It won’t be closely covered by Western media, but on Wednesday, the world’s fourth most populous country and third-largest democracy will stage a historic election. More than 200 million voters will elect a new president, vice president, and about 20,000 state and local officials.
This vote comes at a crossroad moment in the country’s quarter-century history as a democracy.
A little background. Indonesia’s democracy isn’t old enough for voters to take for granted. Its government remained a dictatorship from the time Suharto, a military man, used a purge of communists to seize power in 1965 until a financial crisis catalyzed 33 years of public frustration to force the strongman from power in 1998 and to usher in change a year later.
The next 15 years featured hotly contested elections, but only among candidates representing the country’s most powerful families, who manipulated Indonesia’s political system to keep power for themselves while keeping political outsiders outside.
That ended in 2014 with the election of Joko Widodo (known widely as Jokowi). It was Jokowi’s outsider status as a former furniture salesman who became the sincere, middle-class, can-do mayor of a small Javanese city, and then of Jakarta, the nation’s capital, that lifted him onto his country’s largest political stage.
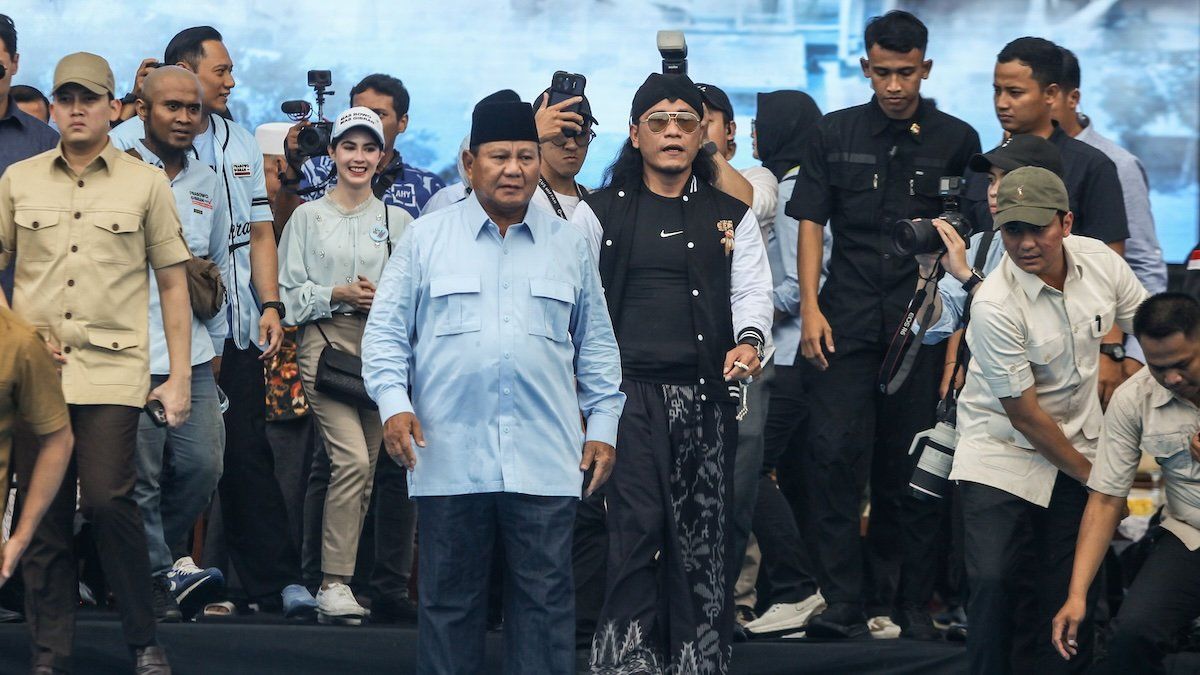
In 2014, Jokowi easily defeated Prabowo Subianto, Suharto’s son-in-law and a former special forces commander with an ugly human rights record, to become president.
But once in power, Jokowi discovered the political clans of an older generation still held leverage, and the only reliable tool to advance much-needed reform was his own personal popularity bolstered by a few political insiders who helped him build a strong parliamentary majority.
In 2019, a newly confident Jokowi beat Subianto again, but this time the president agreed to make Subianto his defense minister, bringing his opposition party into alliance with his government and taking control of parliament.
His government made substantial progress in, for example, improving access to health care, education, and other public services for the poor, developing more affordable housing, and democratizing land policy. He has also helped keep the country’s economy steady and opened a project to build Indonesia a modern new capital city.
Jokowi, who failed in a controversial bid to strike down presidential term limits, now hopes to play political kingmaker. To accomplish this, he’s made a choice that critics say compromises his integrity by promoting the presidential candidacy of Subianto, his morally compromised former rival.
What comes next? Subianto is now trying his own version of the “embrace your former rivals” strategy by pledging to follow in Jokowi’s still-popular footsteps – and, for those who find that strategy too subtle, by making Jokowi’s son his vice-presidential running mate.
Anies Baswedan, Jokowi’s former speechwriter and then education and culture minister, has repeatedly antagonized his former boss and earned his political wrath.
There’s a third candidate, Ganjar Pranowo, a charismatic outsider in the Jokowi mold, and a member of Jokowi’s party, who now finds himself without the outgoing president’s support.
Recent polls give Prabowo nearly 50% of the vote with Baswedan and Ganjar at about 20% each. If no one wins a majority in Wednesday’s first round, a runoff will be held in June.