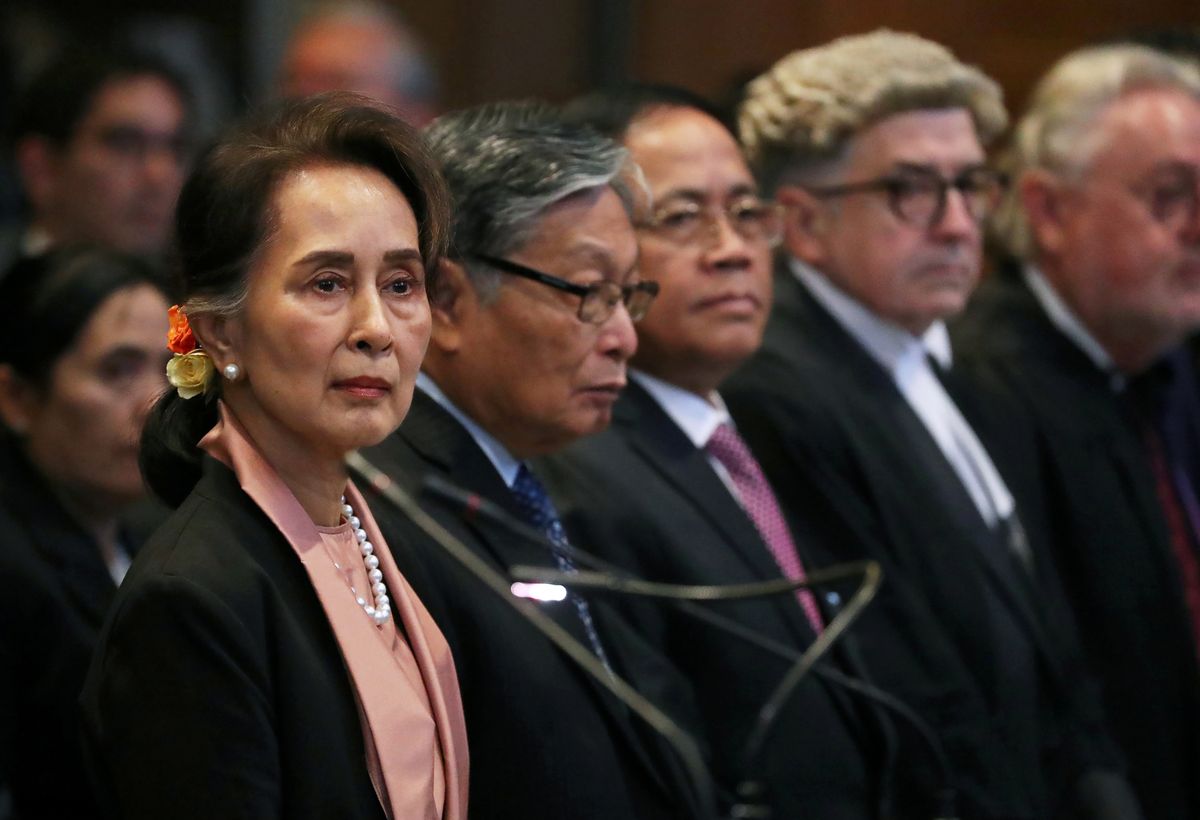
Once a widely heralded human rights champion who was awarded a Nobel Peace Prize in 1991 for advancing democracy in Myanmar, Aung San Suu Kyi has now taken up a different cause: defending her country from accusations of genocide at the International Court of Justice in The Hague.
Yesterday was the court's final day of hearings over that country's military-led crackdown against the Rohingya Muslim minority in 2017, which left thousands dead and forced more than 740,000 people to flee to neighboring Bangladesh. Here's what you need to know about the proceedings.
What is The Hague? It's a city in the Netherlands that is home to the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the International Criminal Court (ICC), two international judicial bodies. The ICJ settles disputes between states over questions of international law. The ICC, on the other hand, investigates and tries individuals who've been charged with war crimes, genocide, and crimes against humanity.
The Myanmar case – These hearings are not focused on the merits of the case, namely, whether Myanmar's military is guilty of acts of ethnic cleansing against the Rohingya people. Rather, the court is being petitioned to issue a provisional injunction ordering Myanmar to protect its remaining Rohingya population. A UN representative recently warned that "crimes with genocidal intent" were still going on in Myanmar's Rakhine state. Though the international court system could take years to rule on a charge of genocide, a temporary injunction could be handed down in the next few days.
Additionally, the ICC has opened an investigation into whether any individuals bear criminal responsibility for atrocities committed against the Rohingya. This effort is impeded, however, by the fact that Myanmar is not a signatory to that court's convention and has no obligation to cooperate with its findings.
Who are the main actors?
Aung San Suu Kyi is not a defendant, but her decision to lead Myanmar's defense, coupled with her checkered political history (she has said that the military operation was used to "clear a locality of insurgents and terrorists" despite ample evidence that the army bulldozed Rohingya villages) has placed her at center stage. She has not only refused to condemn the military's brutal assault on the Rohingya, she has justified the onslaught as a legitimate counterinsurgency against Muslim militants. Suu Kyi continued to defend the military brass this week – the same military that for years kept her under house arrest – scolding "impatient international actors" for lacking understanding of her country's complex social and ethnic composition.
Suu Kyi and the military: strange bedfellows Suu Kyi is Myanmar's de facto political leader, though she is prohibited from serving as president due to an arbitrary constitutional amendment. In practice she has little control over Myanmar's army, which governed the country alone until its leaders reached a power-sharing agreement with Suu Kyi and her party in 2015. Myanmar's complex power-sharing arrangement means that any provocative move by Suu Kyi's pro-democracy camp risks enraging the army, and the resurgence of military domination in Myanmar.