News
The Graphic Truth: The European Union's energy mix
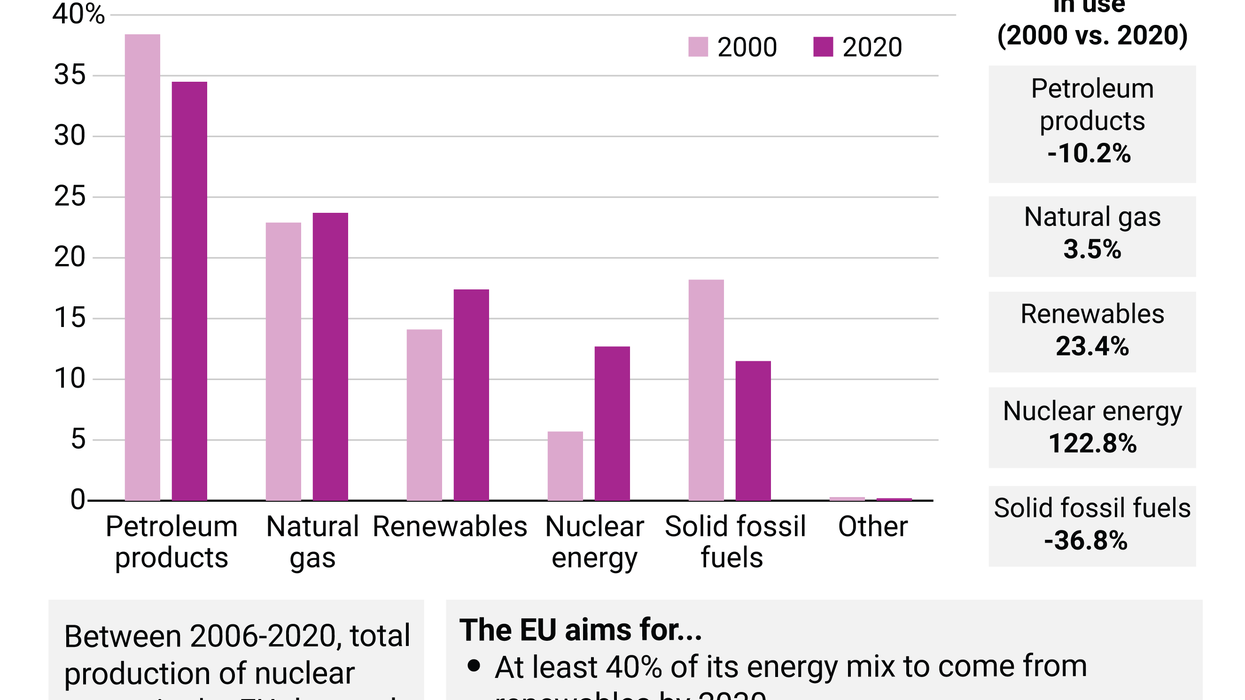
Since Russia invaded Ukraine earlier this year, the European Union has upped its commitments to ditch dirty energy sources, in large part to reduce its reliance on Russian oil and natural gas, and dilute Moscow’s leverage over European geopolitics. But even before the war, EU countries had been working towards diversifying their energy portfolios to meet their ambitious climate goals. In recent years, nuclear power and renewable energy sources have been more widely adopted throughout the bloc, while fossil fuel consumption has dipped. We compare the EU’s energy mix in 2000 and 2020.
Aug 31, 2022