October 24, 2024
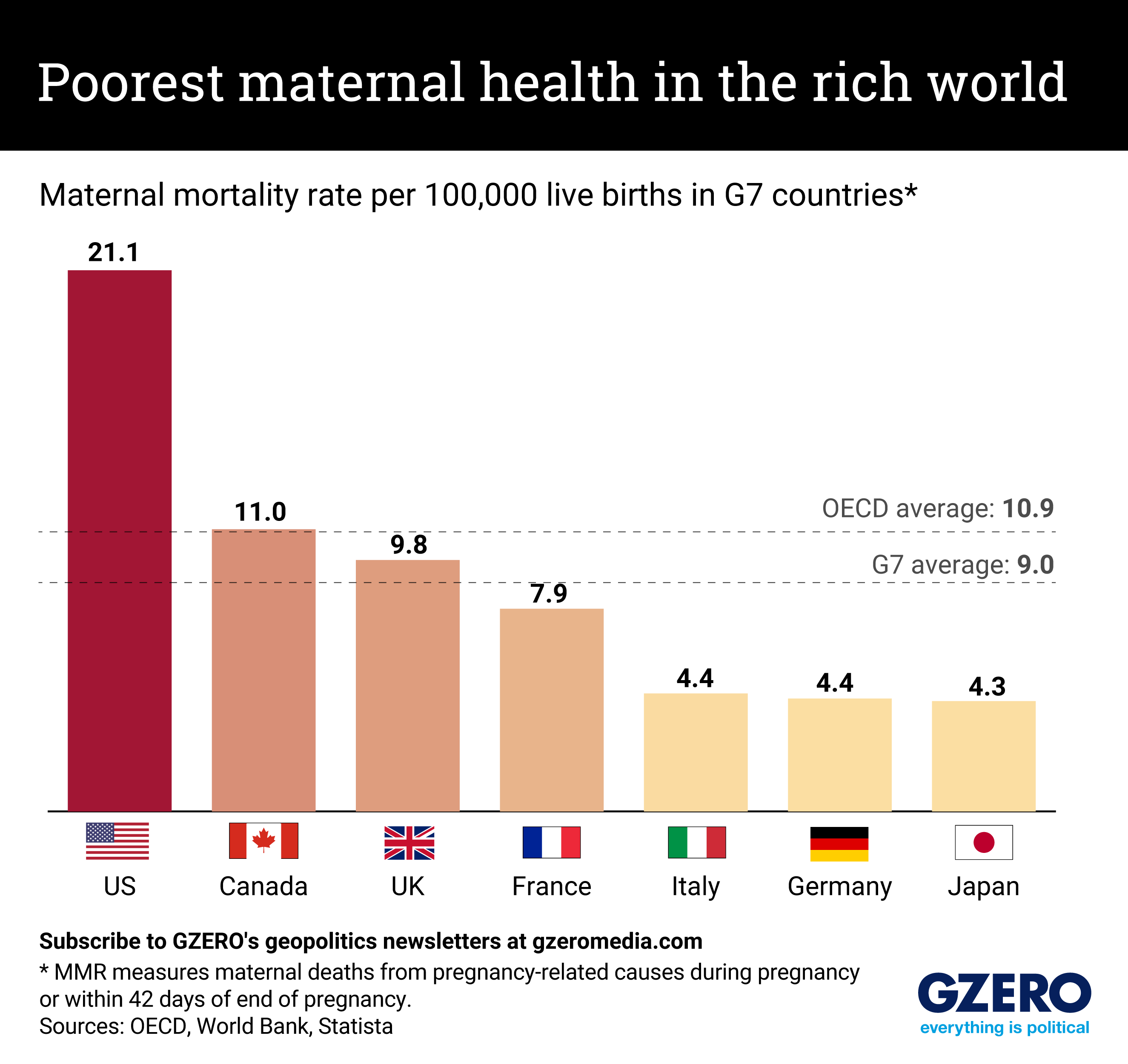
A woman in the US is nearly twice as likely to die from pregnancy-related causes as a woman in Canada. Compared to Japan, Germany, or Italy, the rate is nearly five times higher.
The United States, in fact, has the worst maternal mortality rate of any high-income country in the world. On average in the G7 group of wealthy democracies, nine pregnant women out of every 100,000 will die as a result of pregnancy or childbirth. In the US, it’s more than 21.
Experts point to a range of factors. One is a lack of adequate care during and after pregnancy, including from midwives or doulas, two professions virtually unknown in the US that have been shown to improve maternal health outcomes elsewhere. According to a recent study on America’s maternal health crisis by the Commonwealth Fund, a philanthropy that supports independent health care research, there are just four midwives per 1,000 live births in the US. In Sweden, where maternal mortality is virtually unknown, there are 80.
The US also stands out for its lack of mandatory paid maternity leave, which is shown to support maternal health by helping women manage the stresses of new parenthood.
Lastly, there are pronounced racial disparities in the US: Maternal death rates among Black women are 2.5 times as high as those for white women, and four times higher than Asian Americans. Higher mortality rates for Black women persist even when corrected for educational level, a loose proxy for income.
Here is a look at how maternal mortality rates compare across the G7 countries, with a comparison also to the average in the OECD, a wider grouping of higher-income countries.
More For You
- YouTube
At the 62nd Munich Security Conference in Munich, GZERO’s Tony Maciulis spoke with Benedikt Franke, Vice Chairman and CEO of the Munich Security Conference, to discuss whether the post-1945 global order is under strain or already unraveling.
Most Popular
- YouTube
Zelensky agrees: elections matter #PUPPETREGIME
As more small businesses move sales, payments, and customer relationships online, they unlock new opportunities, but they also become easier targets for cyber-criminals and other threat actors.
TOKYO, JAPAN - FEBRUARY 8: Japan's Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi, leader of the ruling Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), places a red paper rose on the name of an elected candidate at the LDP headquarters on general election day on February 08, 2026 in Tokyo, Japan. Voters across the country headed to polls today as Japan's Lower House election was held.
Photo by Kim Kyung-Hoon - Pool/Getty Images
When Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi called snap elections last month, it was a big gamble. Holding a winter election just four months into her tenure with no real policy record to run on?
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.