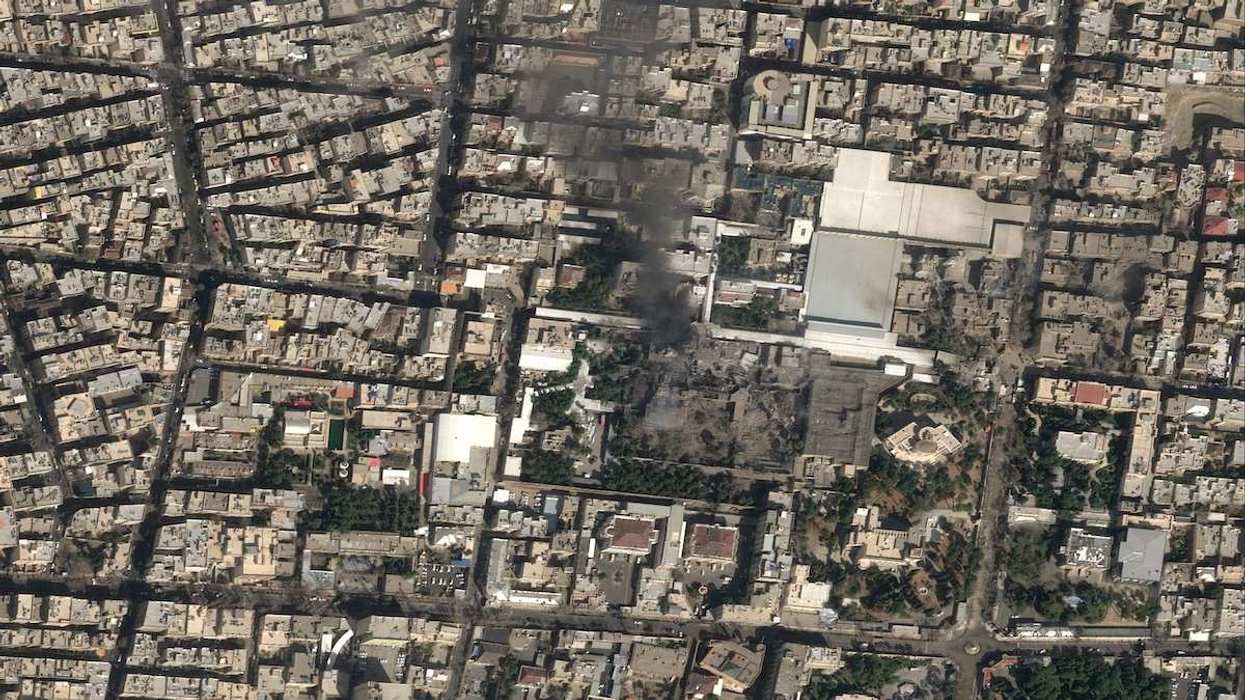
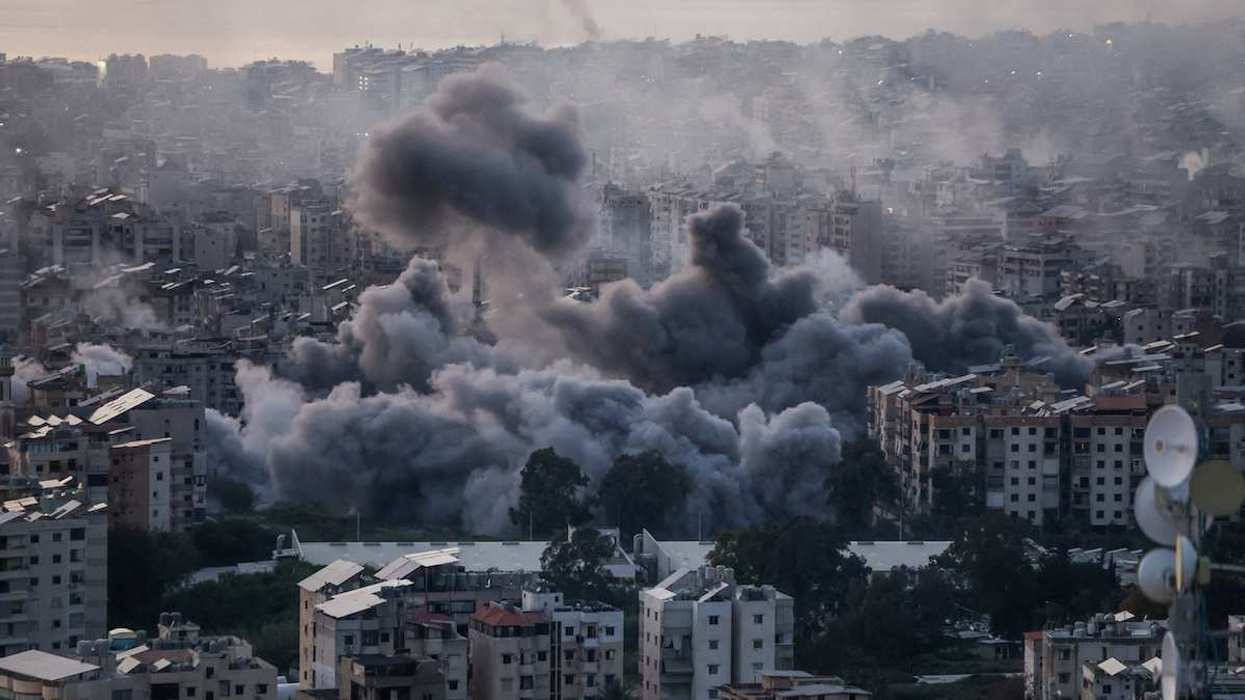
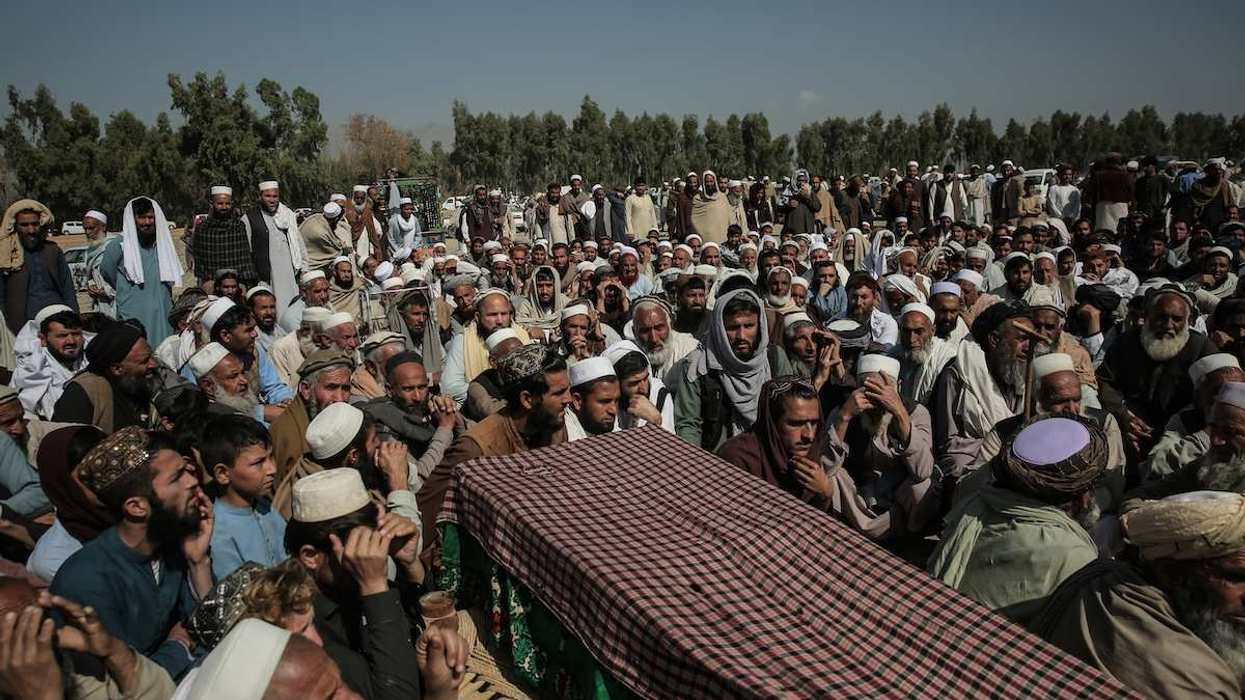
Negotiations are ongoing to end the war in Gaza, with US President Donald Trump urging parties to “move fast” to reach a deal. But that outcome hinges on what comes next: how will Gaza be governed once the conflict ceases? Trump’s 20-point plan proposes to install a technocratic Palestinian authority with no involvement from Hamas, supervised by an international “Board of Peace.” What might this look like in practice, what can history teach us about its possible outcome, and will Hamas accept those terms?
Technocrats and trusteeship
Hamas had already agreed to"a national independent administration of technocrats" in September. Such a regime would be run by non-partisan experts chosen for their competence in various fields, such as infrastructure and financial management, to make and implement policy on a pragmatic, evidence-based basis.
But Hamas has not signed onto Trump’s proposed international supervisory board composed of himself as chair, together with notable public figures such as former UK Prime Minister Tony Blair. The board has been described as an “elite managed trusteeship.” Trump stated that it could entertain “many thoughtful investment proposals and exciting development ideas…crafted by well-meaning international groups.” The proposal sets neither a timeframe nor a path to self rule.
A trip back in time?
Comparisons are already being made to colonial structures imposed by European powers in the 19th and 20th centuries. Starting in 1820, the British controlled much of the region around the Persian Gulf and Red Sea through protectorates, treaty arrangements which saw London handle foreign policy and defense while local potentates ran domestic affairs. The goal was not nation-building, but commerce, to secure shipping lanes east of Suez to India.
That structure changed after WWI, when the League of Nations created the mandate system, supposedly to prepare former colonies for independence, including the British Mandate for Palestine in 1922. But from the start, the mandate suffered from a legitimacy problem: rule without full sovereignty. This “supervision, not control,” as the League framed it, bred resentment and resistance in the form of the Arab Liberation Army. The mandate ended in the Arab-Israeli war, partition, and the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948.
What could this mean for the Board of Peace?
Some critics have decried Trump’s plan as imperialism and a means of commercial gain for the US. The involvement of Blair has also raised eyebrows: Mustafa Barghouti, the general secretary of the Palestinian National Initiative, commented, “We’ve been under British colonialism already.”
But the plan has support from the governments of Qatar, Jordan, UAE, Indonesia, Pakistan, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and Egypt. The plan is also backed by European powers including Spain, Germany, and the UK and France, who recently recognized the State of Palestine, as well as Canada.
Engaging Middle Eastern powers to fund or staff the technocratic authority could mitigate the perception of western colonialism, but without a timetable for sovereignty could also mire regional governments in long-term management of the territory.
Is oversight necessary?
Apart from the terms of the Board of Peace, is any board required at all? Transitional governments can take many forms: Syria is currently transitioning to democracy after decades of dictatorship, starting with votes by an electoral college, but without any foreign oversight. Other nations, like East Timor, successfully transitioned from a colonial regime to self-rule in the early 2000s after a period of oversight organized by the United Nations - but remain dependent on foreign aid for infrastructure building.
Will Hamas ever accept oversight?
Hamas has accepted three points of Trump’s plan: releasing all hostages, surrendering power, and Israel withdrawing troops from Gaza. But it has so far rejected disarmament and Trump’s international board. It remains to be seen whether these are up for negotiation - or deal breakers.