On March 5, 1824, the British governor-general of India, Lord Amherst, declared war on the Burmese empire. The ensuing Anglo-Burmese Wars marked the end of a golden age for what is now Myanmar – and laid the early roots of its present troubles 200 years later.
A rising power. While Myanmar finds itself weak and geopolitically isolated today, it was then a dominant force in Southeast Asia. The Konbaung dynasty had risen from simple village chiefs to conquer the Irrawaddy valley and surrounding highlands, fended off four invasions from Qing China, and fought a bitter series of wars against their Thai archrivals.
By the 19th century, the kings in Ava had turned their eyes westward, taking Manipur and Assam (both in modern India) – and threatening the British base of power in Bengal. In 1823, Burmese troops began skirmishing with British forces along their undefined border.
Costly hesitation. After Amherst’s declaration, 10,000 Burmese troops routed the forces defending Cox’s Bazar in what is now Bangladesh and were expected to march to the capital of Calcutta. But fearing overextension, they declined to advance – a fatal error.
Holding back allowed British forces to regroup and launch a naval invasion of Burma. The Burmese resisted for two years, killing 15,000 British troops and causing an economic crisis in India. But they could not hold out forever and gave up territory and a massive indemnity for peace. The British then helped themselves to the rest of the country in two short wars in 1852 and 1885.
Exploitation and revolution. The British disrupted Burmese society. Indians and Brits formed the administrative core, pushing out Burmese elites, while major landowners imported Indian labor to exploit the fertile soil for rice exports, undermining ordinary farmers. British missionaries spread Christianity, particularly among the ethnic groups in the highlands, disrupting the millennia-old Theravada Buddhist order.
During World War II, the Japanese were only too happy to exploit deep Burmese resentment. They backed a puppet regime of Burmese nationalist revolutionaries, including a young communist named Aung San. But when it became clear that Japan would lose, Aung San shrewdly switched sides and fought for the British, who didn’t dare suppress the popular leader after the war.
His efforts to unite the country seemed promising, and he managed to sign an agreement with all the highland minorities to form a multiethnic, democratic Union of Burma in February 1947, but he was assassinated just five months later, throwing the country into chaos.
Within a year, ethnic militias — many trained and armed by the Allies — were in open conflict with the central government, which has never ceased. To make matters worse, in 1950, Chinese nationalist troops fleeing Mao Zedong’s People’s Liberation Army crossed into northern Burma, where they turned to the heroin trade for support and flooded the highlands with drugs and weapons. In 1962, the military seized power and has remained in a dominant political role since.
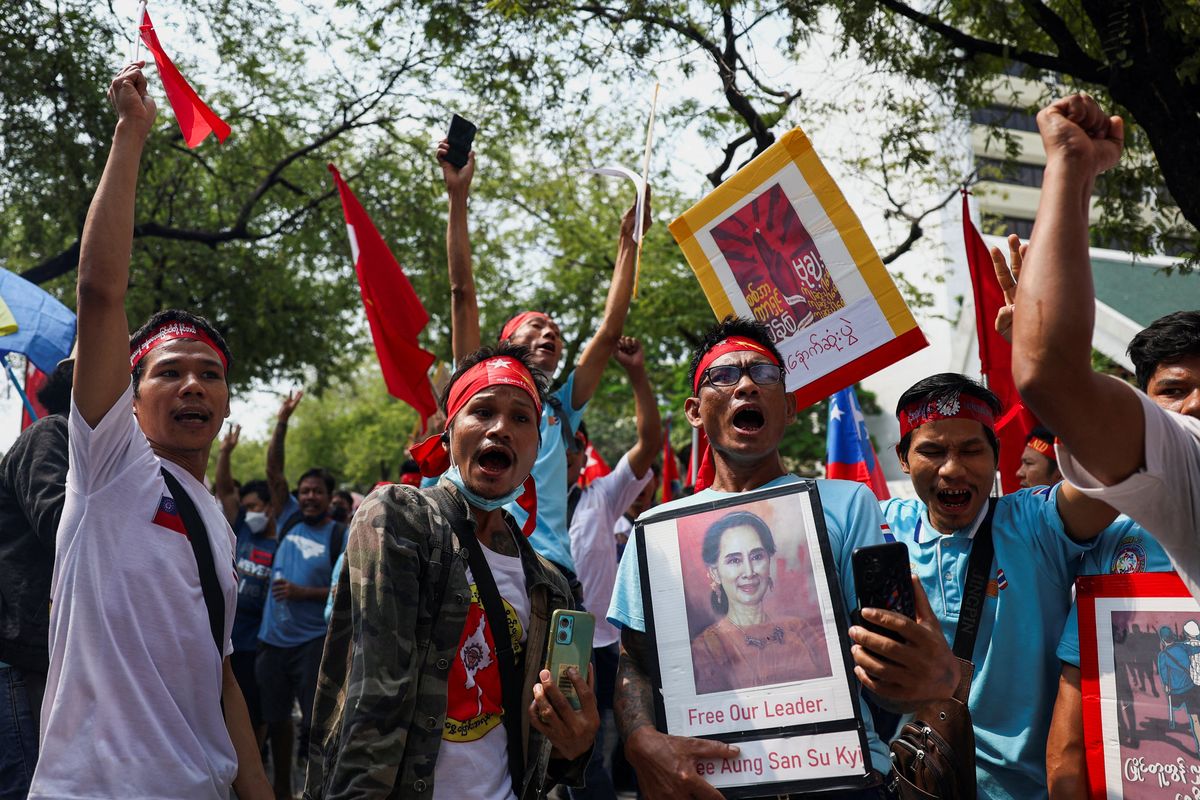
Today, the ethnic conflict overlaps with the civil war that broke out after the 2021 military coup overthrew the democratically elected government of Aung San Suu Kyi (Aung San’s daughter), whose triumph in the 2015 elections seemed to promise better days ahead.