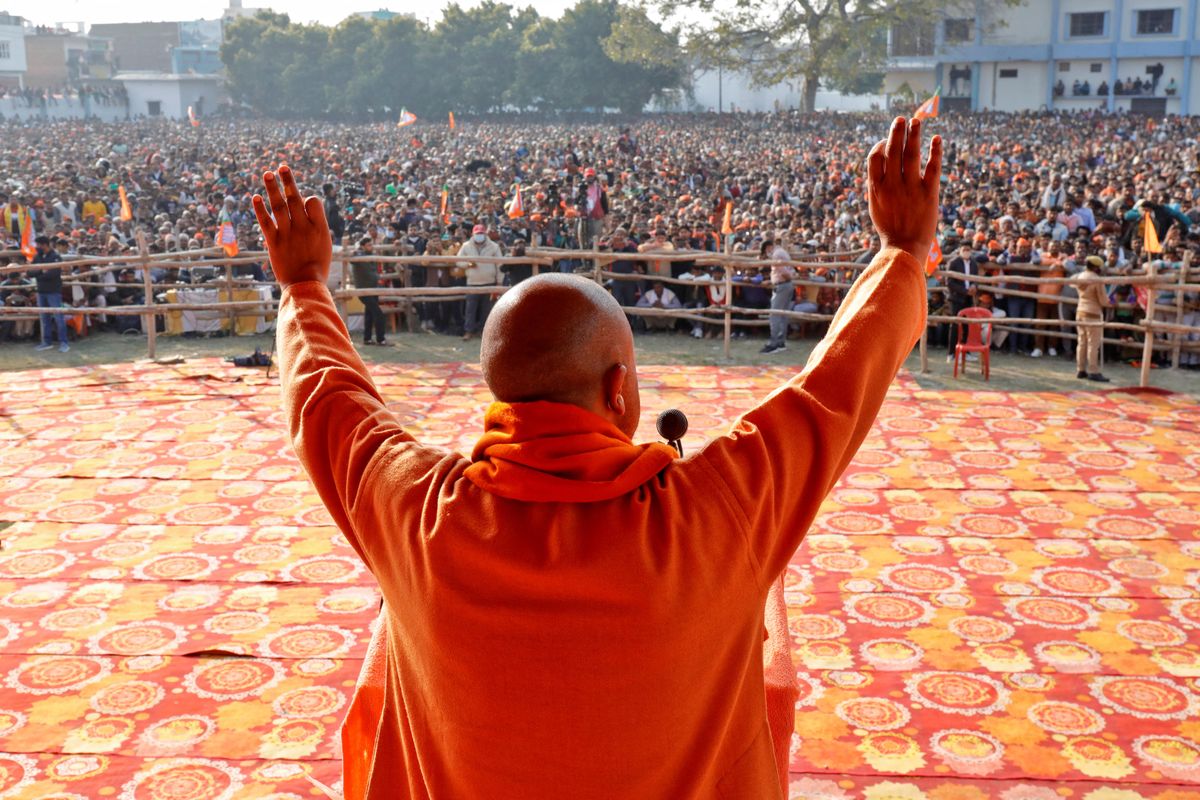
Over 150 million Indians have registered to vote in five state elections that just kicked off and will run through March 7. (Fun fact: 39,598 voters aged 100 and over are registered to vote, according to The Economist.) The biggest electoral battle will take place in Uttar Pradesh, India’s most populous state, which is often seen as a bellwether for national politics. The other states holding elections include Punjab, Goa, Manipur, and Uttarakhand; all but Punjab currently have BJP-led governments.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ruling BJP party has dominated politics in Uttar Pradesh since 2017 – and the PM himself represents the state in Delhi’s Parliament. But the party’s grip on the state could now be weakened. Why? First, at least 20% of Uttar Pradesh residents are Muslims who likely oppose the incumbent chief minister, Yogi Adityanath, a Hindu nationalist who has rallied against marriages between Hindus and Muslims, and has an impressive rap sheet, which includes charges of attempted murder (the case was dismissed in 2019). Second, Modi’s recent drive to reform the country’s farming sector – which gave way to year-long protests – has also hurt the BJP in Uttar Pradesh, an agricultural stronghold with a large rural population. The caste system is also a big factor: Akhilesh Yadav and Kumari Mayawati, former chief ministers, will likely be vying for their caste groups to back them.
Eurasia Group’s Diwakar Jhurani recently said that bread-and-butter issues like access to basic public goods and services, job creation, and infrastructure will also dominate the campaign: “Historical data suggest that Indian voters tend to punish incumbents over dissatisfaction with these issues,” Jhurani says. Opposition parties in all five states will be looking to capitalize on this discontent.