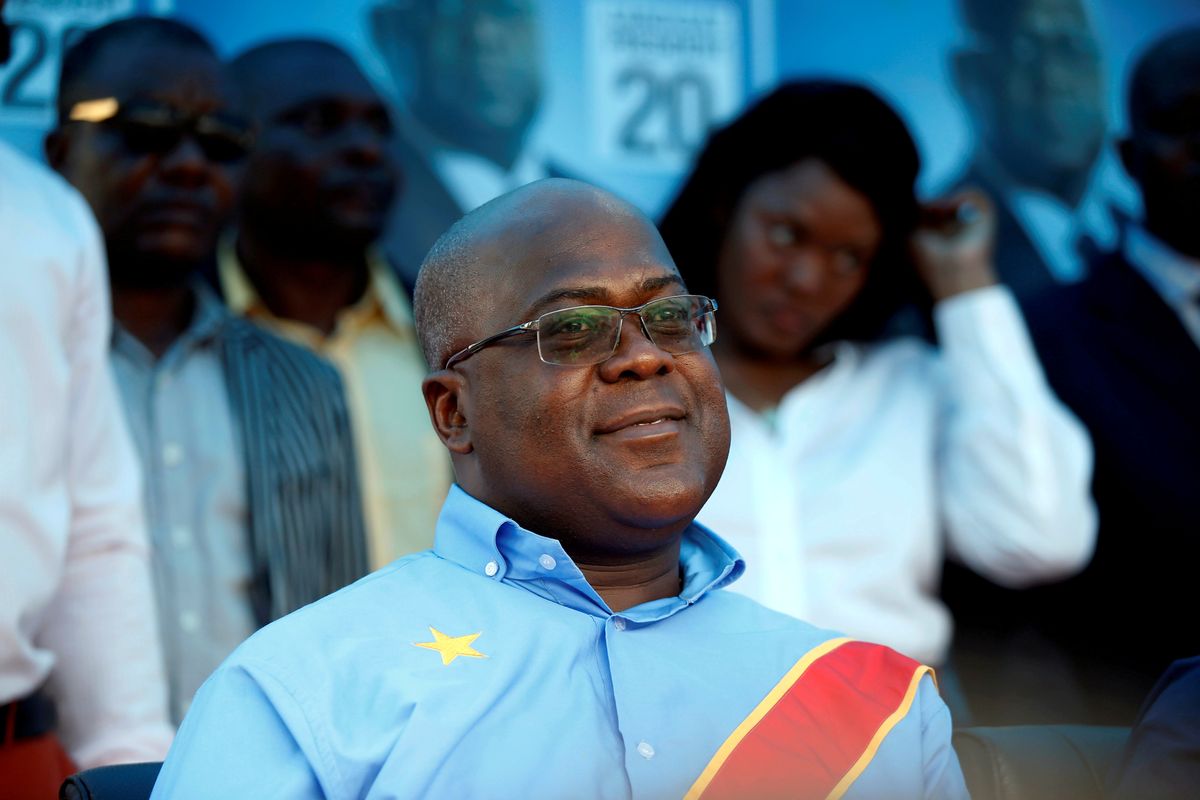
After weeks of rising tensions, opposition leader Felix Tshisekedi was named the winner of the Democratic Republic of Congo recent presidential election. Mr. Tshisekedi himself appeared surprised as he spoke with reporters following Thursday's official announcement. "Nobody could have imagined such a script would seal the victory of an opposition candidate," he said.
Depending on what happens next, Tshisekedi, the son of long-time opposition leader Etienne Tshisekedi, will become the first person to take power in the DRC as the result of an election since the country won independence from Belgium in 1960.
Does this represent the long-hoped-for peaceful transfer of power? Not so fast. Martin Fayulu, another opposition candidate, quickly denounced the result as an "electoral coup" that does "not reflect the truth of the ballots." French Foreign Minister Jean-Yves Le Drian added that the results were "not consistent" with reports from election monitors and that "The Catholic Church of Congo did its tally and announced completely different results." This story is far from over, and the risk of violence in coming days is real.
The bottom-line: Fayulu supporters suspect Tshisekedi's victory may be the result of a secret deal with outgoing President Joseph Kabila, who had come to accept that his preferred successor couldn't win. If so, people of the DRC may get the appearance of transformational change rather than the real thing.