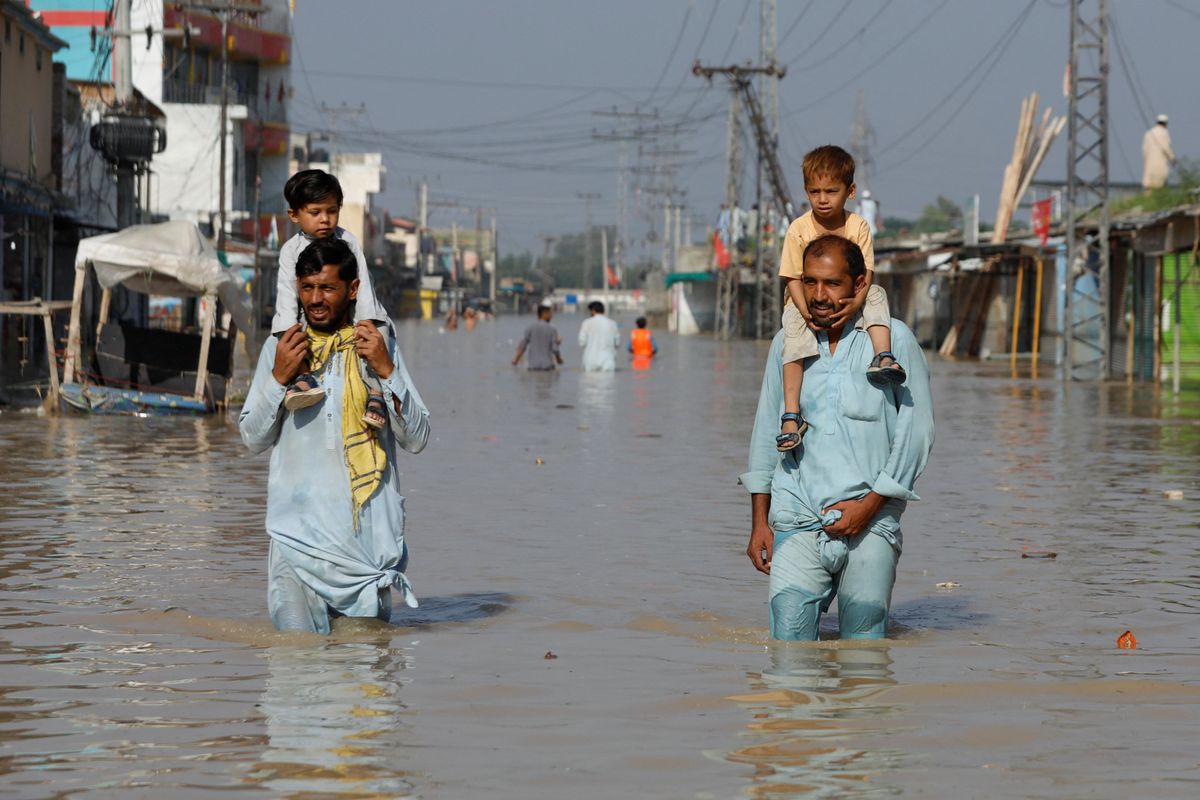
Pakistan is in full-blown crisis mode. More than 30 million people have been affected by unprecedented rainfall and flooding — and one-third of the country is now underwater.
This deadly natural disaster came as Pakistan was already grappling with a series of out-of-hand economic and political crises. What’s the backstory and where might this all be heading?
Background. During the pandemic, many countries took on new debt to insulate their economies from the economic pain caused by rolling lockdowns, closed borders, and business closures. But even before COVID, Pakistan’s economy was struggling to stay afloat as a result of years of economic mismanagement, in large part due to corruption and excessive government expenditure.
Indeed, Pakistan’s public debt surpassed 87% of GDP at the end of 2019, up from about 72% a year earlier. Under former Prime Minister – and cricket champ – Imran Khan, Islamabad was caught in a vicious cycle of borrowing more money from domestic and foreign sources — largely China — to service its existing loans. China, for its part, has also tampered down its investments in the country, in part because its personnel and projects have been targeted by insurgents.
The economic situation was already dire when Pakistan, long thought to be particularly vulnerable to climate change, experienced a series of extreme weather events in recent months. Record-breaking heat caused by global warming exacerbated drought throughout parts of South Asia. Now, deadly flooding has killed 1,100 people in Pakistan and damaged more than 1 million homes.
Unstable politics. With the country’s economy in shambles and Khan at loggerheads with Pakistan’s powerful army, the former PM was ousted in April in a no-confidence vote held by Pakistan’s notoriously corrupt and raucous parliament. Since then, however, sky-high inflation, a plummeting local currency, and unpopular measures like cutting fuel price subsidies have caused current PM Shehbaz Sharif to lose favor with much of the public, perhaps including the military, which directly or indirectly calls the shots in Pakistani politics.
What’s more, Khan has successfully whipped his supporters into a frenzy, holding mass marches on the capital that have resulted in violent clashes between his growing support base and police.
Crucially, the situation is particularly tense at the moment, after Pakistani police recently charged the ousted former PM with violating the anti-terror act for threatening judicial officers in a speech. Khan is currently out on bail after the courts ruled that he couldn't be arrested before Sept. 1. His supporters, meanwhile, have warned they'll march on Islamabad if he's arrested, so things could soon spiral out of control.
An IMF bailout: A double-edged sword
As Pakistan continues to reel from floods, the International Monetary Fund this week approved a $1.1 billion bailout package to help Islamabad stave off default. That’s a good thing for the country, but it won’t come without pain. Pakistanis were furious when the government raised fuel costs — and enforced other austerity measures — to secure the IMF loan.
Pramit Chaudhuri, who heads Eurasia Group’s South Asia desk, believes there will likely be some leeway given the current scale of devastation.
“The IMF has cleared the new tranche,” he says. “The floods will mean the conditionalities will have to be relaxed. For example, the target of achieving a 0.2% GDP primary budget surplus in this fiscal year is a dead letter.”
Islamabad now has the added task of appealing for international aid, with estimates that the floods could cost the economy a whopping $10 billion. Moreover, they’ve destroyed millions of acres of farmland — particularly in the southern provinces of Sindh and Balochistan. This is a catastrophe in a country with a teetering economy and where agriculture accounts for just under one quarter of GDP.
Looking ahead. The Sharif government hopes that the IMF bailout — as well as funds from foreign donors like the Chinese and Saudis — will help ease inflation and get the economy back on the right course before elections, which must take place by Oct. 2023. But is that a pipe dream?
“Imran Khan controls the street, so the government and military are using legal harassment and worse to try and contain him,” explains Chaudhuri. “As long as the economy is stressed he will want to keep up the pressure,” he says, warning that “more social unrest is very likely."