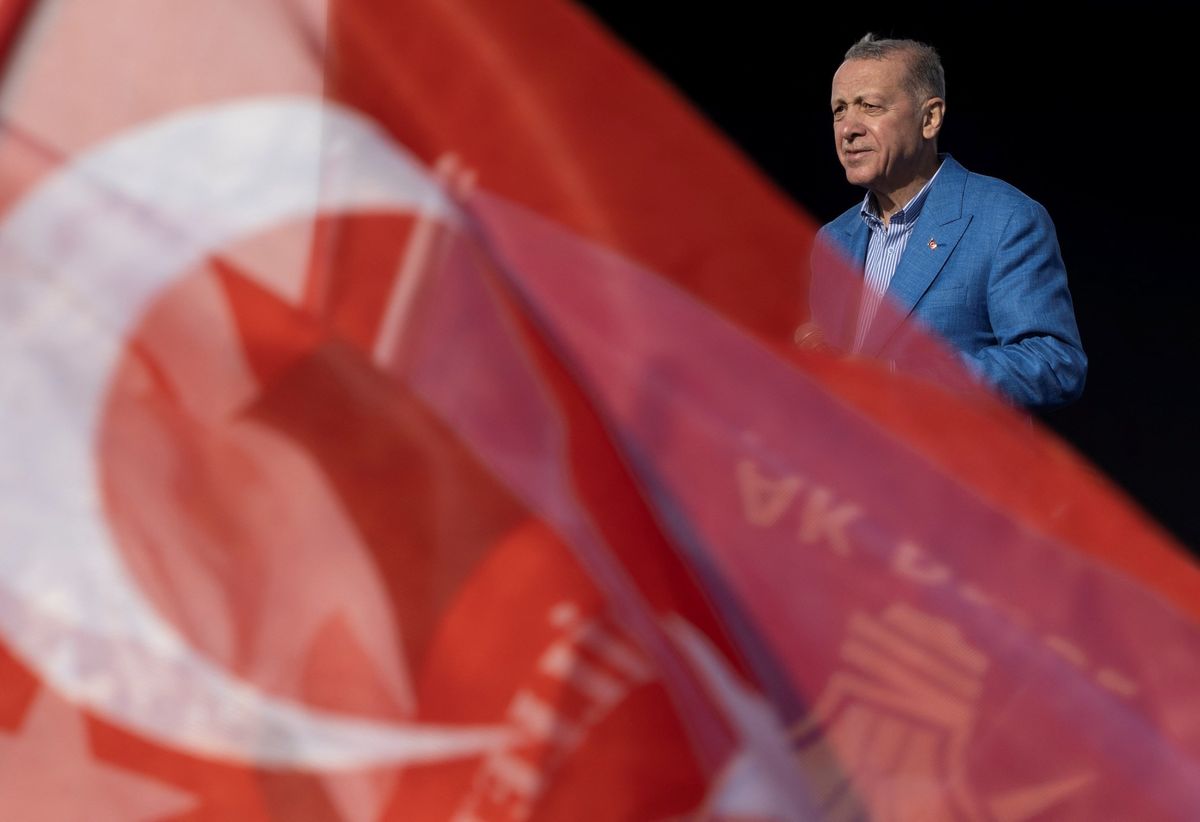
After dominating Turkish politics for two decades, opinion polls suggest that President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan could face his toughest elections ever on May 14. The charismatic, tough-talking politician became prime minister in 2003 after his moderate Islamist party swept to power, breaking with a long tradition of secular government. In 2014, he won the country’s first-ever direct presidential election and then expanded the powers of the office with a new constitution passed in 2017.
A deepening economic crisis – with inflation just under 50% – and a bungled initial response to devastating earthquakes in February have created an opening for an opposition candidate to prevent Erdoğan’s rule from extending into a third decade. That could have implications far beyond Turkey. Though a NATO member, Turkey under Erdoğan has pursued closer relations with Russia and various other policies that have created tensions with its Western partners.
We spoke with Turkey experts at Eurasia Group to get a better sense of what to expect from the upcoming elections.
The polls point to an unusually tight presidential contest – is Erdoğan’s dominance slipping?
Erdoğan’s public support has been steadily weakening since he became president in 2014. His Justice and Development Party (AKP) briefly lost its parliamentary majority in the June 2015 general elections but quickly recovered it a few months later in November snap polls. Ever since, Erdogan and the AKP have had to rely on alliances — primarily with the Nationalist Movement Party, but also some fringe Islamist parties — to maintain his legislative majority and secure reelection as president. Meanwhile, unorthodox policies such as keeping interest rates low despite high inflation have magnified economic challenges, causing fatigue with the AKP’s long rule. First-time voters who have known no leader but Erdoğan are eager for change. While Erdoğan, 69, remains the most prominent Turkish politician, he has largely lost his magic touch for communicating with voters. For example, his reference to the recent earthquakes as “an act of fate” in an effort to downplay their impact stoked more outrage with the government response. All these factors suggest that the Erdogan era is nearing its end — at least in the public psyche.
Who is the leading challenger and what does he need to do to win?
Six opposition parties have joined forces in the Nation Alliance and chosen Republican People’s Party (CHP) leader Kemal Kılıçdaroğlu as their joint candidate. The 74-year-old will be Erdoğan main challenger. To be successful, he needs to maintain the cohesion of a fractious coalition of social democrats, secularists, Islamists, and nationalists. Moreover, he needs to secure the support of Kurdish and left-wing voters. More importantly, Kılıçdaroğlu needs to convince voters that he can effectively preside over a six-party coalition and work with a diverse legislature to fix Turkey’s economic problems. On a practical level, the opposition will have to ensure the security and integrity of the ballot and the vote count.
What does Erdoğan need to do?
The president needs to energize his conservative, Islamist, nationalist base. To that end, Erdoğan will use scare tactics. He will try to associate Kılıçdaroğlu with terrorism, citing his support among pro-Kurdish parties. (Turkey has suffered from a long-running battle with militant Kurdish separatists that has claimed tens of thousands of lives.) Erdoğan will also play on pious voters’ fears of a return to the hardline secularism of pre-AKP governments, insinuating that Kılıçdaroğlu will not respect their religious beliefs. Meanwhile, Erdogan will use the advantages of incumbency — electoral handouts, control of the bureaucracy, influence over the media, etc.— to undermine the opposition campaign.
Is fraud likely?
There have been disputes and allegations of wrongdoing in every Turkish election since 2014. Those involved arbitrary pauses to vote-count updates, allegations of multiple voting, acceptance of irregular ballots, blocking of poll observers, and a forced re-run of the Istanbul mayoral election in 2019. Similar risks exist for the upcoming polls.
How likely do you think it is that Erdoğan would try force a re-run of this election?
If Erdoğan loses the presidential election by a very narrow margin (by less than 1% of the total vote), he could lean on the Supreme Election Council to force a repeat of the election, as he did when his party’s candidate lost the Istanbul mayoral election by less than 14,000 votes to the CHP candidate. (The CHP went on to win the re-run with 800,000 more votes than the AKP.) If Erdoğan manages to cling onto his parliamentary majority with a surprise win in the legislative elections being held at the same time as the presidential vote, he will likely be more inclined to seek a re-run. Should Kılıçdaroğlu win the presidency with a wide margin (more than 2% of the total vote) and the opposition secure a comfortable majority in parliament, Erdogan would be less likely to disrupt the electoral process.
Is violence expected around the elections?
The offices of the AKP and opposition parties in various provinces — including Istanbul — have been attacked by gunmen and vandals. Kılıçdaroğlu has also faced some aggressive heckling and threats around his public gatherings, which caused him to cancel some rallies. Some opposition politicians have also voiced concern over an assassination attempt against Kılıçdaroğlu. While major unrest is unlikely, spontaneous outbreaks of violence are possible in the lead-up to the elections. If there were blatant election disruptions or a very close race, that could trigger demonstrations and street violence, too — albeit likely limited.
Edited by Jonathan House, Senior Editor, Eurasia Group.