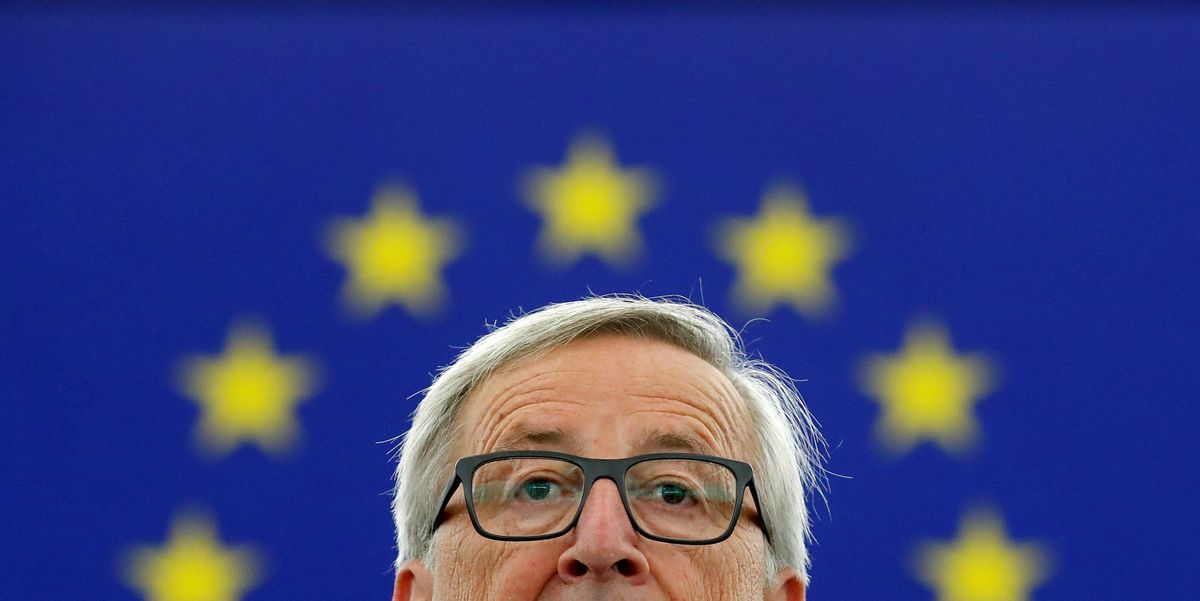
Earlier this morning, European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker delivered the final State of the European Union address of his tenure from the European Parliament in Strasbourg. The speech included a few important new proposals but was mostly filled with flowery rhetoric and calls for further solidarity within the 28-member bloc.
Citizens across Europe, for their part, mostly tuned out. And who can blame them? Bland technocratic pronouncements aren’t exactly a draw these days, particularly when domestic politics are aflame across the continent.
So what do Europeans care about these days; how do they see their future; and what – if anything – do they expect from Brussels?
Here’s some perspective, from three distinct vantage points:
Pocketbook issues at home. Europeans are worried, first and foremost, about their own economic well-being. In 14 countries within the EU, respondents listed unemployment or health and social security as the top challenge facing their national governments, according to the latest Eurobarometer survey. But perceptions of economic well-being vary widely within the Union: while 90 percent of Germans and 86 percent of Swedes describe the state of their country’s economy as “good,” only 11 percent of Hungarians and 2 percent of Greeks feel similarly.Brussels and borders. When it comes to their expectations of Brussels – that is, those distant technocrats – immigration outstrips all other issues as citizens’ top concern for the bloc as whole. They want Brussels to better secure Europe’s borders. In Hungary and Italy, national governments are actively testing the bounds of what the EU is willing to tolerate in terms of the treatment of immigrants.
It’s no coincidence that Juncker announced in his speech today a plan to strengthen Europe's border forces, by adding 10,000 new guards by 2020, to deal with these concerns. At the same time, the European Parliament is set to vote to put into motion a process to punish Hungary for flouting EU norms on migrant policy. But stripping it of its EU voting rights would a require a unanimous vote, which remains unlikely.
Trust in the European Union is still high. Europeans broadly support the EU’s core pillars—including the euro currency and free movement of people across internal borders. In fact, even if they find Brussels’ sprawling bureaucracy dull and tedious, a growing proportion of Europeans trust EU institutions more than national ones, even if those numbers vary somewhat from country to country. In every country in the Union, a vast majority (over 70 percent) continues to support the free movement of people across national borders. A majority in all 28 member-states say they “feel they are citizens of the EU.”
The bottom line: Europe is coping with many challenges today, from the rise of far-right euroskeptic governments, to an uneven economic recovery, to Brexit negotiations – but trust, support, and optimism about the bloc’s future has improved as a whole among its citizens over the past few years, whether they pay attention to what Brussels has to say or not.