May 30, 2024
As the 2024 US election approaches, immigration is among the most important and polarizing issues in American life.
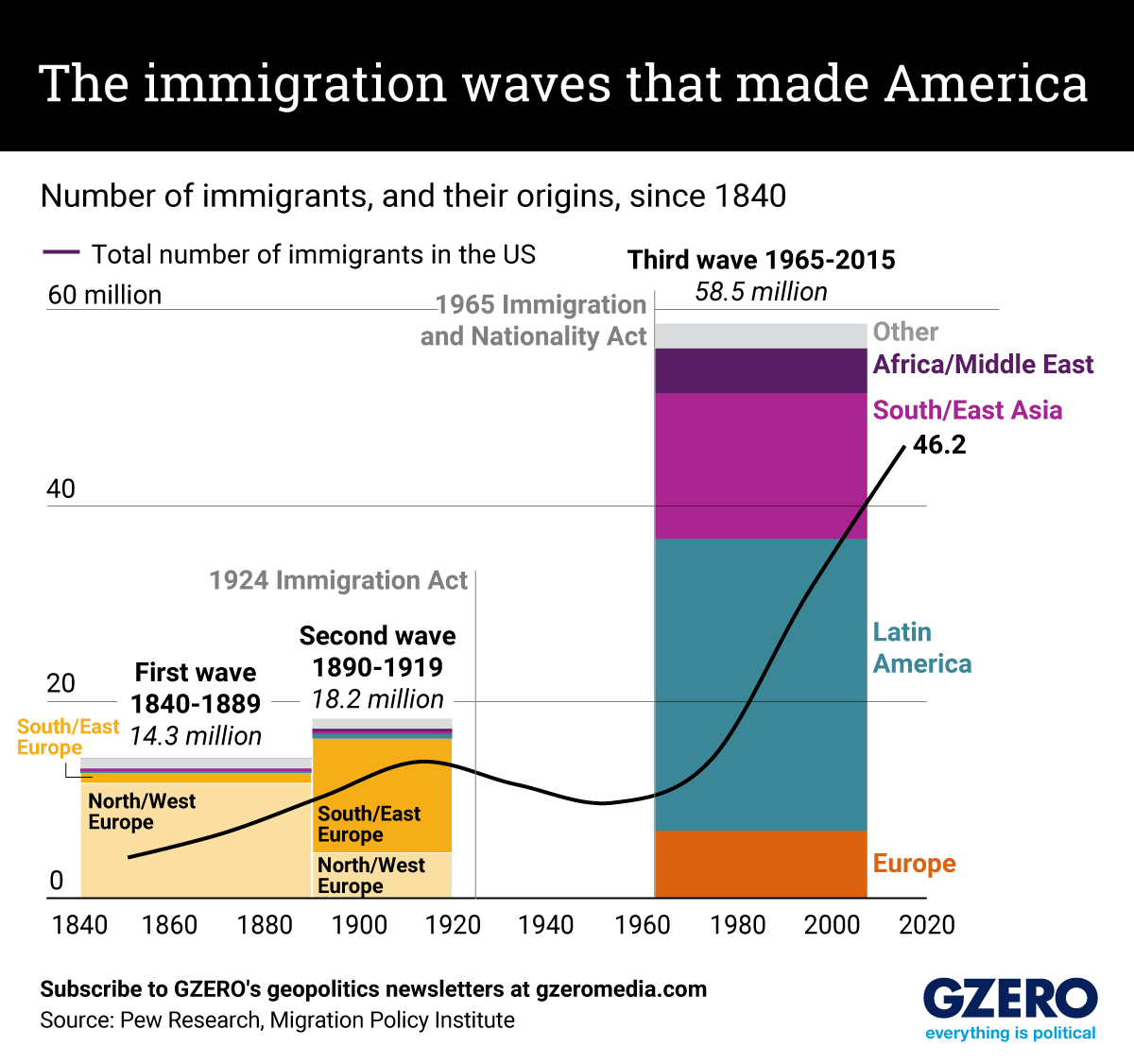
The United States is, of course, a nation of immigrants. But their origins have changed a lot over the past 150 years, as have the laws that govern who can, and can’t come in.
Since the mid-19th century there have been three major waves. The first, mainly from Northern and Western Europe, came at a time when there was little federal immigration policy at all, with the notable exception of a racist law banning immigrants from China.
The second wave, coming chiefly from Southern and Eastern Europe, provoked a sizable backlash against Catholics and Jews who were seen as economic, political, and even genetic threats to America.
This led to a sweeping 1924 law that imposed national quotas, dramatically reducing overall immigration. That law held sway until a 1965 reform abolished the quotas and eased entry for family members of immigrants.
That marked the start of the third wave, which dwarfs the earlier two in size and has come mainly from Latin America and Asia.
Here’s a look at the overall number of immigrants in the US and their countries of origin in the three great waves. Note that these numbers capture only legal entries. The phenomenon of undocumented migration – which began at large scale only over the past several decades – is not reflected here.
From Your Site Articles
More For You
- YouTube
In this Quick Take, Ian Bremmer breaks down the growing tensions between the US and Iran, calling it "the next area of potential large-scale conflict where President Trump is interested in changing the facts on the ground."
Most Popular
A flood victim stands at her flooded home after weeks of heavy rainfall in Boane District, Maputo, Mozambique, January 19, 2026.
REUTERS/Amilton Neves/File Photo
392,000: The estimated number of people displaced across Mozambique by recent rain-induced floods. Severe flooding in the southern African nation, as well as in South Africa and Zimbabwe, has killed over 100 people.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.