March 13, 2025
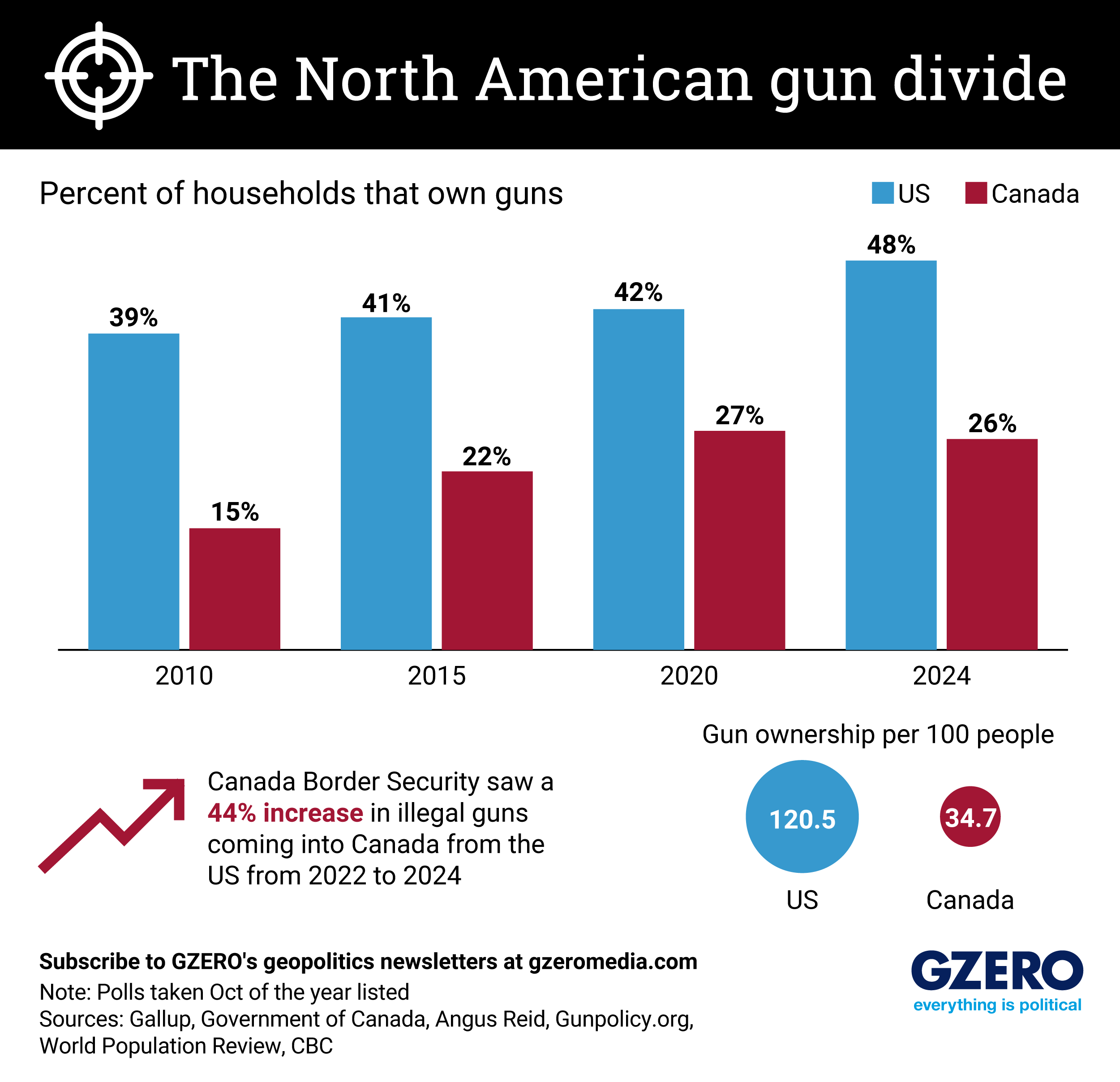
Gun ownership rates have been rising in both the US and Canada, despite the two countries having drastically different firearms regulations. In the US, there are some federal protections, such as mandatory background checks for firearm purchases from licensed dealers, and restrictions on machine gun and suppressor ownership, as well as rules barring convicted felons and the mentally ill from owning guns. But the Second Amendment’s right to bear arms, coupled with lax gun laws in some states, and a cultural emphasis on personal protection, has enabled gun ownership to become widespread.
In Canada, however, guns are primarily viewed as tools for hunting or for sport, and ownership is subject to strict regulations, including certified coursework and background checks. Moreover, nearly 200 types of assault-style firearms are banned. As a result, the US far surpasses Canada in personal firearm ownership. There are 120 guns per 100 people in the US – yes, more than one per person – compared to 35 per 100 people in Canada.
But guns in the two countries are also deeply connected. Relaxed restrictions on buying firearms in many states along the US-Canada border have fueled a surge in illegal gun smuggling into Canada. From 2022-24, Canadian border security saw a 44% increase in firearms illegally entering from the US. The issue is under renewed scrutiny as the Trump administration imposes tariffs on Canada, pressuring it to curb fentanyl trafficking. Many Canadians argue that the illegal flow of US firearms poses an equally serious threat to public safety.
More For You
Bad Bunny during the Super Bowl LX halftime show press conference at Moscone Center.
Kirby Lee-Imagn Images
100 million: The number of people expected to watch the Super Bowl halftime performance with Bad Bunny, the Puerto Rican superstar and newly minted Album of the Year winner at the Grammys.
Most Popular
Think you know what's going on around the world? Here's your chance to prove it.
- YouTube
An imminent US airstrike on iran is not only possible, it's probable.
Americans are moving less — and renting more. Cooling migration and rising vacancy rates, especially across the Sunbelt, have flattened rent growth and given renters new leverage. For many lower-income households, that relief is beginning to show up in discretionary spending. Explore what's changing in US housing by subscribing to Bank of America Institute.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.