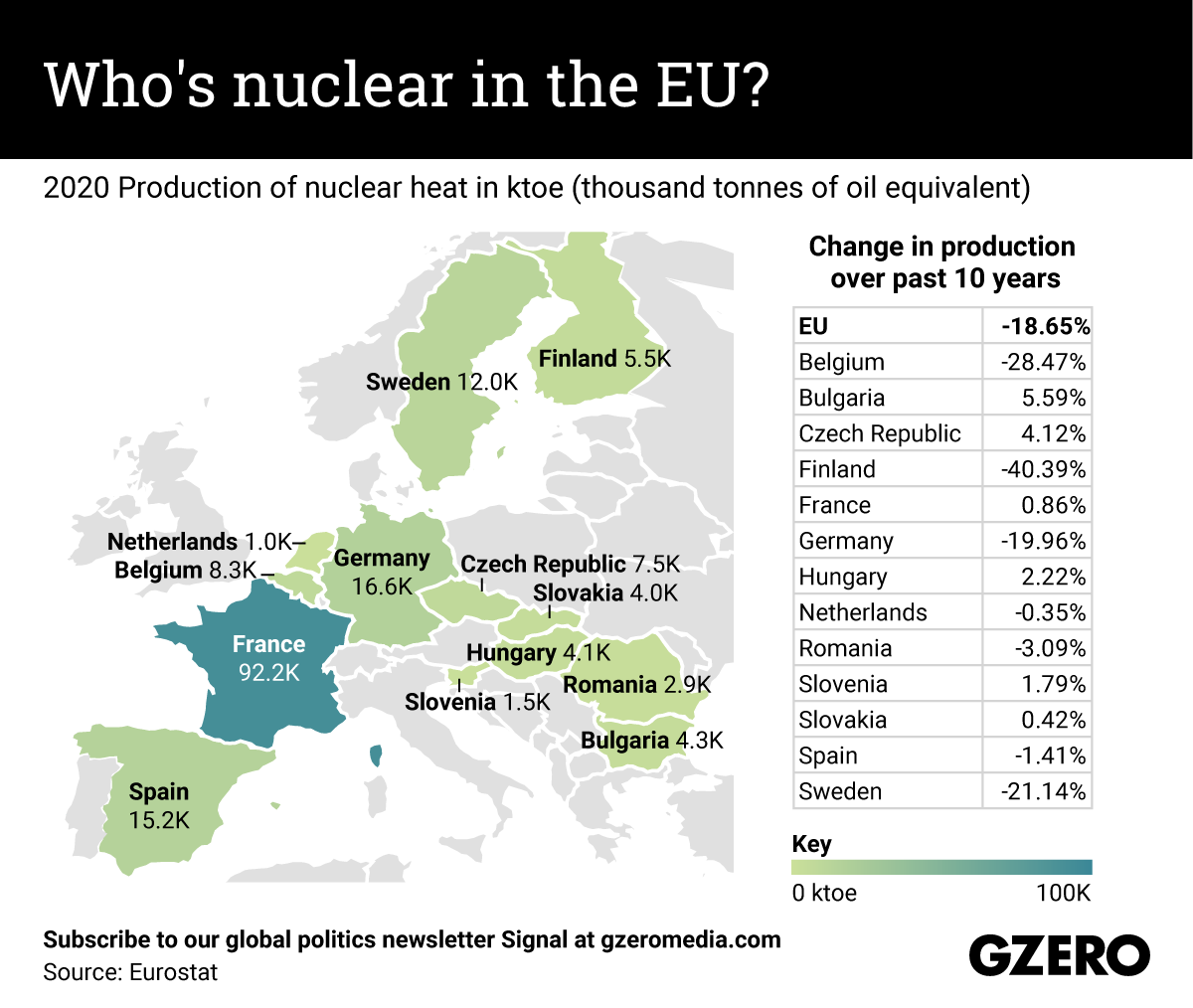
When Russian troops shelled the Zaporizhzhia nuclear plant in southeastern Ukraine on Friday, many feared it could cause a Chernobyl-like catastrophe. But even before this event, the status of nuclear energy within Europe has been a massive point of contention. Since the Fukushima disaster in 2011, European Union states have bolstered their guidelines for nuclear power safety, but some have been trying to phase it out altogether. Last month, the European Commission outlined how nuclear energy could be labeled a “green” investment (presuming the plants can safely dispose radioactive waste). Critics labeled the move as “greenwashing,” and Austrian Chancellor Karl Nehammer tweeted that “Nuclear power is neither ‘green’ nor sustainable.” So how might this latest scare in Ukraine change Europe’s nuclear calculus, if at all? We take a look at which EU states produce the most nuclear heat, and how that’s changed since 2011.
More For You
At the Munich Security Conference, a group of global technology providers, including Microsoft, announced the Trusted Tech Alliance — committed to shared, verifiable principles for trusted, transparent, and resilient technology across borders. At a moment of economic volatility and zero-sum technological competition, countries and customers are demanding greater accountability from technology providers. The Alliance addresses this by bringing together companies from across Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America around shared commitments: transparent governance, secure development practices, supply chain oversight, open digital ecosystem, and respect for the rule of law—ensuring the benefits of emerging technologies strengthen public trust while driving job creation and economic growth. Learn about the Trusted Tech Alliance here.
Most Popular
- YouTube
Europe looks increasingly prepared to defend itself without America. Ian Bremmer and Ivo Daalder assess what that means for NATO, Ukraine, and the future of the West.
Ian Bremmer sits down with former US Ambassador to NATO Ivo Daalder to unpack a historic shift in the transatlantic alliance: Europe is preparing to defend itself without its American safety net.
- YouTube
Europe can no longer rely on the US and must step up to defend its own future, Ian Bremmer reports from the Munich Security Conference.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.