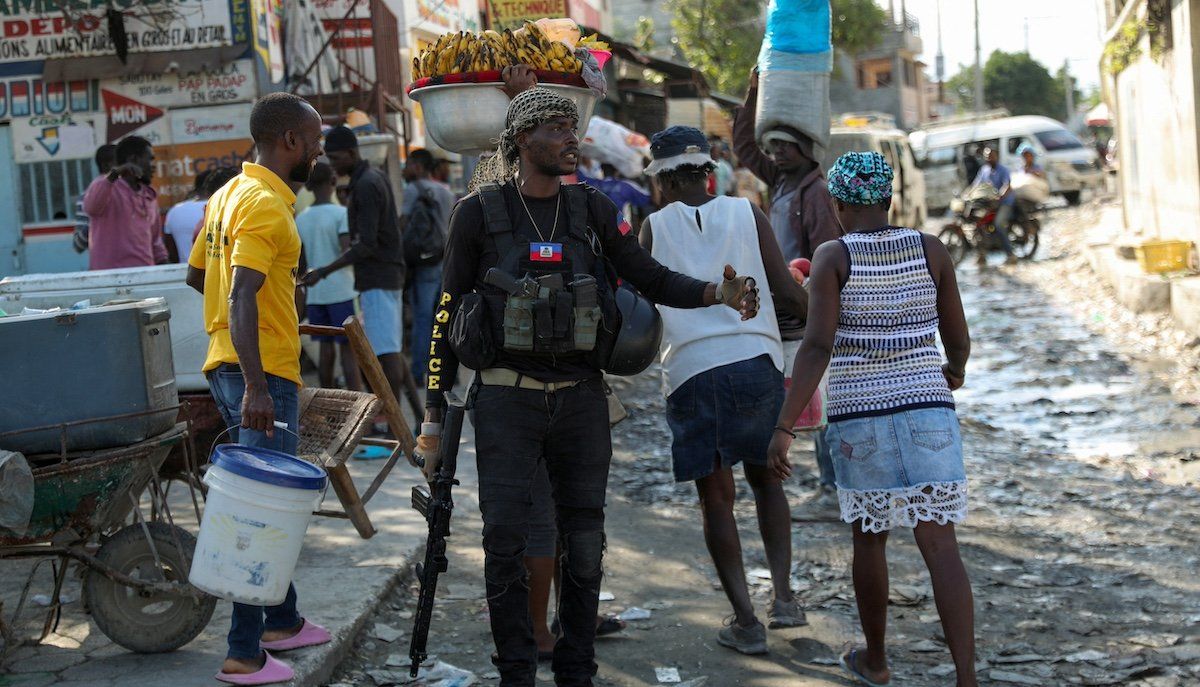
Prime Minister Ariel Henry is refusing calls to resign and remains stranded outside Haiti while the leader of the country’s largest gang alliance, Jimmy Chérizier, threatens civil war.
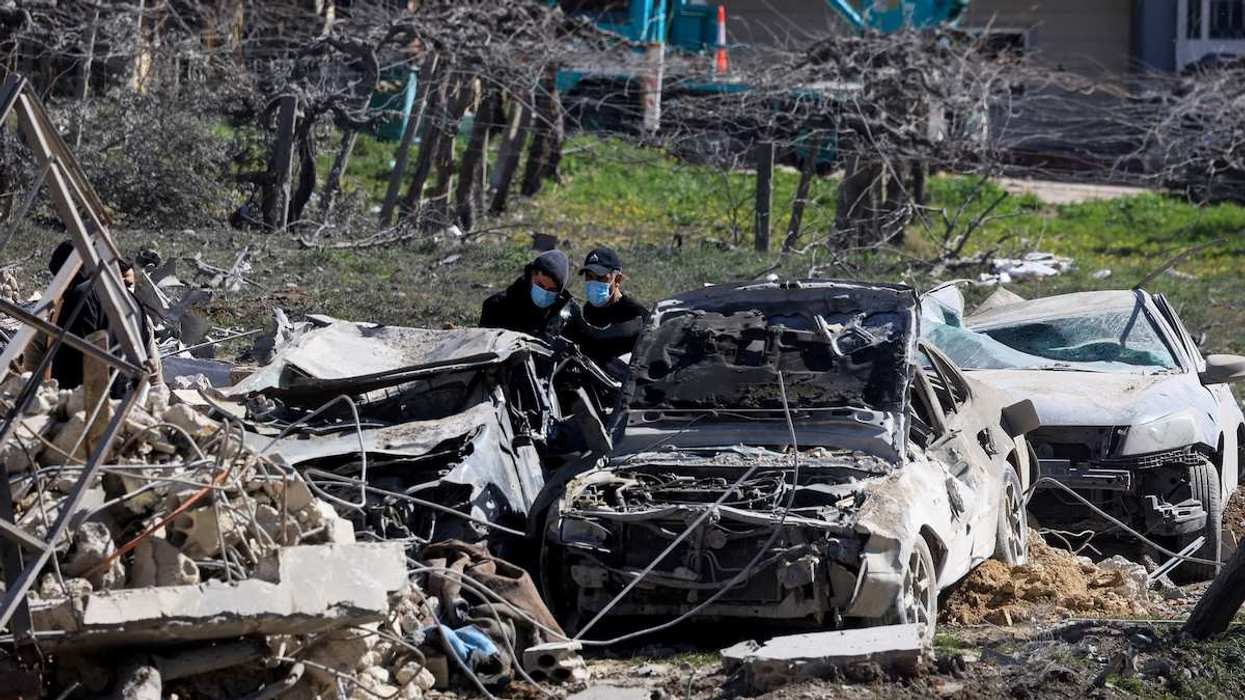
Henry visited Nairobi last week in an attempt to secure a Kenyan-led intervention force to help bring peace to Haiti. But heavily armed gangs took advantage of his absence and launched assaults against Haiti’s two largest prisons and the international airport in Port-au-Prince, paralyzing the country. Henry has since tried but failed to return to Haiti.
Washington responded to the chaos on Wednesday, calling for an “urgent” political transition, and the UN Security Council met behind closed doors to discuss next steps. Henry’s predecessor, Claude Joseph, told CNN that political groups within Haiti are discussing a plan for a three-member transitional council that will select an interim president to organize elections.
Why the power vacuum? Haiti has not held polls since 2016, has no elected officials in office, and Henry and his government are widely seen as illegitimate. He came to power unelected after President Jovenal Moïse was assassinated in 2021 but has been unable to prevent men like Chérizier from seizing 80% of the capital and unleashing intense physical and sexual violence on ordinary Haitians.
Two names to watch: Guy Philippe and Chérizier. Philippe played a leading role in the 2004 coup and is pressing for a council of his choice to put him in power. Chérizier, however, is the man with the most firepower.
Danny Shaw, a Haiti expert at the Council on Hemispheric Affairs, says Haitians don’t see Chérizier, aka Barbecue, as a panacea.
“Overwhelmingly within Haiti – besides Barbecue's own base down in Delmas – they say he's an opportunist. They say he's not trustworthy,” says Shaw.
During his recent visits, Shaw also hasn’t seen much enthusiasm for the long-awaited Kenyan-led police mission, which is again in doubt. Despite Washington’s efforts to stay at arm's length, Shaw says many Haitians fear the deployment will amount to a “US invasion and occupation in blackface” that will fail to resolve the nation’s crises.