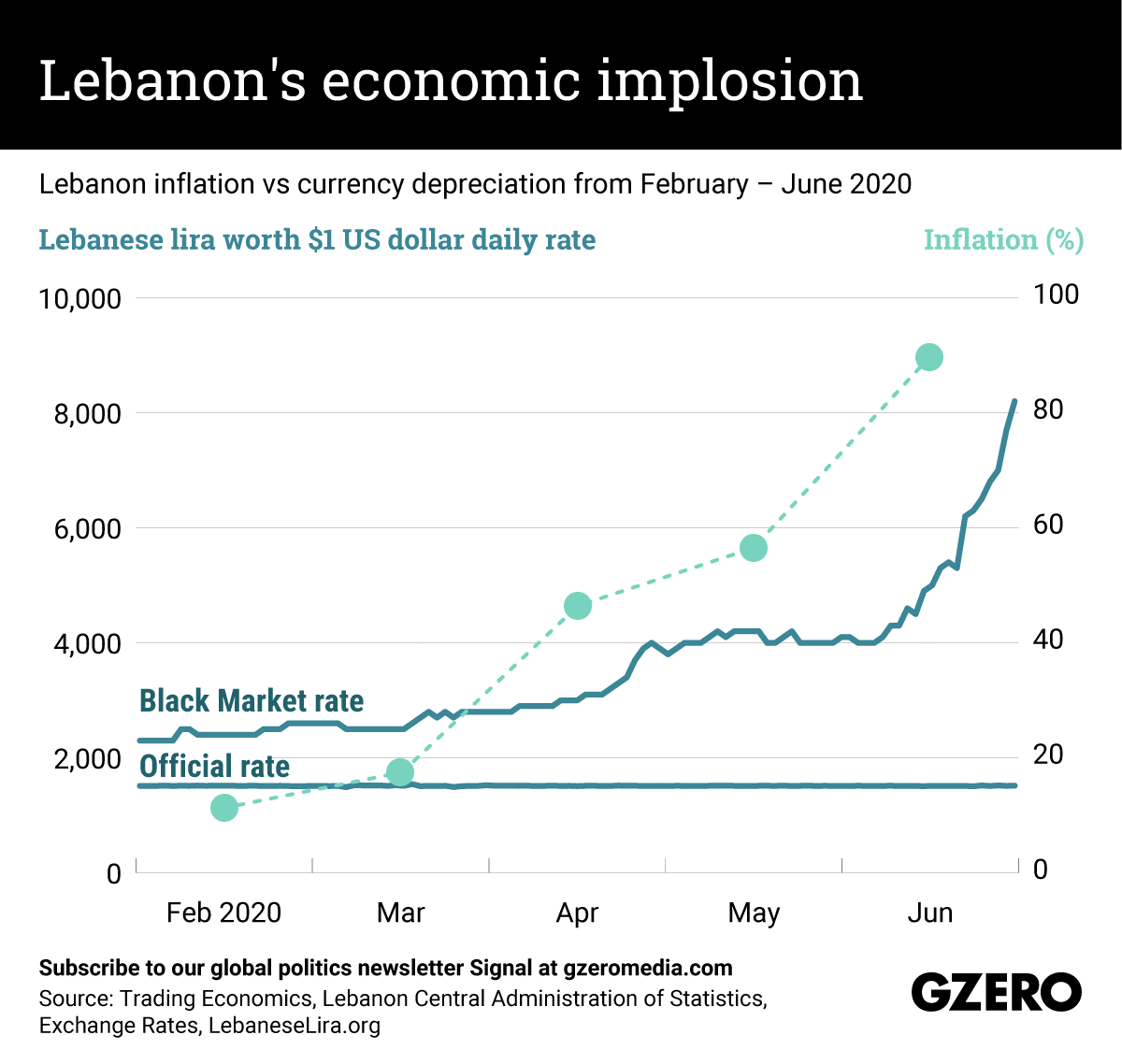
Even before last week's explosion — which killed over 200 people, turned downtown Beirut into rubble, and forced the government to resign — Lebanon was already in economic dire straits. The value of the local currency has plunged following decades of corruption, mismanagement and political chaos, dragging about half of the population into poverty. Since the beginning of 2020, the depreciation of the Lebanese pound (on the black market, while the official rate remains somewhat pegged to the US dollar) and soaring inflation have increased the price of basic goods beyond what most citizens can afford, and wiped out pensions and salaries. If the situation does not improve soon, Lebanon could see unprecedented levels of hunger — and international assistance may not be enough to feed everyone. We compare how the Lebanese pound has traded with the US dollar amid rapidly rising inflation over the first half of the year.
More For You
In this "ask ian," Ian Bremmer explains why the Trump administration may be looking for a way out of the US–Israel war with Iran, even as Israel appears determined to keep fighting.
Most Popular
Center-right Colombian Sen. Paloma Valencia will head into May’s presidential election with some momentum, after 83% of voters opted to vote in the right-wing primary on Sunday – which she won comfortably.
There’s a striking gap in how Americans and Israelis view the US-Israeli war on Iran. Polling done by the Israel Democracy Institute showed the attacks have overwhelming support among Israelis.