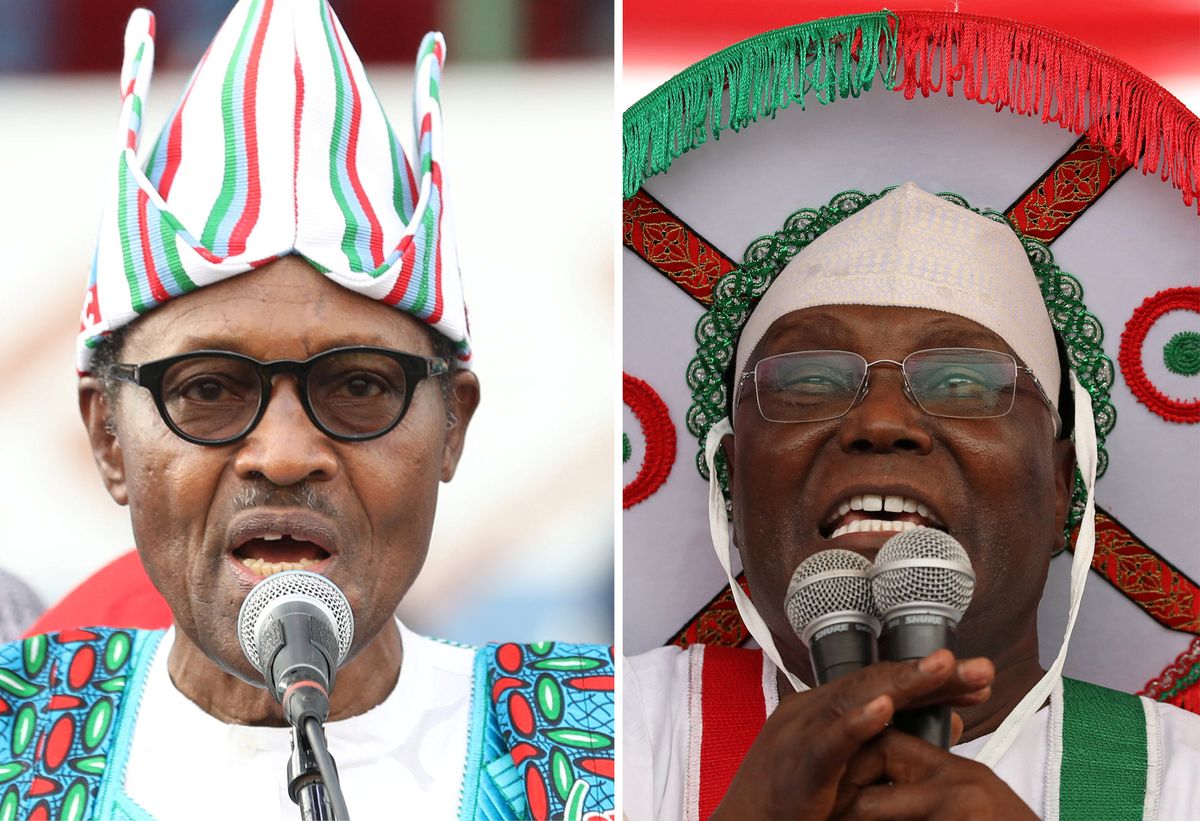
Four years ago, Nigeria made history. The 2015 presidential election marked the first time that a Nigerian president lost an election, accepted defeat, and passed power to the opposition. Given that Nigeria is the most populous country and largest economy in Africa, that was good news for the entire region.
Well, tomorrow voters will return to the polls to decide whether to grant a second term to current President Muhammadu Buhari, or to demand he hand over power to his opponent, the business tycoon Atiku Abubakar. The choice is decidedly underwhelming.
Mr. Buhari's record over the past four years has been mixed. The oil-dependent economy is only barely emerging from a deep recession, and the unemployment rate has doubled to more than 23 percent since he took office. Some 84 percent of Nigerians think the government is corrupt. The security situation remains dicey: although Mr. Buhari had early success against the Islamic militants of Boko Haram, the group has been on a fresh tear lately. Meanwhile, violence between farming and herding communities – often with a Christian vs Muslim overlay – has surged in recent years.
What's more, persistent rumors about Buhari's poor health have reinforced the sense that the country is run by a leader without sufficient vision or energy. It's never good when your president has to deny publicly that he has died and been replaced with a body double or clone.
But the alternative to Mr. Buhari inspires little enthusiasm. Mr. Abubakar is a former customs boss who has built a vast corporate conglomerate and used his fortune to curry political support. He says he wants to use privatizations as a way to spark economic growth – a critical challenge given that roughly half of Nigeria's 190 million people live in extreme poverty – but critics worry that he just wants to enrich his cronies by handing them lucrative state assets.
The vote is expected to be very close. On balance, Mr. Buhari probably has an edge – he enjoys the natural advantages of being an incumbent, and there has been some turbulence within Mr. Abubakar's campaign and party machine down the homestretch. But this election is still very much up for grabs.
The wildcard scenario: Mr. Abubakar has warned that the military might interfere with voting to help Buhari win, and there are lingering concerns about the potential for vote rigging. If the election result is inconclusive, or at least close enough that one side refuses to accept defeat, there is some risk of violence.
The bottom line: Just four years after a peaceful and orderly transfer of power that was a model for the region, Nigeria is in a tough spot: a reasonably smooth election would grant power to one of two deeply uninspiring leaders, while a contested ballot could deal a deep blow to democracy in Africa's largest country.