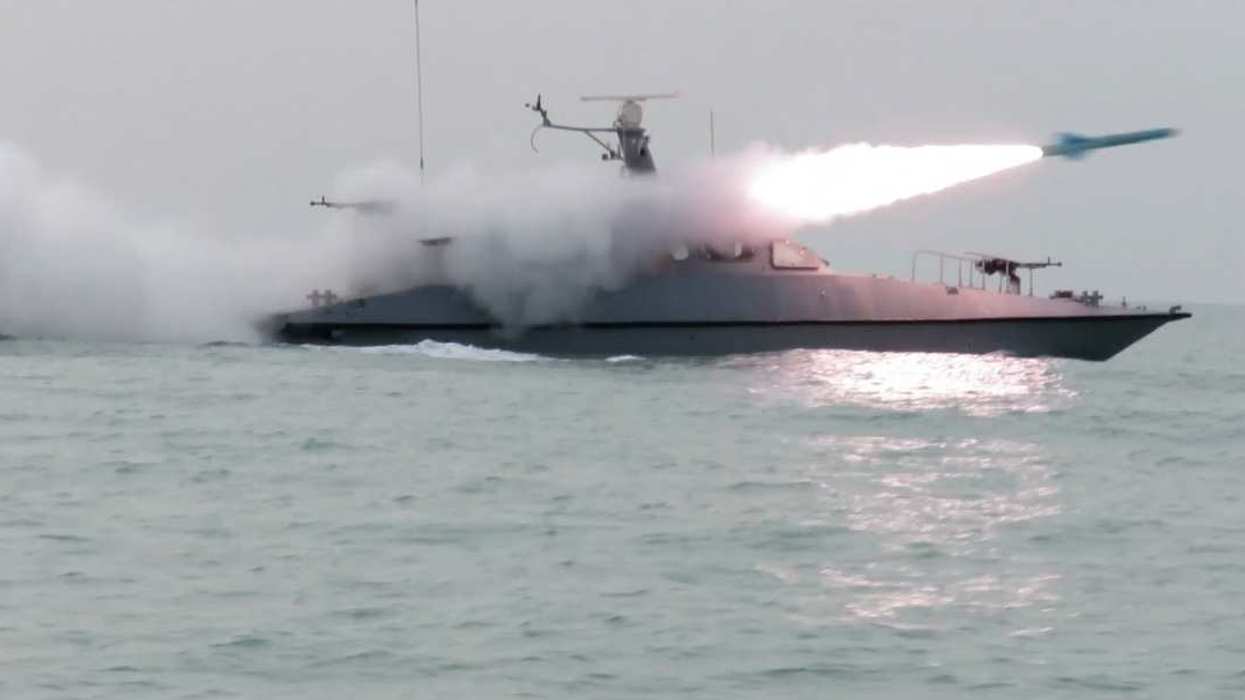
Ukrainian and Western leaders aren’t the only ones criticizing Russia’s decision to suspend its participation in the Black Sea Grain Initiative, a deal brokered by the UN and Turkey that allows Ukraine to ship grain across the Black Sea to the rest of the world. On Tuesday, a senior official in Kenya’s foreign ministry tweeted that Russia’s decision to exit the Black Sea Grain Initiative is a “stab on the back” (sic) with rising global food prices, one that “disproportionately impacts countries in the Horn of Africa already impacted by drought."
That’s not a good sign for a Russian government that’s worked hard in recent months to persuade developing countries that the Kremlin cares more about their well-being than Americans and Europeans do. Russia has insisted that Ukraine’s grain has gone mainly to rich countries, but Ukraine has provided Afghanistan, Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, Sudan, and Yemen with 625,000 tons of emergency food supplies over the past year as part of the Black Sea agreement, according to the UN.
Turkey’s President Recep Tayyip Erdogan has said Russia’s Vladimir Putin wants to return to the deal, as Russia did after a brief suspension last November. More criticism from poorer countries might speed up that reversal.