GZERO World Clips
Should we be worried about population decline?
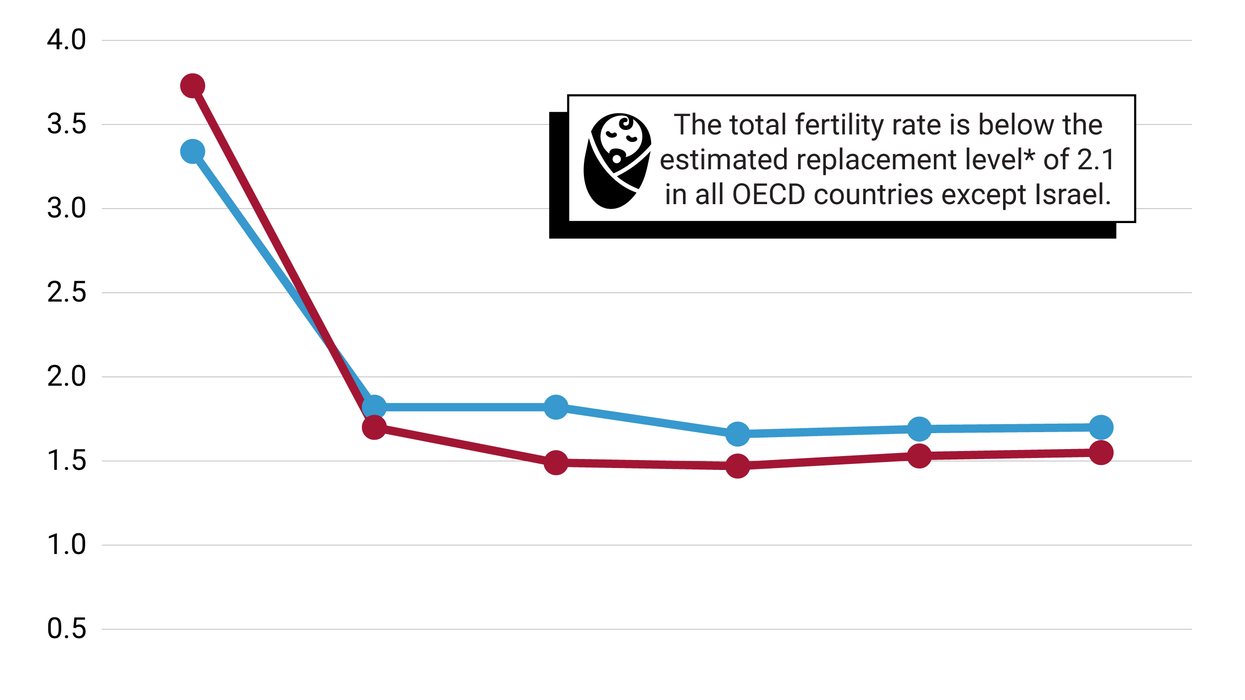
How worried should we be about falling birth rates around the world? For years, experts have been sounding the alarm about overpopulation and the strain on global resources, so why is population decline necessarily a bad thing? On GZERO World with Ian Bremmer, demographic expert Jennifer Sciubba, President & CEO of the Population Reference Bureau, warns governments are “decades behind” in preparing for a future that’s certain to come: one where the global population starts decreasing and societies, on average, are much older.
Nov 19, 2024