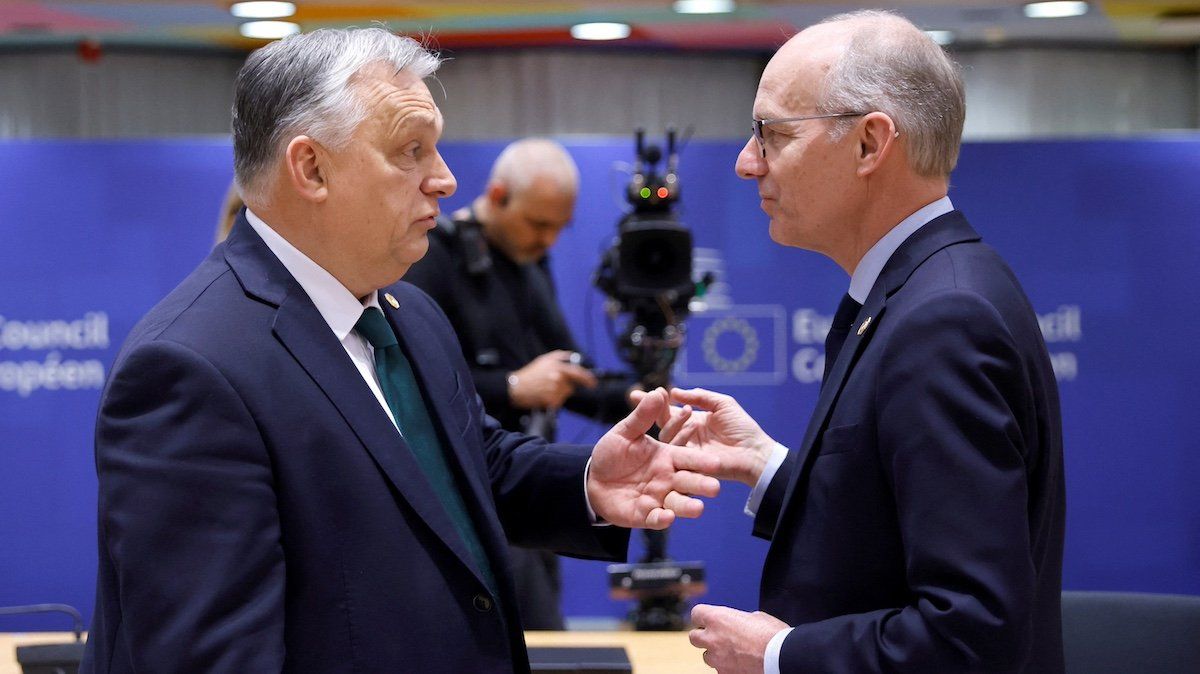
Serial political blackmailer Viktor Orban, Hungary’s prime minister, upset other EU leaders in December by vetoing a plan meant to provide Ukraine with a multi-year €50 billion EU aid package. The EU must, Orban insisted, pledge to revisit the plan each year the money was scheduled for disbursement – with any member retaining the right to veto the plan midstream.
This is money Kyiv needs to keep the lights on, and to pay pensions and salaries, as its war with Russia grinds on. Growing uncertainty over the future of US aid for Ukraine tied to America’s November elections added urgency to the request.
Leaders of the other 26 EU member states had decided that Orban wanted to use future veto threats to give himself more long-term negotiating leverage to win new EU concessions, and at a summit meeting on Thursday, they drew a line. Possibly in exchange for quicker disbursement of the remainder of €20 billion in EU funds already earmarked for Hungary – money currently locked up over corruption and human rights concerns – Orban accepted a plan that allows for future reviews of the Ukraine plan, but without a future veto.
In short, the EU played hardball, and Orban caved.