On Saturday night, just days before the US government was set to run out of money, US President Joe Biden and House Speaker Kevin McCarthy reached an agreement to raise the debt ceiling. The deal is, as expected, a modest compromise that includes more spending cuts than Democrats were initially willing to make, but less than Republicans wanted.
In exchange for avoiding a catastrophic default and kicking the can down the road until Jan. 2025, the US government will keep nondefense spending almost flat in the 2024 fiscal year and increase it by only 1% the following year. The agreement will fully fund veterans care but nix unspent COVID money and claw back some IRS funding, expand (some) work requirements for SNAP beneficiaries, and fast-track environmental approvals for energy projects.
Now it only needs a thumbs-up from Congress this week. Despite opposition from progressives and the GOP's Freedom Caucus, the bill is expected to pass in the House and get overwhelming support in the Senate. But don't be surprised if we're having this conversation again right after the 2024 election.
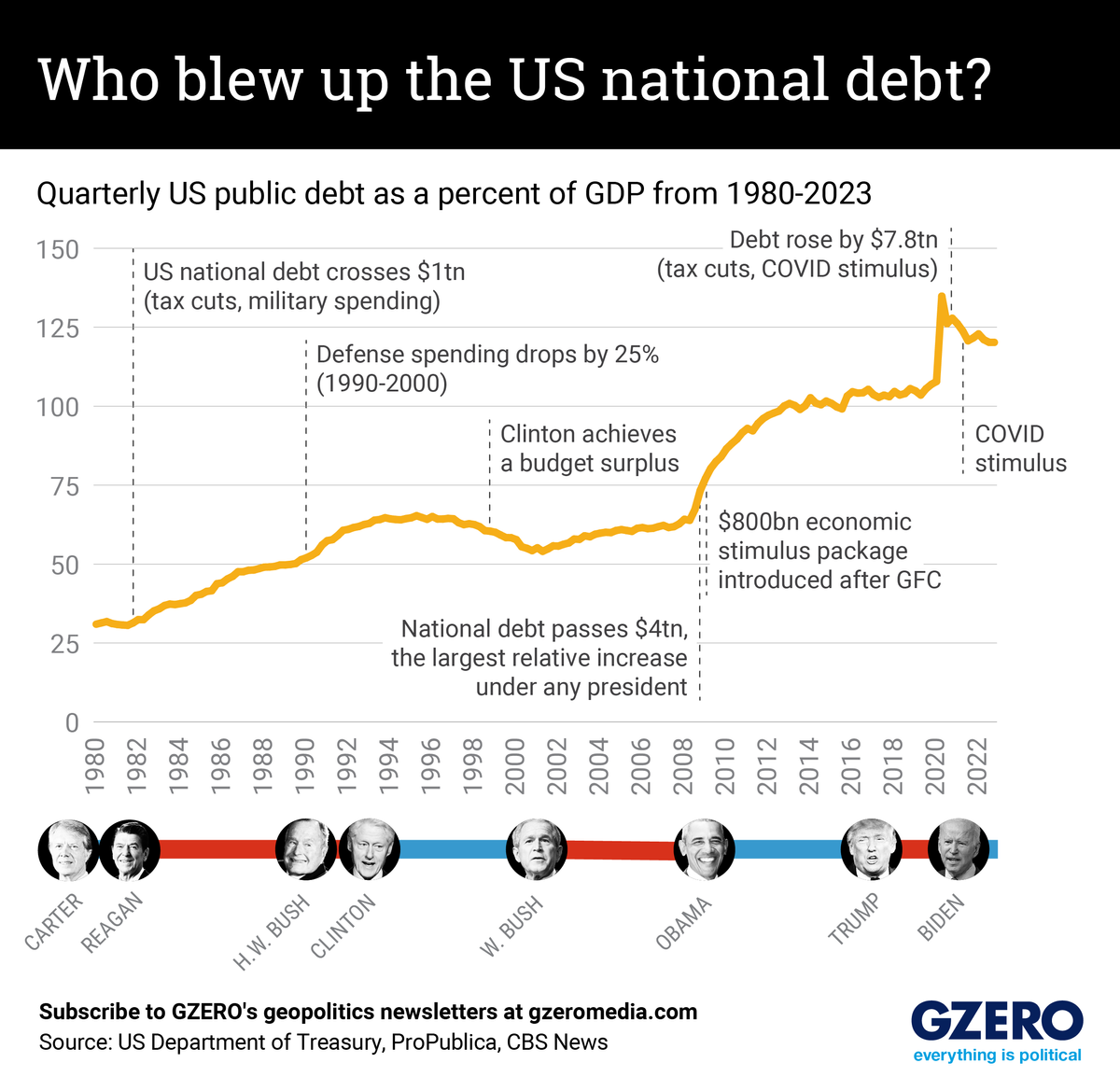
Indeed, prior to the Biden-McCarthy deal, there was plenty of finger-pointing over who was to blame for the US creep toward fiscal purgatory. Democrats blamed Republicans for refusing to raise the debt ceiling without preconditions, while Republicans said that Dems’ overspending landed the country in this mess in the first place.
But a look at US federal debt compared to GDP over the past four decades – which highlights America’s ability to pay back its debt – shows that both Democratic and Republican spending and fiscal policies have fueled the country’s current imbalance. We look at these figures dating back to 1980.