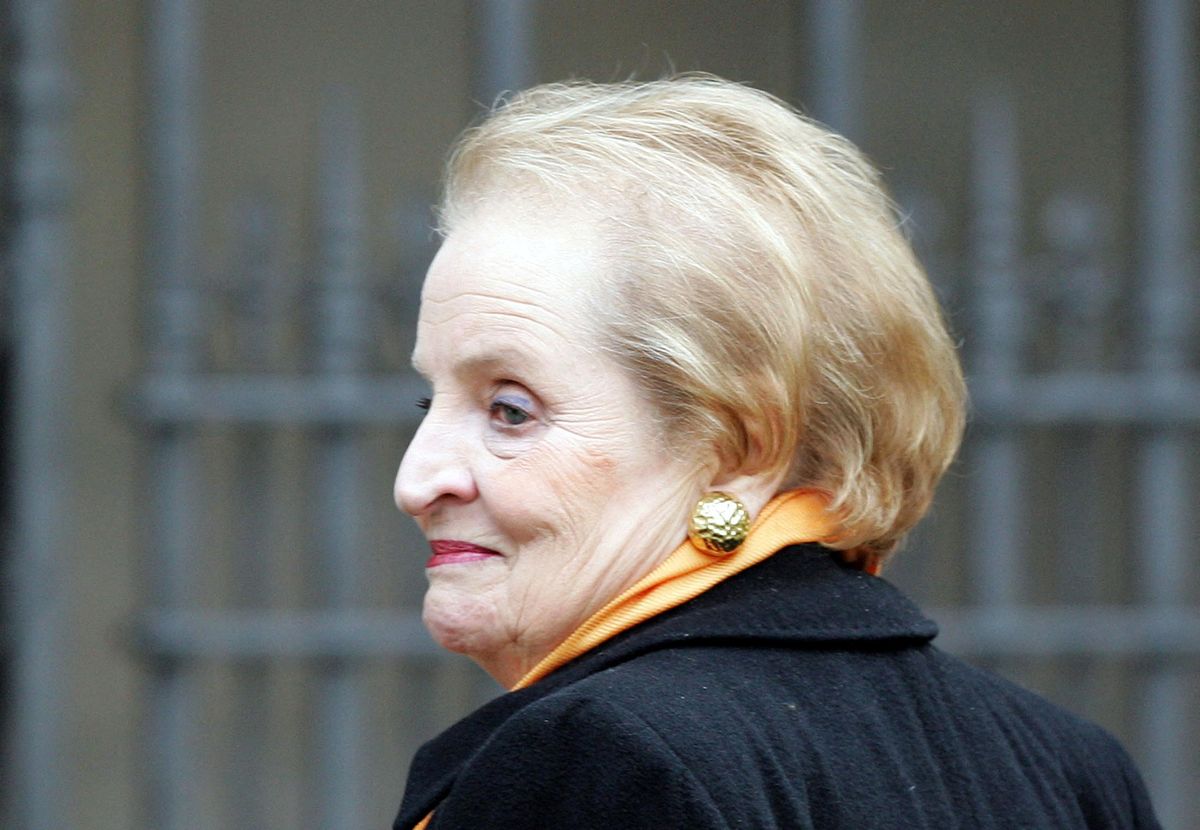
She was born Marie Jana Korbelová in 1937 in Czechoslovakia, a young democracy trapped between Hitler’s Germany and Stalin’s Soviet Union. The daughter of a diplomat, she became a refugee at a young age — a Czech Jew who would be raised as a Catholic with false stories about her family history.
After spending the war years in London, her father accepted a post at the Czech embassy in Belgrade in what was then Tito’s Yugoslavia. This was Marie Jana’s first experience of dictatorship. Sent away to school in Switzerland, she learned to speak French and changed her name to Madeleine. After the Communists took power in her native Czechoslovakia, the family emigrated to the United States. The 11-year-old Madeleine Korbel arrived at Ellis Island on November 11, 1948.
On Wednesday, she died as Madeleine Albright, one of the most remarkable and unique foreign policy figures of the late 20th century.
As US secretary of state during Bill Clinton’s second term, Albright, the first woman to hold the post, brought together a razor-sharp diplomatic mind with an unusually personable and approachable style. She believed that ordinary people could, and should, understand the foreign policies that were being carried out in their name.
Having fled persecution by both the Nazis and the Communists, Albright was keenly aware of the dangers of illiberalism and authoritarianism. In recent years, her fears about this only grew — her last book, published in 2018, was titled Fascism: A Warning. But she also bore the stain of failure to stop the Rwandan genocide during her tenure as UN ambassador. It was, she said, her greatest regret.
In many ways, her time as secretary of state in the late 1990s is a throwback to the very last moments when the US was truly a unipolar superpower. This was before 9/11 rattled America, and before China really captured Washington’s attention. Before the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan tarnished America’s image abroad and frayed its society at home, and most certainly before Russia began to pose a challenge again to US interests.
Yet, Albright’s signature policy moves echo through today. She was a firm advocate of NATO’s expansion into the former Eastern Bloc in 1998, and one year later she backed the alliance’s bombing of Serbia to stop Belgrade’s slaughter of the Kosovars in 1999. Both moves infuriated a relatively unknown figure in the Russian administration at the time: Vladimir Putin.
Albright, 84, left behind a world that cannot have made her happy — a world in which authoritarianism is resurgent, and a divided America seems unsure of its global role. But as she wrote in her memoirs: “The goal we seek, and the good we hope for, comes not as some final reward but as the hidden companion to our quest. It is not what we find, but the reason we cannot stop looking and striving, that tells us why we are here.”
In a New York Times editorial published just last month on the eve of Russia’s invasion, Albright wrote that “instead of paving Russia’s path to greatness, invading Ukraine would ensure Mr. Putin’s infamy by leaving his country diplomatically isolated, economically crippled, and strategically vulnerable in the face of a stronger, more united Western alliance.”
Marie Jana Korbelová knew what it was to be a refugee. Madeleine Korbel learned firsthand about dictatorship. Madeleine Albright understood the importance of defending political values, even at the risk of great cost.