The cherry blossoms aren’t the only thing that flower anew every spring. Around the world there are several international crises and conflicts that reliably heat up as the weather changes. Here’s a look at three important ones to keep an eye on in the coming months:
In Afghanistan, when the snows melt, the fighting gets worse. The Taliban have already begun their perennial “spring offensive” and fresh violence could doom already fragile hopes for a new political breakthrough. Earlier this year, the weak US-backed Afghan government offered a comprehensive peace to the Taliban, but the group has refused to put down its arms or talk with Kabul until US forces leave the country — which isn’t in the cards. With Islamic State affiliates also increasing attacks, the situation in Afghanistan will only deteriorate further in the coming months.
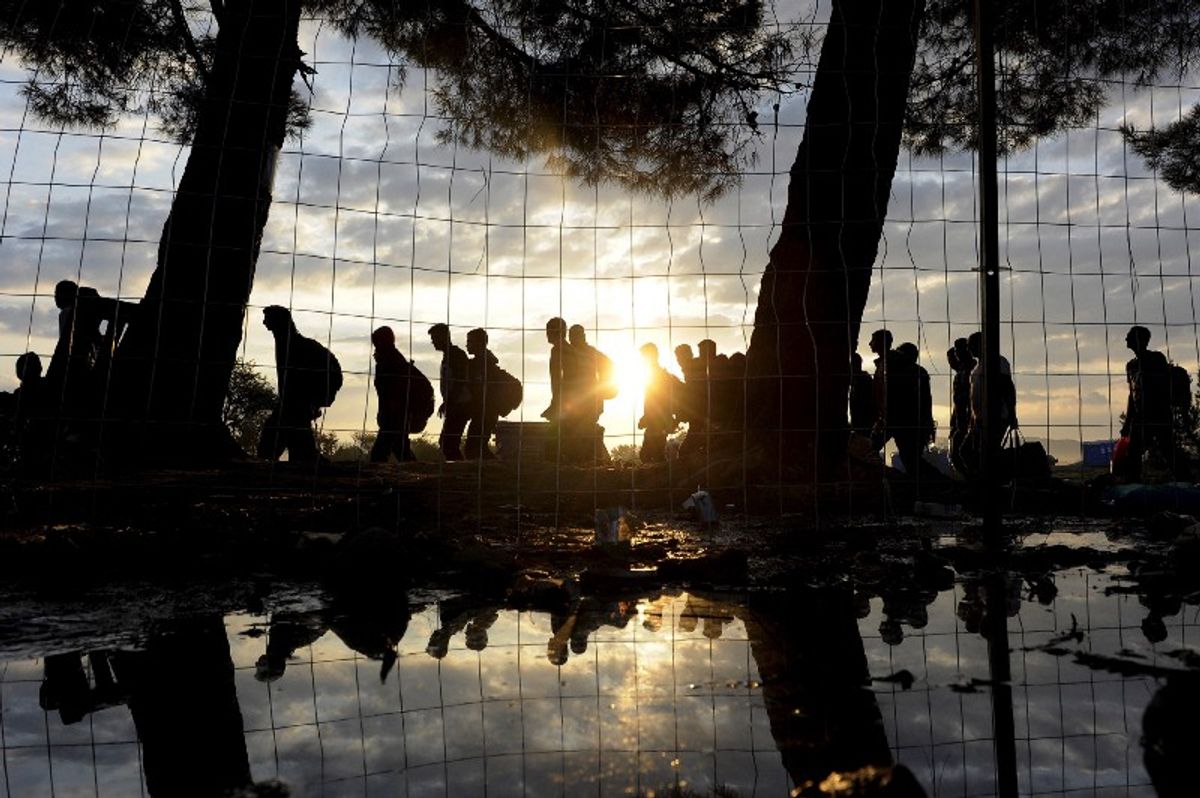
Warmer weather also means more refugee flows across the Mediterranean to Europe. While those flows have fallen since Italy and Libya reached an accord on controlling migrant smuggling in early 2017, fresh political uncertainty in Libya could make things more difficult this summer, and even a modest uptick in arrivals will ensure that refugee policy remains a hot-button issue across Europe. Nowhere is that more true than in Italy itself, which has yet to form a government after an election defined by anti-immigrant furor.
Lastly, to Nigeria, where clashes between nomadic herders and farmers in the central and southern parts of the country have left nearly 10,000 dead since 2011. Desertification of pasture lands in northern Nigeria has forced herders to stay in central zones deeper into the spring, leading to conflict with local farmers. The violence, which now rivals the war with Boko Haram in severity, is likely to affect Nigeria’s 2019 presidential election — it is concentrated in several swing states. President Muhammadu Buhari, who is seeking re-election, has been slow to react.