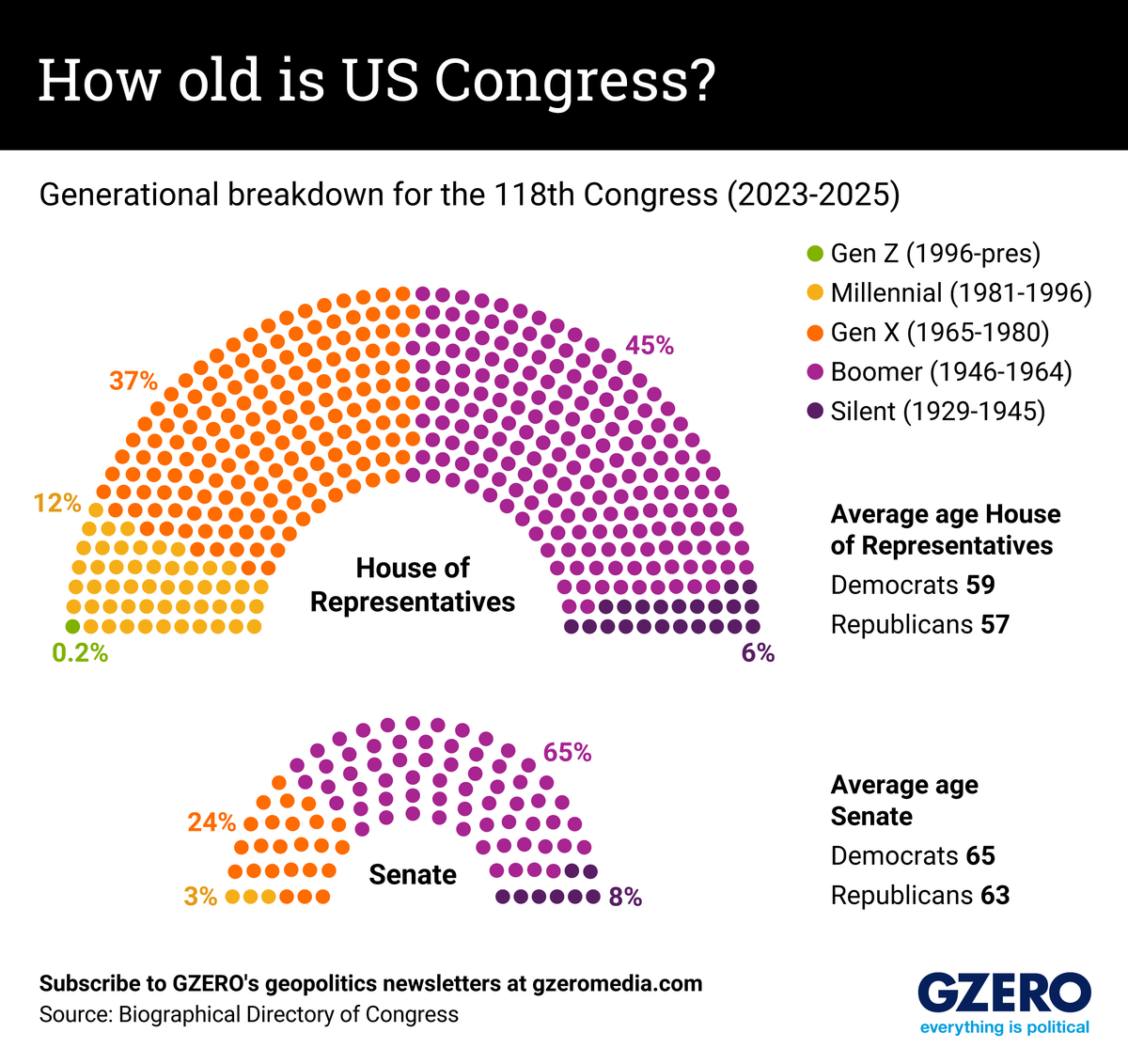
Recent headlines of Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell, 81, struggling to speak and Sen. Dianne Feinstein, 90, appearing confused in hearings have left some Americans concerned that their leaders are staying in power past their prime.
In Congress, baby boomers and the Silent Generation make up 54% of all members. The Senate’s median age, 65.3, has risen by three years since 2017, while the House’s dropped slightly from 58.4 to 57.9. In 2023, the first Gen Z representative was elected, joining the ranks of 13 others under the age of 35.
The Democratic Party skews older, with 17 House members from the Silent Generation compared to five across the aisle. This is likely because Democrats value seniority in committee leadership positions and don’t have term limits like the Republicans.
These age concerns go beyond health and mental fitness; they question whether a gerontocratic government will adequately prioritize slow-moving crises, from climate change to mounting federal debt, whose consequences aren’t immediate but will shape the future for younger generations.