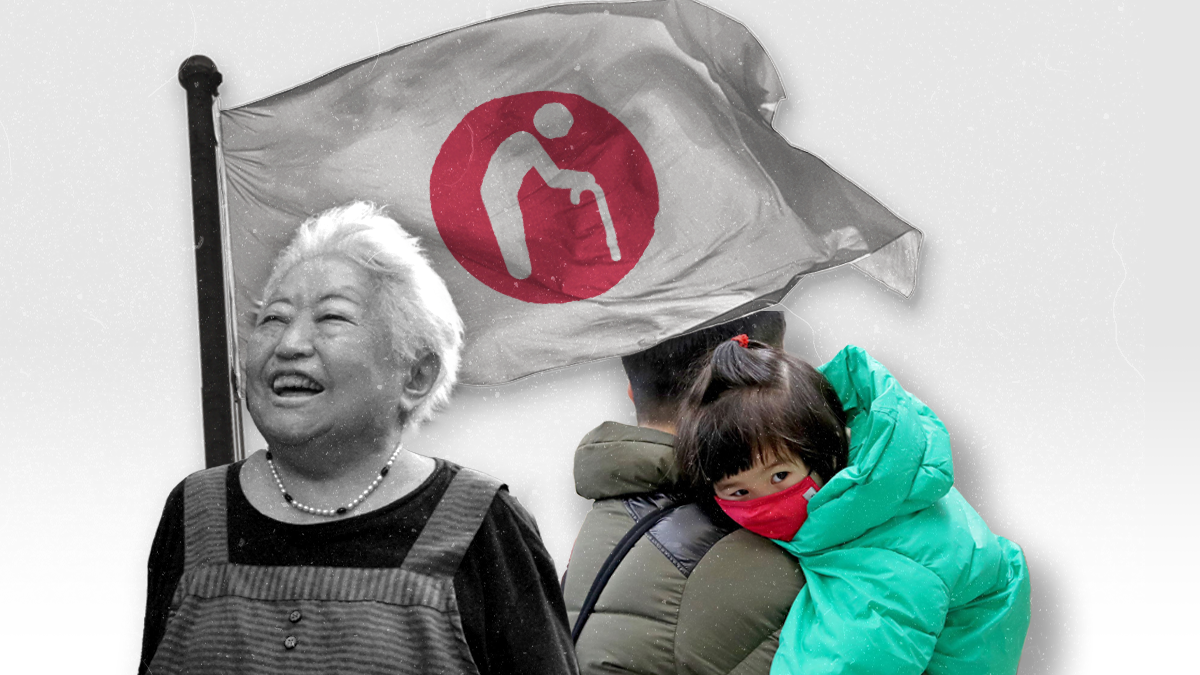
What if a hypothetical government, overtaxed by an aging, shrinking population, decided to ask its seniors to make the ultimate national sacrifice to voluntarily die?
That’s the premise of "Plan 75," a 2022 indie film that predicts a grim dystopian and not-too-distant future for a fictional Japan, where the elderly are offered compensation to submit to euthanasia and avoid being a burden to society when they turn 75.
Sure, it’s just a movie, but nowhere is more at risk of a demographic implosion than Japan. With a median age of 49, it’s the world's oldest country, and 28% of people are 65+. The nation of 125 million — whose annual births dropped below 800,000 for the first time in 2022, eight years earlier than forecasted — is expected to lose almost one-third of its population by 2060.
As its population shrinks, Japan’s government is running out of time. “It is now or never when it comes to policies regarding births and child-rearing,” PM Fumio Kishida said on Monday during a speech in parliament.
For the first time, he’s made reversing Japan’s declining fertility rate (1.38 births per woman) an urgent priority — as time-sensitive as doubling defense spending to counter military threats from China and North Korea.
Indeed, Kishida warned, “our nation is on the cusp of whether it can maintain its societal functions.” Within decades, the GDP of Japan, now the world’s third-largest economy, might contract to the point where it struggles to keep the lights on because it won’t have enough productive workers.
The declining births are a "huge pothole on Japan’s road to economic growth," says David Boling, Eurasia Group’s lead Japan analyst.
"It means Japan has to squeeze more and more productivity out of fewer and fewer people. Technology, artificial intelligence, and robotics can help gain back some of that lost productivity," he explains. "But it can only go so far.”
There are two ways to boost Japan's dismal birth rate from the domestic supply side. First, encourage couples to have more kids by paying them money. Second, support families with further economic benefits like paid parental leave or subsidized childcare. Kishida says he plans to double the national budget for families and create a new government agency to get Japanese to make more babies.
But "it’s not that simple," says Boling. "The government has provided financial incentives in the past and created a cabinet minister for dealing with the low birthrates. But the [births] continue to drop."
Meanwhile, Japanese women are giving birth less because fewer are getting married. Although that’s mostly due to more economic opportunities for them, many are also reluctant to tie the knot due to traditional domestic gender roles that put almost all the burden on women to take care of the house and kids.
There is something else Kishida could do that would actually fix the problem: welcome immigrants with families.
Unfortunately, for decades immigration has been a political taboo in Japan due to centuries of self-imposed isolation and a long-held defense of ethnic homogeneity among the right. Even an acute labor shortage in recent years has only resulted in slight relaxation of one of the world's strictest immigration policies.
"Rapidly increasing immigration would probably be the fastest way to reverse the population decline. But Japan resists that option," says Boling. For Japan to reverse course, he adds, "there must be a sea change in attitude about the benefits of immigrants."
Finally, Japan’s demographic erosion will be closely watched by its two East Asian neighbors, who view it as a cautionary tale they must avoid at all costs. China recently admitted its first population drop since 1961, while South Korea has reported the world’s lowest fertility rate for three years in a row.
If things really go south, would Japan implement Plan 75? Certainly not, but the director wouldn’t be too surprised if it did.
"After the film's release, I encountered the voice of people who strongly desire to have this option because they are afraid of their future living as the elderly," says Chie Hayakawa. "I feel that we Japanese are covered with [such a] sense of resignation and hopelessness [that we] cannot believe or expect our government to bring any solution to it."