Viewpoint
How is China dealing with its biggest #MeToo case?
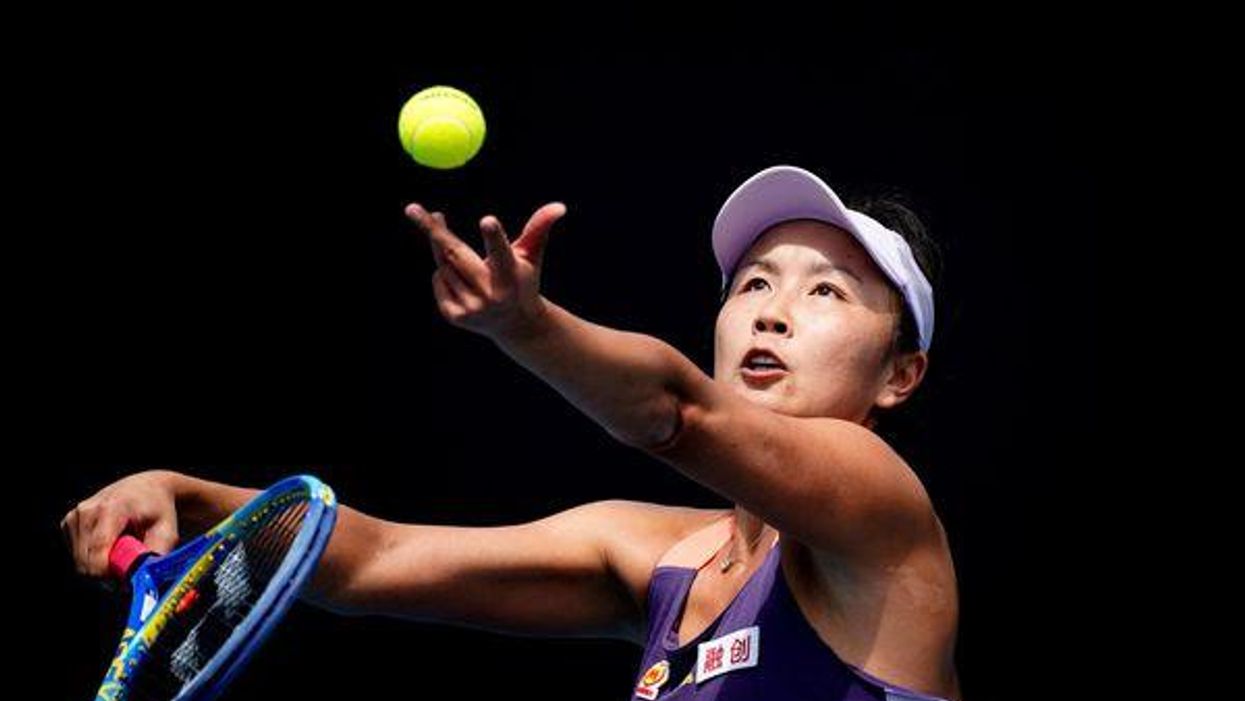
Chinese tennis star Peng Shuai’s disappearance after accusing a former high-ranking official of sexual assault has prompted global public outcry — and a WTA boycott. But in China, her allegations were scrubbed from the internet. What does that tell us about Beijing's attitudes towards the #MeToo movement, and threats to the ruling Communist Party? We asked Eurasia Group analyst Allison Sherlock.
Dec 19, 2021