October 07, 2024
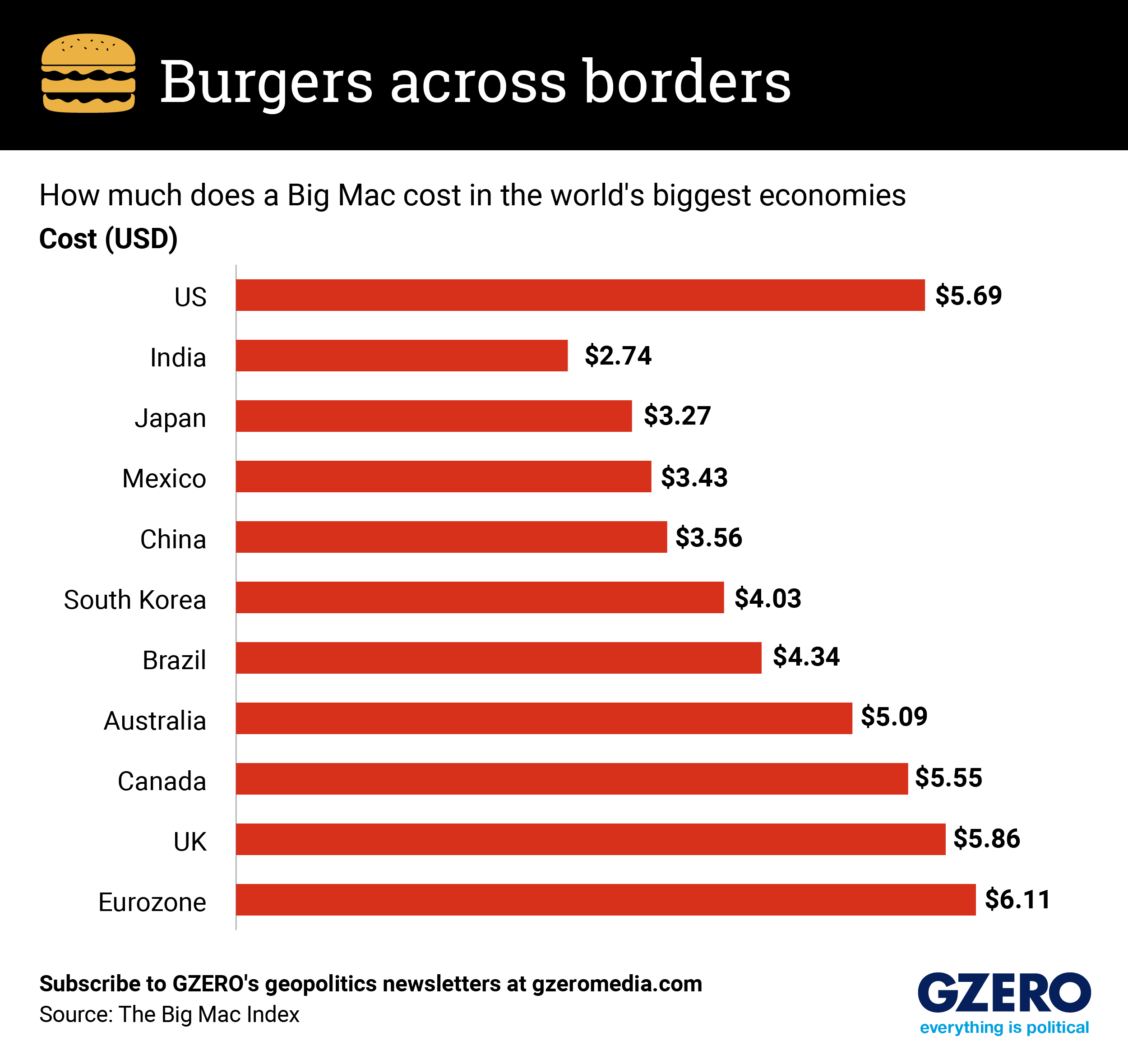
So you’ve heard of Bidenomics, but what about burgernomics? Allow us to introduce you to the Big Mac Index, which uses the price of a McDonald's Big Mac to assess whether currencies are over- or undervalued relative to the US dollar.
The index shows purchasing (patty) power, or the gap between productivity and living standards, between countries. It compares the local price of a Big Mac in different countries, converted to US dollars. But it's also a good measure of inflation – a hot topic for the US election, with Kamala Harris and Donald Trump both arguing that they have been better stewards of the economy. Of course, both administrations were majorly affected by COVID, which also had an impact on Big Mac prices.
Before the pandemic, you could buy a Big Mac for $4.82 – or a crisp $5 bill with change to spare, but today, you pay $5.69. This might seem like a win for Trump, but in terms of wages, the story is more complicated. In 2020, an average worker could afford about five Big Macs with an hour’s pay, but now, one hour of work could buy you 5.4 Big Macs. This reflects how, since March 2023, wage growth has outpaced inflation, with the average American’s hourly pay increasing by 5.9%, while prices have jumped just 4.1%.
More For You
- YouTube
For many in Iran, it’s a waiting game for how long Ayatollah Khamenei has left to live.
Most Popular
An army soldier stands guard at a post at the Friendship Gate, following exchanges of fire between Pakistan and Afghanistan forces, at the border crossing between the two countries in Chaman, Pakistan February 27, 2026. Picture taken with a mobile phone.
REUTERS/Abdul Khaliq Achakzai
In a 30-minute call on Thursday, President Donald Trump reportedly told Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky he wants to end the war with Russia as soon as possible — aiming for a deal by summer, but ideally within weeks.
Former British ambassador to the U.S. Peter Mandelson leaves his residence after he was released following his arrest by London police on Monday on suspicion of misconduct in public office, following the release of U.S. Justice Department files linked to the late financier and convicted sex offender Jeffrey Epstein, in London, Britain, February 26, 2026.
REUTERS/Toby Melville
The ghost of Jeffrey Epstein continues to haunt the world.
Think you know what's going on around the world? Here's your chance to prove it.
© 2025 GZERO Media. All Rights Reserved | A Eurasia Group media company.