Disproportionate burden. Despite accounting for a small amount of global carbon emissions, small island developing states are on the front lines of the climate crisis, facing unique challenges as a result of climate-induced ocean warming and rising sea levels. Consider that most of the Bahamas is expected to be underwater by 2050, while the entire Maldives could be submerged by the end of the century.
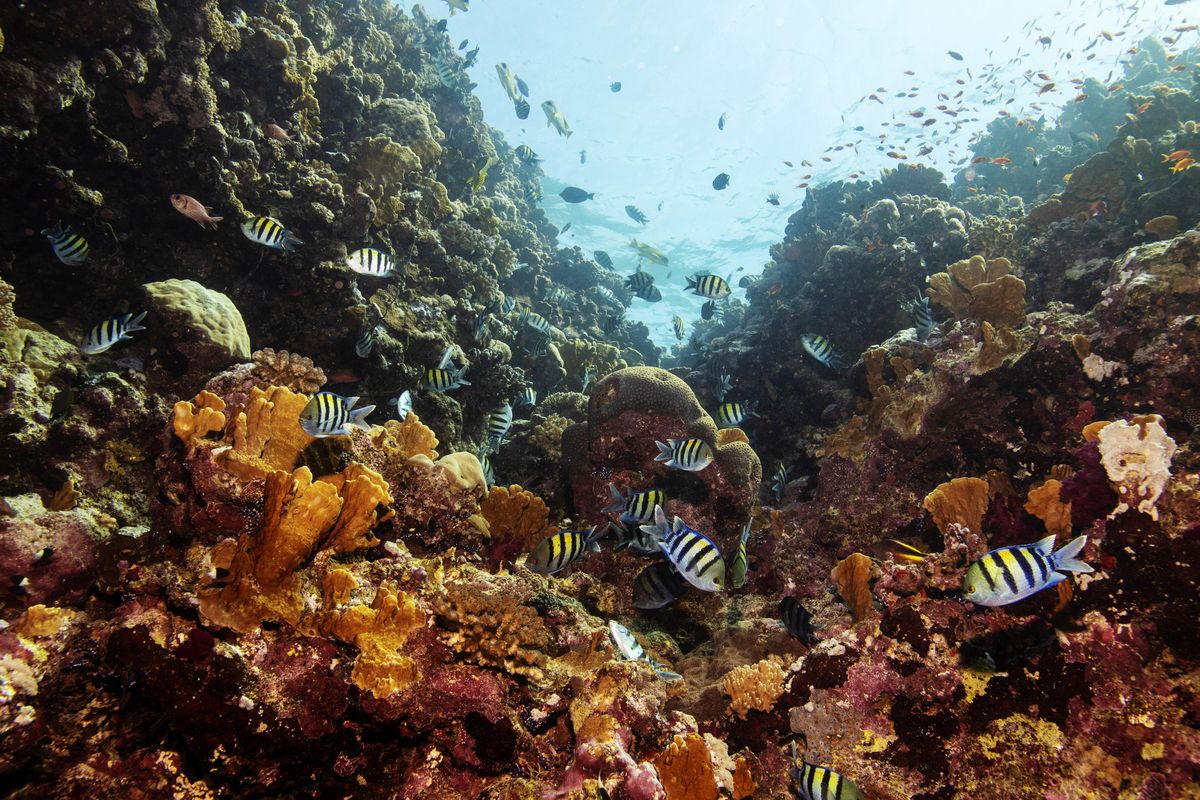
At the same time, current trends threaten marine life (coral reefs, algae, turtles, fish) that sustain many of these island communities. Take the tuna trade, for example. Degradation of the ocean could reduce annual tuna catch in the Pacific by 10 percent over the next three decades, analysts say. This is a massive problem for islands like the Marshall Islands, where agriculture and fishing accounts for over 15 percent of GDP.
What are these islands doing about it? Ocean states like the Maldives have been pushing for global action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions that have led to more destructive weather events (cyclones, hurricanes) in recent decades. They have also been the driving force behind the inclusion of targets in the Sustainable Development Goals 2030 agenda designed to "conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development." To date, 97 countries have signed onto a binding international agreement on sustainable fishing.
On issues of marine life preservation, many island nations have been batting above their weight, closing off marine protected areas to preserve Earth's biggest ecosystem and protect the economic interests of their communities. For Grenada, an island of 112,000 people in the Caribbean, protecting essential marine life habitats has sought to raise the productivity of lucrative (fish) products.
But these initiatives could prove futile if top emitters don't limit their global greenhouse gas emissions — fast. Together, China and the US account for roughly 40 percent of global emissions. Chinese and Indian emissions, particularly from coal, remain the single most lethal threat to the climate, according to Eurasia Group's Gerry Butts.
While these countries have pledged to reduce their carbon output in the medium term, massive gaps persist. President Xi Jinping has not outlined a solid blueprint for how China plans to get to Net Zero by 2060. Meanwhile, India, the world's third largest emitter of carbon dioxide, is embroiled in a back-and-forth with rich nations in North America and the EU about whether the latter should spend more on helping developing countries realize their climate action plans with less stringent requirements.
Sharing the load. While small island developing states are particularly vulnerable to many of the problems caused by the warming climate, it is clear that these nations, with tight purse strings and limited resources, cannot go it alone as sea temperatures reach their highest levels in a million years. Since they are largely at the mercy of large economies responsible for the vast amount of damage, the only solution is a global one.