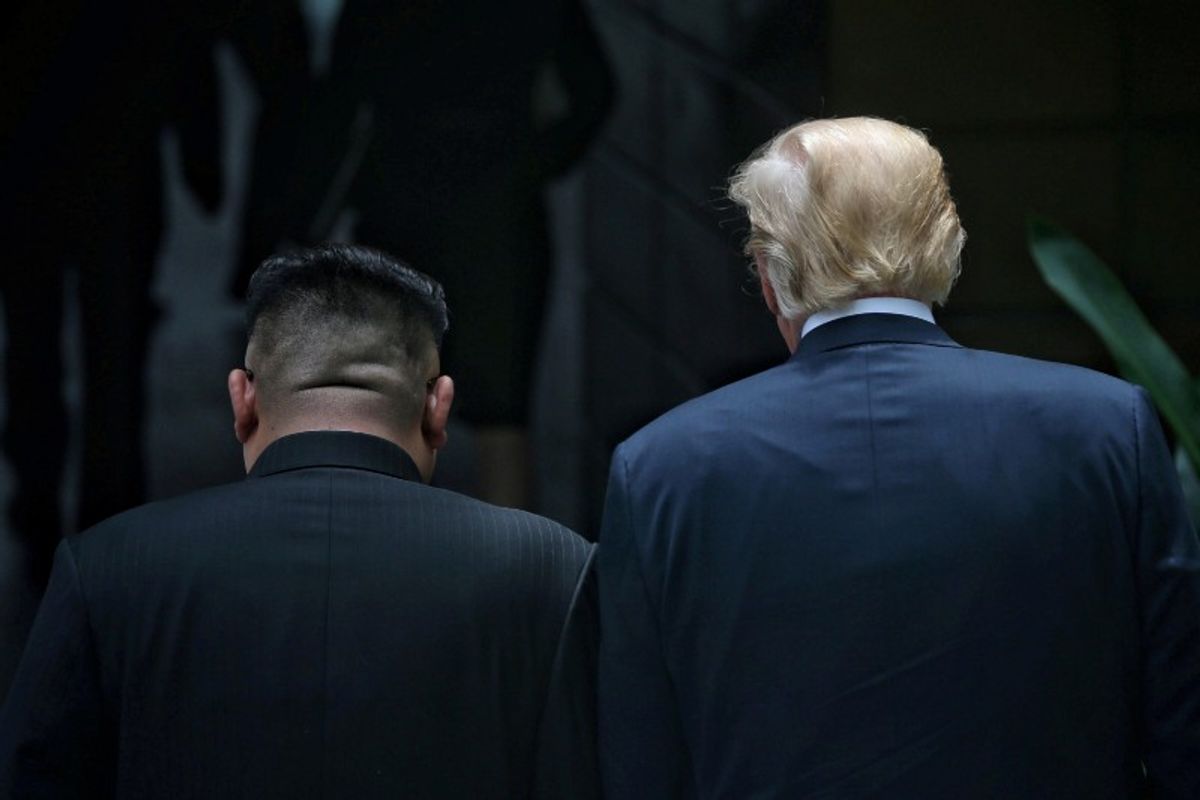
Over the past twelve hours, all eyes have understandably been on Trump and Kim, but there are three other key players whose interests are at play. Here’s what each wants and worries about:
CHINA: More than anything, Beijing wants peace in the neighborhood as it seeks to increase its strategic and economic clout in Asia at Washington’s expense. Any diplomatic process that reduces the prospect of war or promises a reduction of US forces on the peninsula is a win that China will cautiously support. The biggest danger for Beijing — aside from a diplomatic collapse that puts peninsular war or regime change back on the agenda — is that the Kim-Trump relationship goes too well in a way that enables Pyongyang, an unwieldy but still valuable client state, to seek alternatives to Beijing’s patronage.
SOUTH KOREA: No one has hustled the diplomacy harder than South Korean President Moon Jae-in. Seoul, which lives under constant threat of North Korean bombardment, has the most to gain from a normalization of relations between North Korea and the United States. Reducing the security threat from the North and opening the way to economic opportunities above the 38th parallel would be huge wins for Moon, and most South Koreans are in favor of a formal peace treaty between the two nations. Moon’s got two big concerns: first, that in a bid to win Kim’s confidence, Trump cuts back the US security umbrella for South Korea too quickly for Seoul’s comfort (Trump’s concession on military drills, for example, caught the South Koreans by surprise); second, that he gets caught in the middle of an unconventional diplomatic process driven by two unpredictable leaders that ultimately falls apart.
JAPAN: Tokyo is the US’ closest ally in the region, though these days that doesn’t mean what it used to — just ask the Germans or the Canadians. Tokyo wants to see an agreement that cools tensions on the peninsula, and it has its own interests in securing the return of Japanese citizens abducted by North Korea decades ago. But Japan doesn’t have a seat at the table here, and Tokyo worries that Trump may ultimately cut a deal that puts America First while leaving Japan out in the cold: say, by accepting a commitment from Kim to freeze testing of long-range missiles that can hit the US, but without scraping his short-range missiles and other chemical and biological weapons that could still threaten Japan.