Graphic Truth
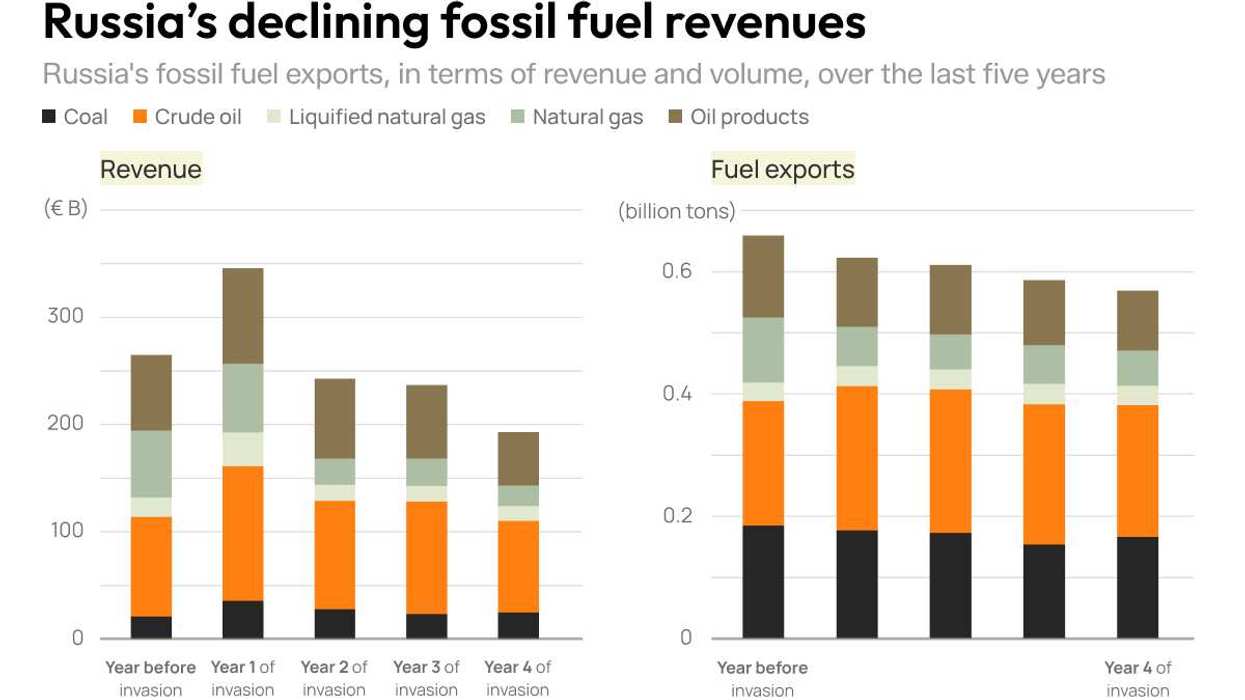
Graphic Truth: Russia’s declining fossil fuel revenues
In terms of volume, Russia’s fossil fuel exports have declined a little since the full-scale invasion of Ukraine began in 2022. In terms of revenue, they’ve dropped significantly.
Feb 24, 2026