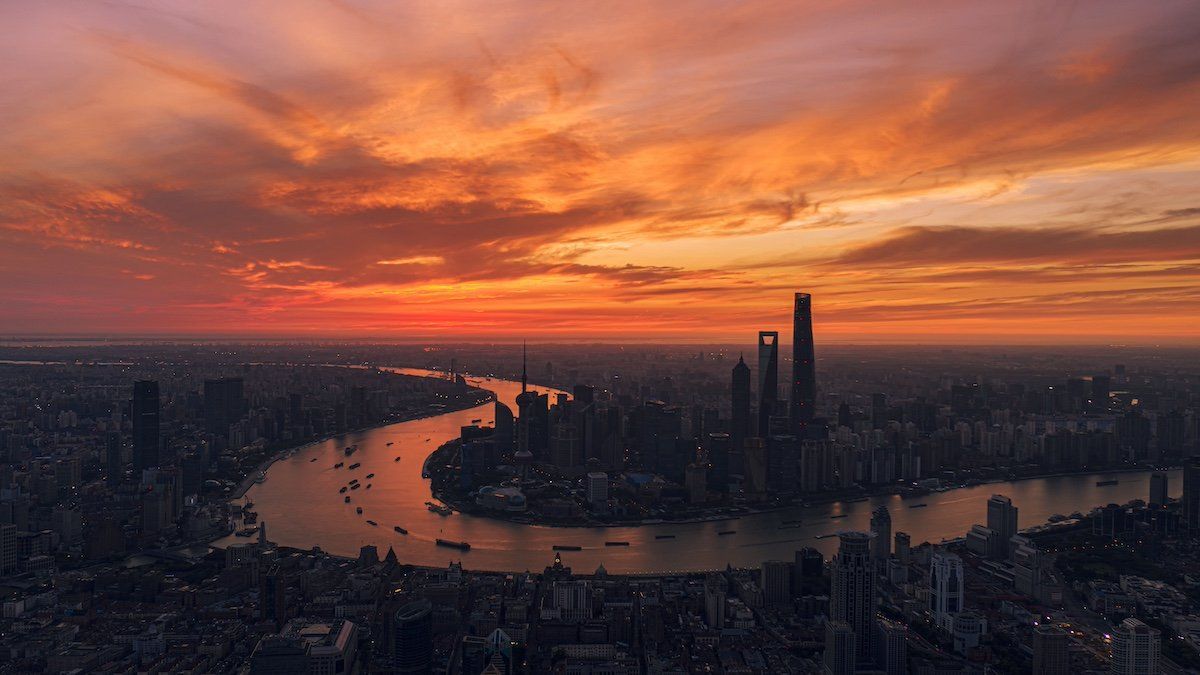
It’s been a bad month for Chinese stock markets. Since Jan. 1, the Hang Seng China Enterprises index has plunged 11%, after losing 14% last year. The benchmark CSI 300 index for domestically traded stocks has shed more than 5%, after accounting for the renminbi’s drop against the dollar. A slide that started in 2021 has now erased $6.3 trillion from Chinese and Hong Kong equities, a sell-off that is reshaping geopolitical dynamics in Asia, particularly for India.
Compared to China, India has emerged as a darling of global investors, with indices like the Nifty 50 and BSE Sensex reaching record highs. JPMorgan hails India as its number one market in Asia, crediting companies adopting a “China plus one” strategy. Foreign investment is up, with firms like Apple, Maruti Suzuki, and a host of drug companies increasing production on the subcontinent.
What’s driving the switch?
China’s “economic malaise” has been making headlines for some time. Its real estate sector is in deep crisis, while unemployment and disillusionment among young people are rampant. While Beijing claims the country enjoyed economic growth of 5.2% last year, not all economists believe the numbers. All of which makes investors nervous and looking for other options.
What could this mean for the rest of the world?
While some observers think a slowing economy could temper China's aggressive foreign policy and trade practices, others think it could up the military ante for President Xi Jinping. Economic woes could undermine Xi’s leadership, creating the need for a distraction or rallying point to keep his hold on power. That could spell trouble for some of China’s neighbors such as Taiwan and the Philippines.It could also make it more difficult for China to continue using its Belt and Road Initiative to curry favor with governments in the region. Since 2018, China has committed or invested over $150 billion in the economies of Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Pakistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Afghanistan, and is now the biggest foreign investor in Maldives, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. If China’s money runs low, so could its influence – opening the door for rival powers, like India, to fill the vacuum.