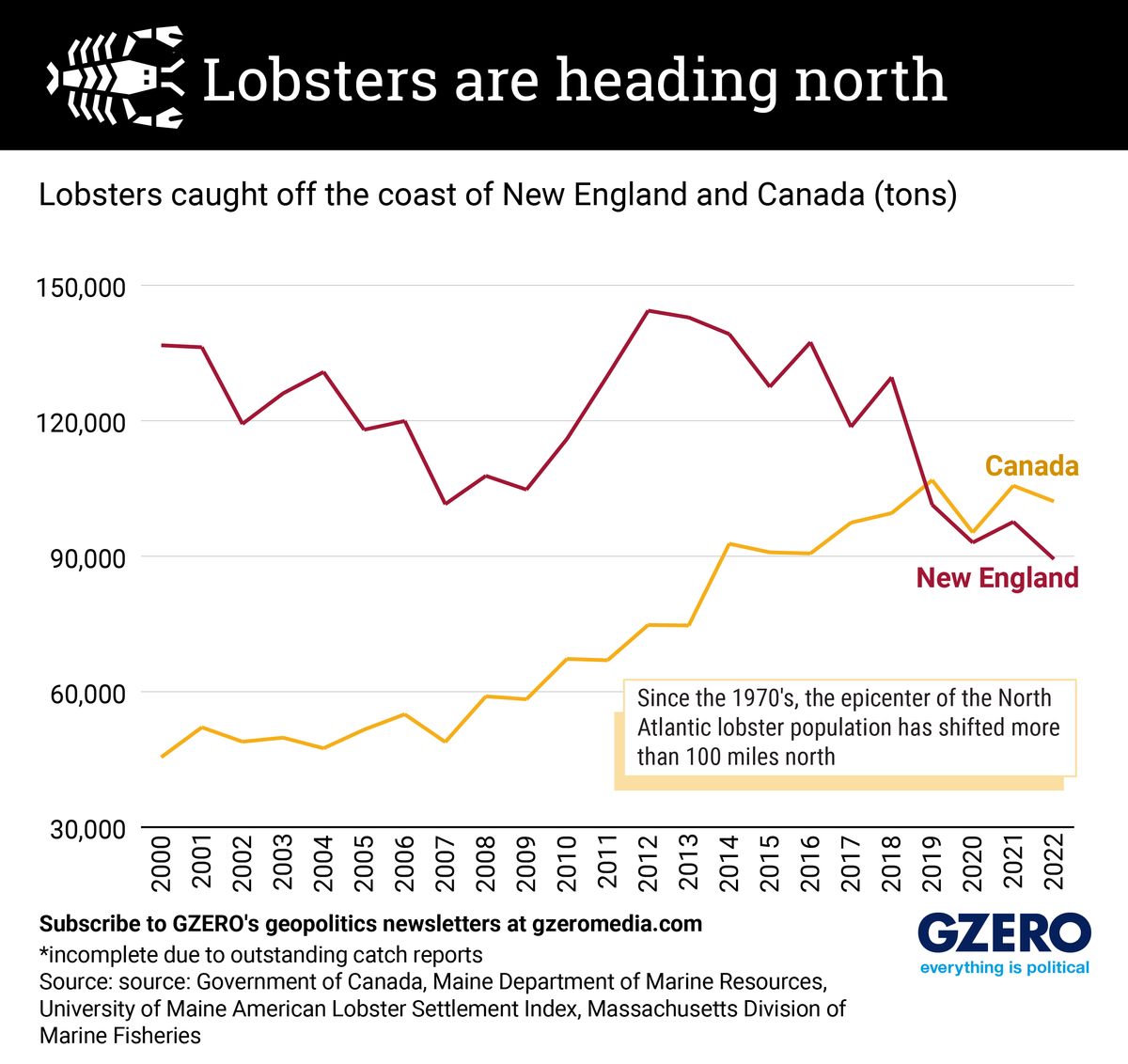
It has been impossible to ignore climate change this summer. July was the hottest month on record, there have been unprecedentedly destructive wildfires and floods across Canada, and water temperatures in the southern United States are skyrocketing. But ocean temperatures further north are also on the rise. The Gulf of Maine, which stretches from Cape Cod to Nova Scotia, is one of the fastest-warming ocean territories on the planet, and that is bad news for the US lobster industry.
Lobsters are very sensitive to rising temperatures, causing the North Atlantic population to move north over the last 50 years in search of chillier waters. Initially, this northward trend benefitted coastal Maine as lobsters fled Rhode Island and Massachusetts. But even Maine’s lobster catch has been steadily declining to Canada’s benefit. Canada’s lobster industry is experiencing a boom, achieving record profits in 2022.
We examine the effect of this northward shift in lobsters by looking at the amount of lobsters caught in New England and Canada over the last 22 years.