While much of the world’s attention is on the Gaza Strip, tensions and violence are rising in the West Bank. Here are the basics:
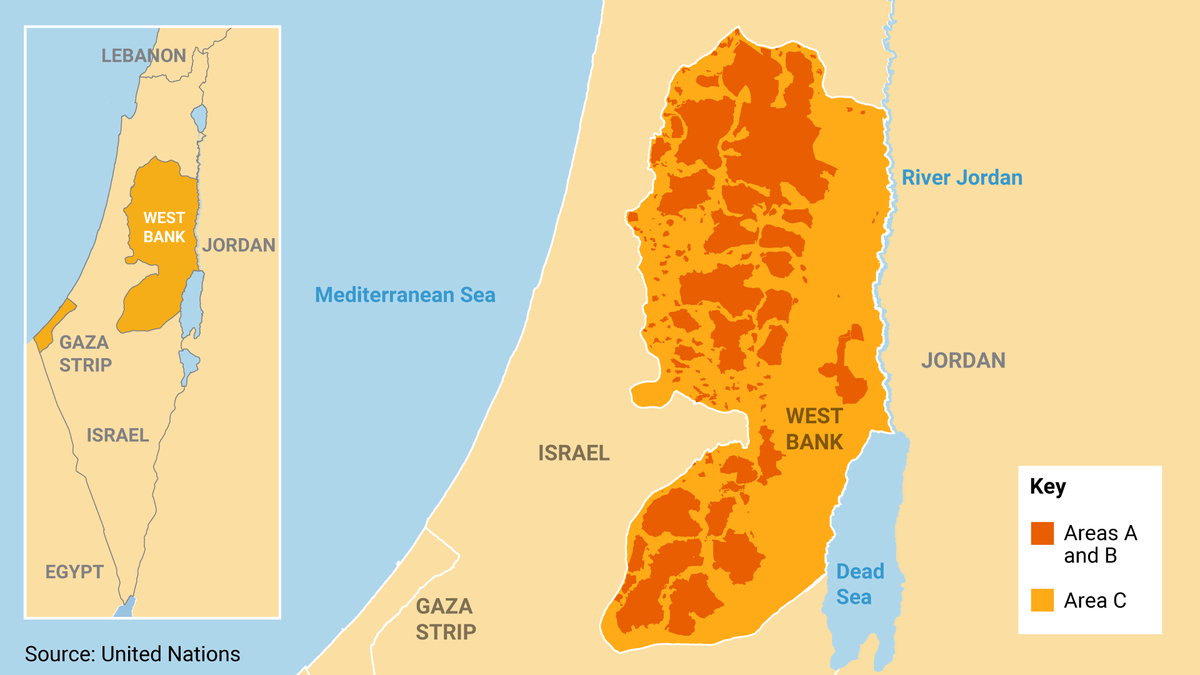
What is the West Bank? A 2,200-square-mile enclave — larger than Rhode Island, smaller than Luxembourg — that has been under Israeli military occupation since 1967. It has a population of 3 million Palestinians, and nearly 700,000 Jewish settlers who live in communities known as “settlements,” which are illegal under international law.
Why is it called the “West Bank”? Because it lies along the west bank of the Jordan River, which now forms the border between the lands under Israel’s control and the Kingdom of Jordan. The West Bank and the Gaza Strip were both included as part of the Arab State that the UN proposed in its 1947 plan to partition Palestine between Arabs and Jews. Arab rejection of that plan, and the subsequent Arab-Israeli War of 1948, left the West Bank under Jordan’s control.
How did Israel get control of the West Bank? Israel won the territory from Jordan in 1967, during the Six-Day War.
What happened after that? Under the pretext of bolstering its defenses against future attacks by its Arab neighbors, Israel built hundreds of Jewish settlements and less formal settlement outposts in the West Bank. These settlements, which are protected and funded by the Israeli government, have often uprooted Palestinian homes and entire villages. Some settlements are populated by ultra-religious Jews who wish to live near ancient Jewish lands and holy sites in the area.
The Israeli government has also used military security or environmental conservation laws to restrict Palestinian access to vast areas of the West Bank. Along with the settlements, these interventions have turned the Palestinian-inhabited areas of the West Bank into a land archipelago of more than 160 non-contiguous areas.
Who governs the West Bank? Under the Oslo Accords of the 1990s, which were meant to pave the way to a two-state solution, a government called the Palestinian Authority (PA) has some powers, including policing and security functions, over Palestinian population centers in the West Bank. These areas are known as Areas “A” and “B.” All other areas, known as “Area C,” are under Israel’s control. Area C covers more than 60% of the West Bank.
Who controls the Palestinian Authority right now? The secular nationalist Fatah Party, the main rival to Hamas, rules the PA and has recognized Israel since the 1990s. The PA president is Mahmoud Abbas, known by his nickname “Abu Mazen.” General elections have not been held since 2006, when Hamas’ narrow victory led to a brief war between Fatah and Hamas. When it ended, Hamas was in power in Gaza, while Fatah held its ground in the West Bank.
Can Palestinians move freely through the West Bank? No, they are subject to a number of permanent or temporary checkpoints along key roads linking Palestinian areas. Jewish settlers have access to their own roads and infrastructure, which Palestinians are not permitted to use.
Can Palestinians from the West Bank enter Israel? Yes, but they must have special permits, often tied to work — day labor in Israel is a major source of income for the West Bank economy. In 2002, citing security concerns after a wave of suicide bombings in the 1990s and a violent uprising against the occupation that began in 2000, Israel began building a 440-mile “separation barrier” with the West Bank.
Who pays for running the West Bank? Israel funds the areas it controls. It also collects tax revenue on behalf of the Palestinian Authority, and has the power to unilaterally withhold this revenue from the PA if it chooses.