It’s been 75 years since Secretary of State George C. Marshall implored the United States to help Western Europe rebuild after the devastation of World War II. The result was the Marshall Plan, an economic assistance program that saw the US dole out $14.3 billion dollars (the equivalent of $$150 billion today) to help rebuild Western Europe. Sixteen countries benefited from the program.
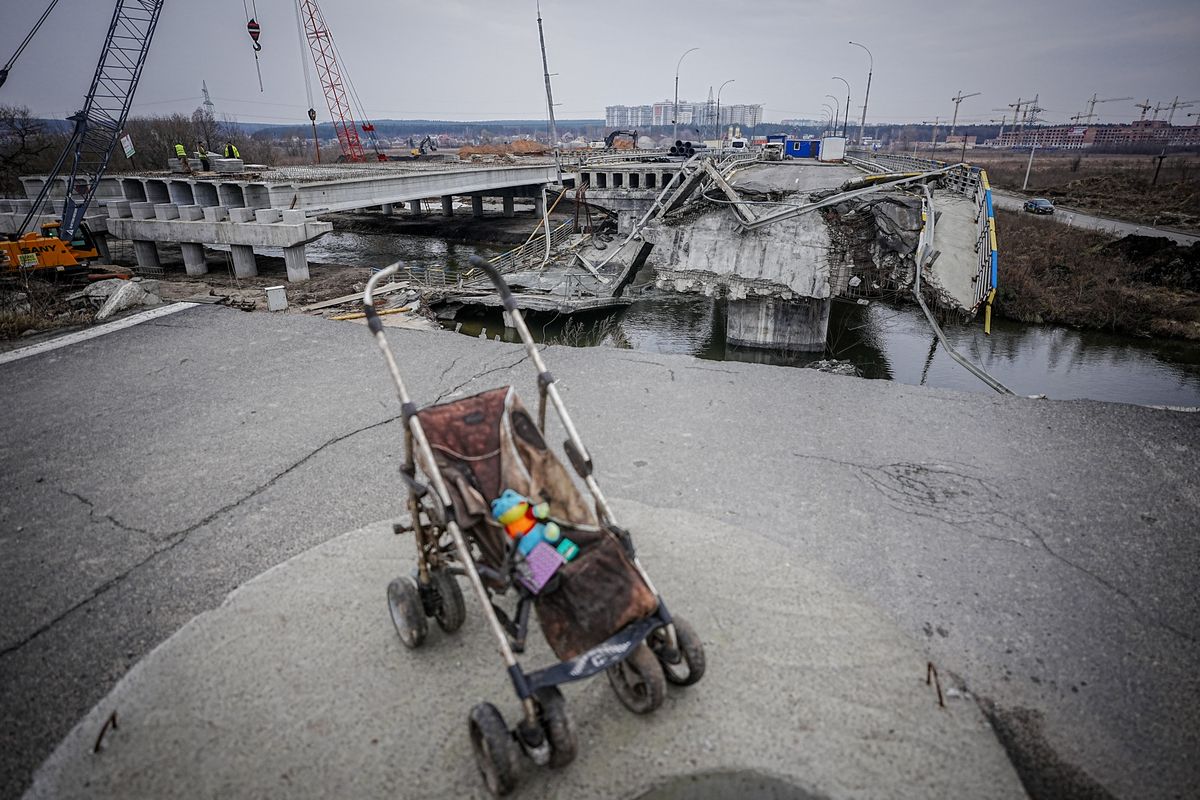
Another major reconstruction effort now looms in Europe as the war rages on in Ukraine. So far, Russia’s invasion has cost Ukraine $135 billion dollars worth of damage. It has wiped out 15 years of economic growth, slashed GDP by 29%, and pushed 1.7 million Ukrainians into poverty. Just cleaning up the rubble over the next decade will cost an estimated $5 billion, according to the World Bank.
The war in Ukraine is the most costly military conflict on European soil since the 1940s. So as world leaders plan for its recovery, the Marshall Plan offers a sound model. Back then, the US needed to boost economies – both in Europe and at home – and ward off the expansion of Soviet communism. This time, the stakes for the US are not as high, and the US isn’t the only country in a position to assist Ukraine.
What motivated the Marshall Plan?
When Marshall proposed his idea, Europe was still reeling from the war – infrastructure in ruins, people starving, economies broken. But having the US lead the way in rebuilding Western Europe wasn’t entirely philanthropic, and the Republican-led Congress did not approve spending $14.3 billion for the good of mankind.
Marshall argued that it was in the US’s best interests to help Europe recover its economies and build a stable democratic region because doing so would create open markets for US goods. It would also help form a strong Western alliance to help keep communism in check.
But does the US have the same interests in Ukraine?
Since the US is the primary provider of military support to Ukraine, says Jason Bush, a senior analyst with Eurasia Group, the feeling in Washington is that the European Union should take the lead in civilian matters. This will eventually include reconstruction.
But the US has said this before: When the Marshall Plan was proposed, many in postwar America were thinking: “Don’t be a Santa Claus.” In other words, Americans felt they had done enough for Europe during the war and that it should now solve its own problems.
Who will pay to rebuild Ukraine?
Rebuilding Ukraine will be far more costly than the Marshall Plan. The World Bank estimates it will cost at least $540 billion, and Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has put a trillion-dollar price tag on rebuilding his country.
Ukraine can’t go it alone. Even before the war, Ukraine had economic woes and was a frequent recipient of IMF support. It has needed IMF assistance 11 times since 1992, and Ukraine’s GDP in 2019 was lower than it was in 1988.
The US won’t foot this bill by itself. Eurasia Group’s Alex Brideau, a Central Asia expert, notes that there is “less political interest in providing massive levels of foreign assistance, in general, which will make it harder for US leaders to build support for a comprehensive aid program.” This is especially likely if a Republican – members of the GOP have voiced concern over US spending in Ukraine – wins the presidency in 2024.
There has also been conjecture that Russia could be forced to pay reconstruction costs. The West could confiscate the $300 billion it has in frozen reserves from the Russian Central Bank. Bush, however, thinks this is unlikely as it would face too many legal hurdles and set a dangerous precedent.
So that leaves the EU, which seems to recognize that it will be the leader in reconstruction efforts. According to the Stockholm Centre for Eastern European Studies, “the EU should play a leading role in organizing donors since the guiding principle of reconstruction is to make Ukraine a fully-fledged EU member state.” This sentiment was echoed in a recent speech by European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen who called for “A Marshall Plan for Ukraine,” though she also called for the private sector to play a significant part in rebuilding efforts.
As for how the EU will manage it, Eurasia Group’s Ali Wyne expects Brussels will face “significant pressure to authorize common borrowing.” That means that the EU would collectively issue loans to Ukraine.
Why should the West rebuild Ukraine?
According to Bush, the EU has a “geopolitical imperative” to rebuild Ukraine “much as rebuilding Western Europe after World War II was seen as a geopolitical imperative for the US at the time.”
Just as Washington worried about the spread of Soviet influence then, today there are fears that an economically unstable Ukraine could be vulnerable to renewed Russian attacks.
In the long term, Ukrainian reconstruction will be geared toward it gaining EU membership. This means reconstruction efforts will go beyond recovering Ukraine’s economy to modernizing its infrastructure and reforming its government institutions. Indeed, a major concern for the EU and the US will be Ukraine’s history of corruption, an issue Zelensky seems intent on rooting out. Improvement on this end will be part of the litmus test for foreign aid moving forward.
The biggest obstacle to any reconstruction plan, of course, is the continued fighting in Ukraine. The Marshall Plan was implemented with Nazi Germany in the rearview mirror; today the end to the fighting is nowhere in sight.
“Even if the fighting has ended, perhaps through some kind of shaky ceasefire,” Bush notes, “the likelihood is that the military threat Ukraine faces from Russia will remain intense.”
__________________
Subscribe to GZERO Daily to get the world's best (and free) global politics newsletter every day.