Analysis
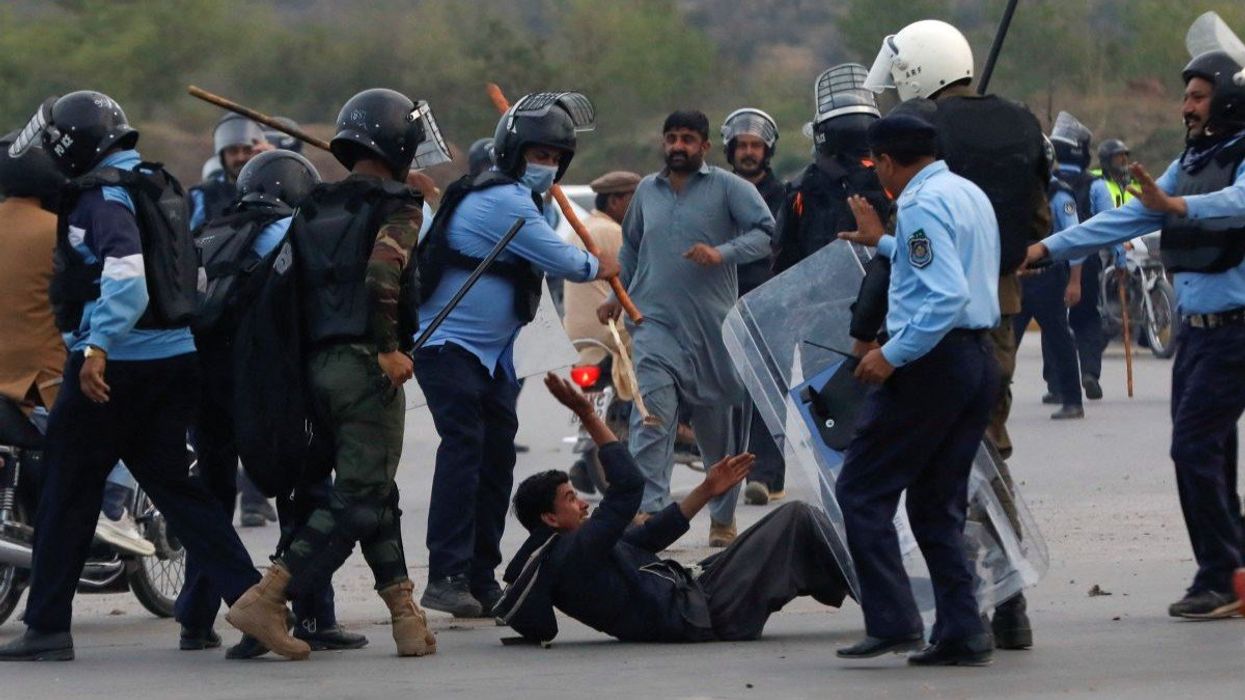
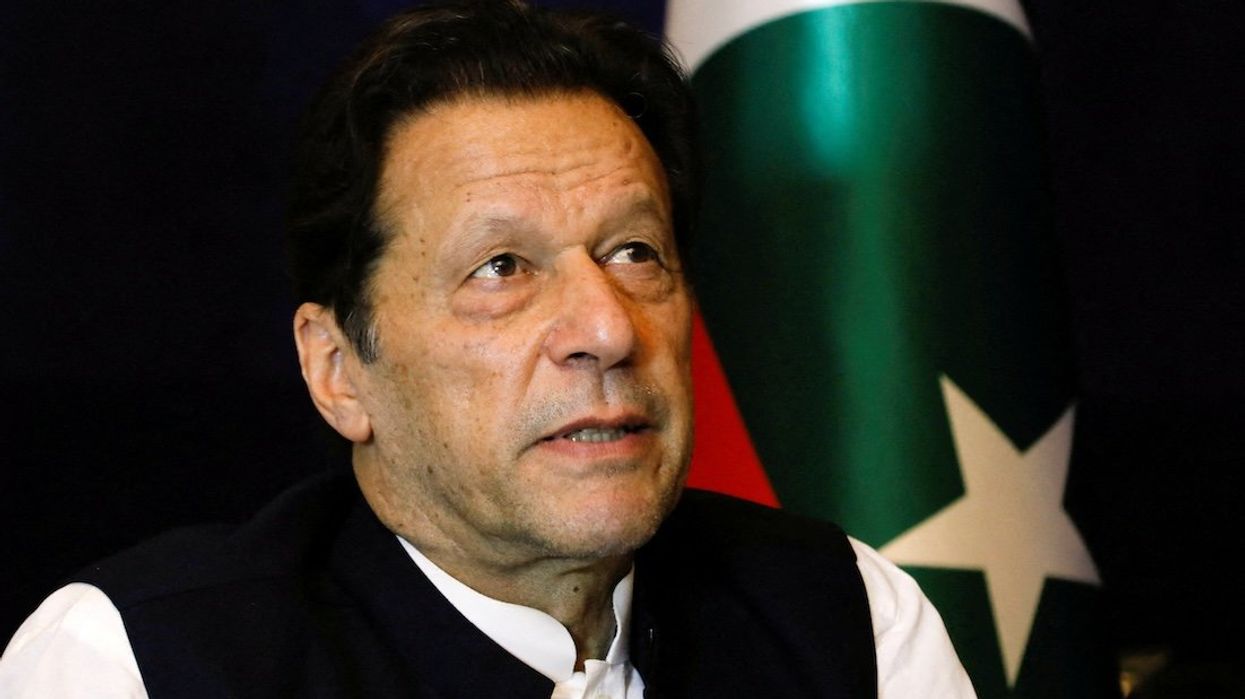
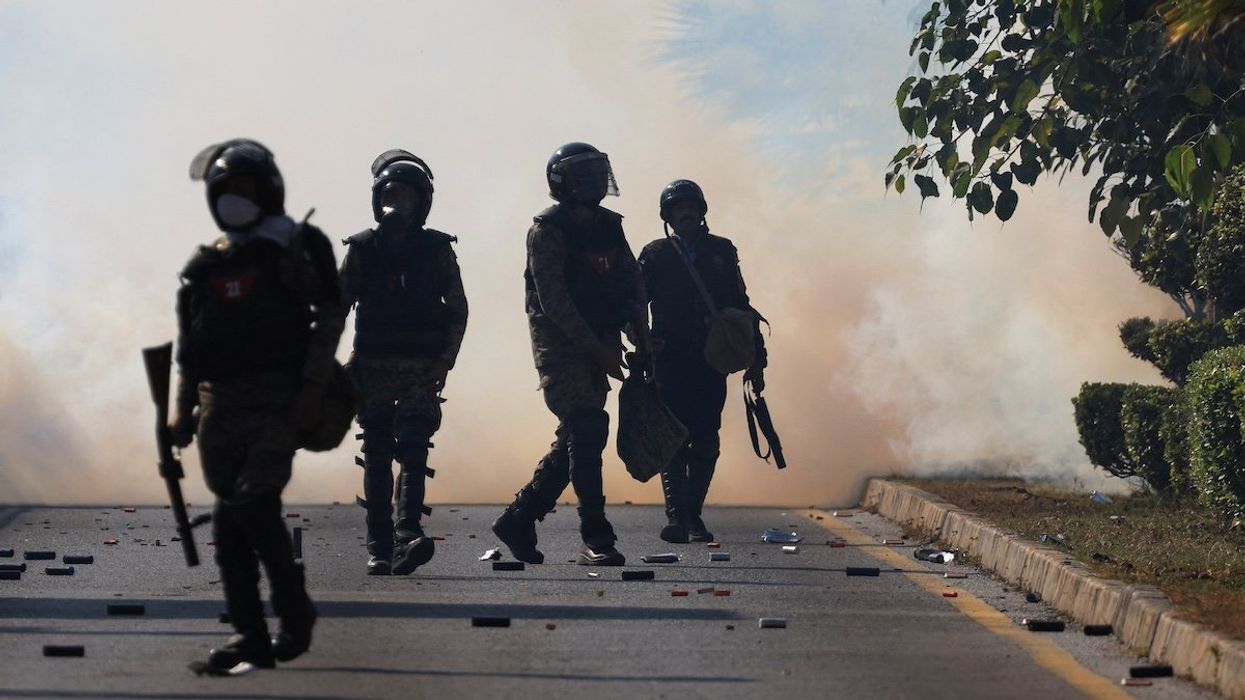
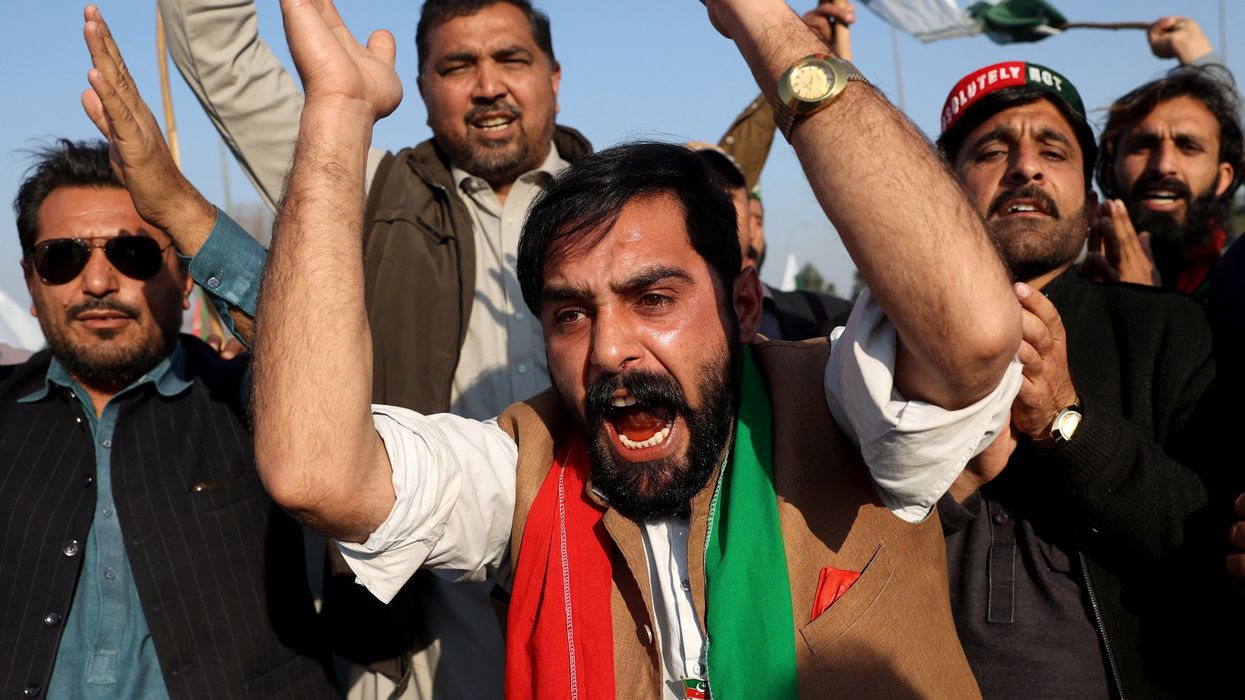
Pakistan slides deeper into autocracy
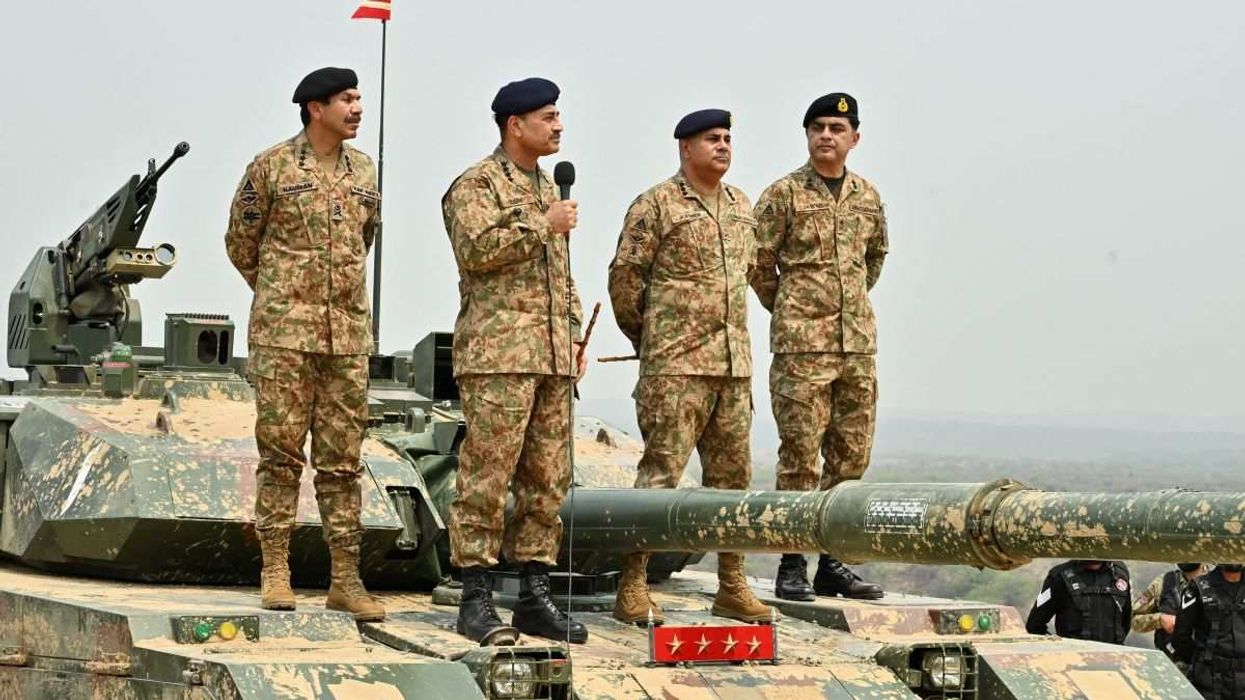
Field Marshal Asim Munir, the country’s de facto leader, consolidated his power after the National Assembly rammed through a controversial constitutional amendment this month that grants him lifelong immunity from any legal prosecution.
Nov 25, 2025