UNRWA: What is it?
In the days since Israel accused employees of UNRWA of participating in Hamas’ Oct. 7 attacks, the US and at least nine other countries have temporarily suspended funding for the UN agency, which provides humanitarian aid and social services to the roughly 6 million Palestinians classified as refugees in Gaza, the West Bank, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon.
What is the origin of UNRWA?
The United Nations Relief Works Agency was created in 1949 by the recently founded United Nations to provide humanitarian aid and economic support to the roughly 700,000 Arabs of Palestine who fled or were driven from their homes during the Arab-Israeli war of 1948.
What does UNRWA do?
It runs schools and health clinics, delivers humanitarian aid, food, and cash assistance to the poor, and runs basic microfinance programs. The agency employs about 20,000 education staff, who run more than 700 schools, and more than 3,000 health staff working at roughly 170 hospitals.
Who funds it?
UN members who donate to its budget. In 2022, the US was the largest single donor country, giving about a third of UNRWA’s $1.2 billion budget, or $343 million. The combined contributions of the EU and its member states amount to about 40% of the budget. Saudi Arabia is the largest Arab donor, coming in with $27 million. Among other leading countries from the Global South, India donated $5 million, Russia gave $2 million, and China just $1 million. You can see the full list here.
How important is Gaza in UNRWA’s work?
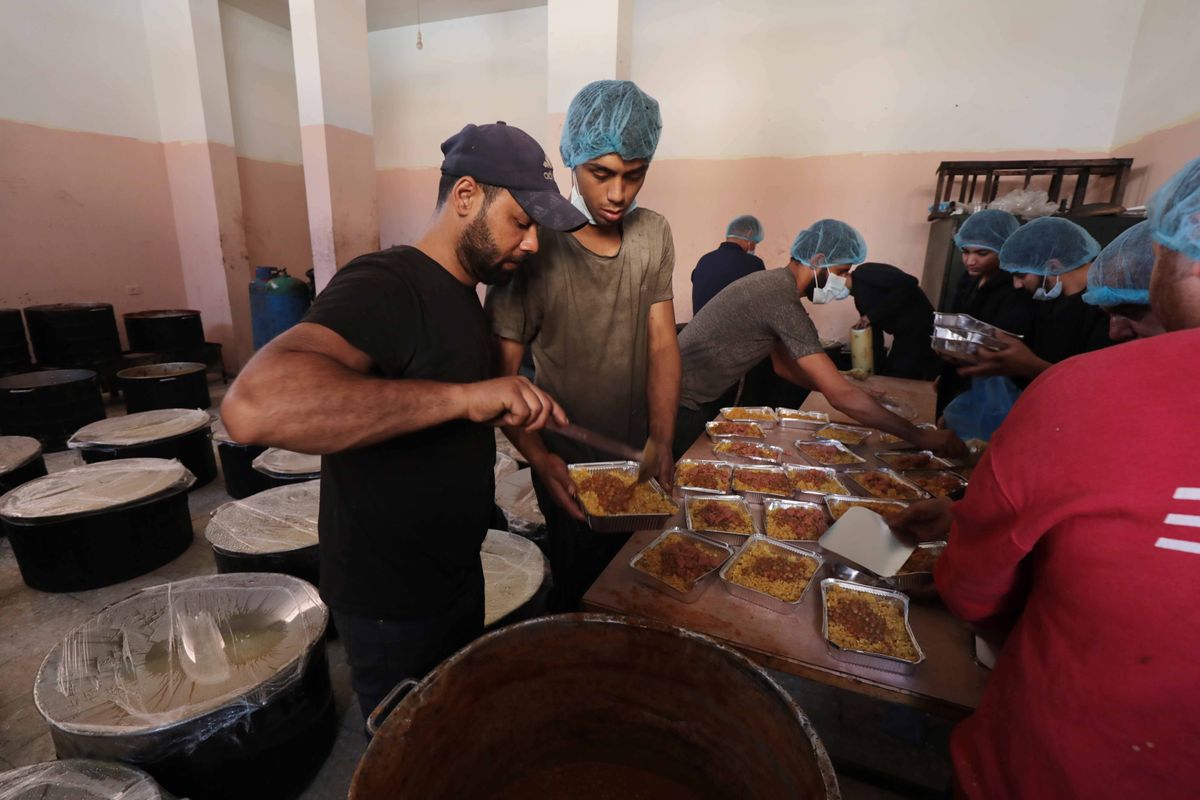
About half of the agency’s total staff is employed in Gaza alone, and it is the strip’s largest employer after Hamas and the Palestinian Authority. Since Hamas came to power nearly 20 years ago, a security blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt has kept the enclave largely cut off from the outside world. As a result, UNRWA is a critical source of aid and services for the strip’s roughly 2 million people, 75% of whom are refugees.
How will the funding cutoff affect UNRWA?
UNRWA says that without a resumption of funding, it will be unable to continue functioning in Gaza beyond February and that this could lead to a humanitarian catastrophe. Even before Israel’s recent siege, bombardment, and invasion, between 60% and 80% of Gazans lived in poverty, according to the World Bank and the UN. Since Oct. 7, more than 80% of the population has been displaced. Nearly half are sheltering in UNRWA-run facilities. The UN is warning that if UNRWA’s activity is curtailed, a famine will be “inevitable.”
What are the controversies surrounding UNRWA?
Successive Israeli governments have criticized UNRWA for fomenting anti-Israeli sentiment in its schools, taking a political position in the Israel-Palestine conflict, and lending support to Palestinian militants. On Monday, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu – who has long called for UNRWA’s dissolution – said the agency is “riddled” with Hamas.
What is the relationship between Hamas and UNRWA?
The militants of Hamas are the governing authority in Gaza, and their movement is deeply rooted in the strip’s religious and social institutions. In principle, this makes it almost impossible for UNRWA to operate without interacting with Hamas or employing its sympathizers.
Abetting or participating in a militant attack, of course, is a different story. UNRWA says it has terminated the employees allegedly involved and opened an investigation into the issue.
What is the relationship between UNRWA and Israel?
Despite its criticisms of UNRWA, Israel relies on UNRWA to distribute aid and provide services in Gaza. If UNRWA were dissolved or incapacitated, Israel’s army would, in principle, have to take on this task itself.