China hints zero-COVID shift, censors online protesters
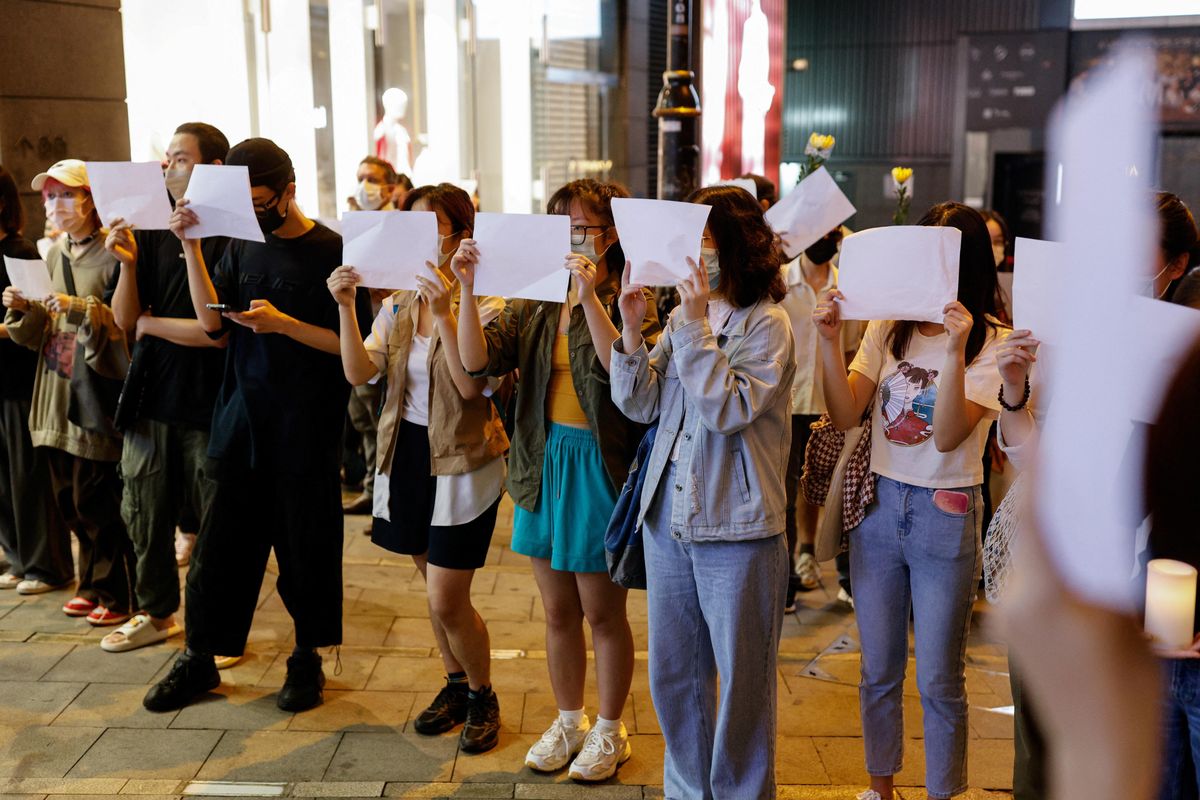
Chinese people who can't wait to ditch zero-COVID — basically everyone except the government — got a glimmer of hope Thursday, when the senior official overseeing the policy said that China was entering a "new stage" in taming the virus. Although what that means is unclear, his comments follow moves by several big cities to relax lockdown rules. Meanwhile, now that most COVID protesters are off the streets, Xi Jinping's censors have taken the fight to cyberspace. They'll have to get creative because Chinese netizens are now ranting about zero-COVID with the online equivalent of the now-verboten blank sheets of paper: sarcastic memes or words that sound similar to Xi or resign. Interestingly, the government outsources content moderation to social media companies that use a mix of humans and artificial intelligence. Exhaustion with zero-COVID might be the biggest test to date of a system that’s not designed to be perfect but rather effective enough at wiping out critical voices.
Some rare good food news out of Ukraine
The UN says it is on the verge of brokering a deal to resume Russian ammonia exports via a Black Sea port in Ukraine. What’s ammonia anyway? The smelly gas is a key ingredient in nitrate fertilizer, which is needed to help plants and seeds grow. Russia and Ukraine are both major global exporters of grain and fertilizer, and disruptions to the output of both due to the ongoing war have led to a global food crisis that’s plunged some 47 million people into “acute hunger,” with import-reliant Africa and the Middle East particularly hard hit. The resumed use of this ammonia pipeline is crucial to avoiding mass food shortages in a year’s time. This comes after a deal brokered by Turkey in the summer saw grain exports pick up again after a Russian blockade caused global shortages and record-high food inflation in developed and emerging economies while bringing poor countries like Somalia to the brink of famine.
A weakened Ramaphosa likely to stay on
South Africa’s embattled President Cyril Ramaphosa could be forced out of office after an independent body found he may have covered up the theft of a large wad of cash from his game farm in 2020. It’s alleged that Ramaphosa, who was elected in 2018 to head the African National Congress – Nelson Mandela’s party – on an anti-corruption platform, illegally stashed up to $4 million at his farm and paid off thieves who stole $580,000 stuffed under his couch (you can’t make this stuff up)! Ramaphosa’s political future now hangs in the balance as he waits for the ANC to vote on Dec. 16 on whether he should lead them into the next general election in 2024 and for parliament to decide whether to impeach him. It is unlikely given that a two-thirds majority – including half of ANC’s parliamentarians – would need to back the motion. Though the ANC has been plagued by infighting since Ramaphosa replaced party stalwart Jacob Zuma in 2018, not enough ANC members will be willing to switch sides to show Ramaphosa the door.