What We're Watching
Authorities try to arrest impeached South Korean president
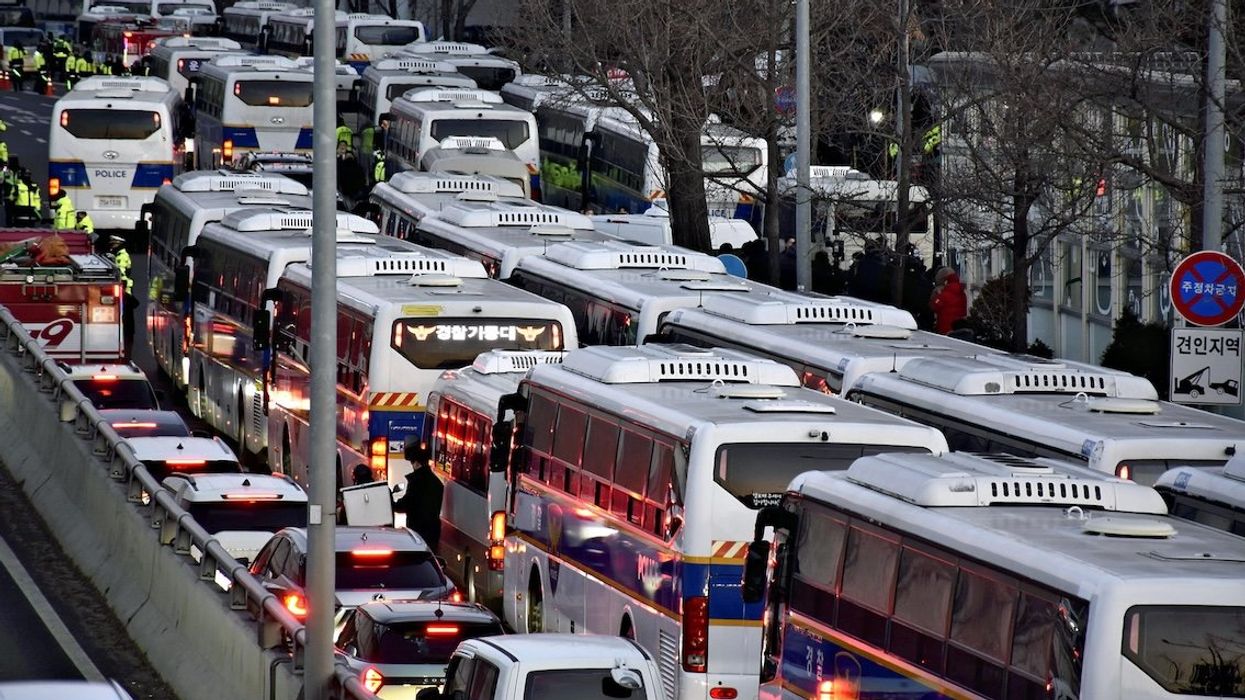
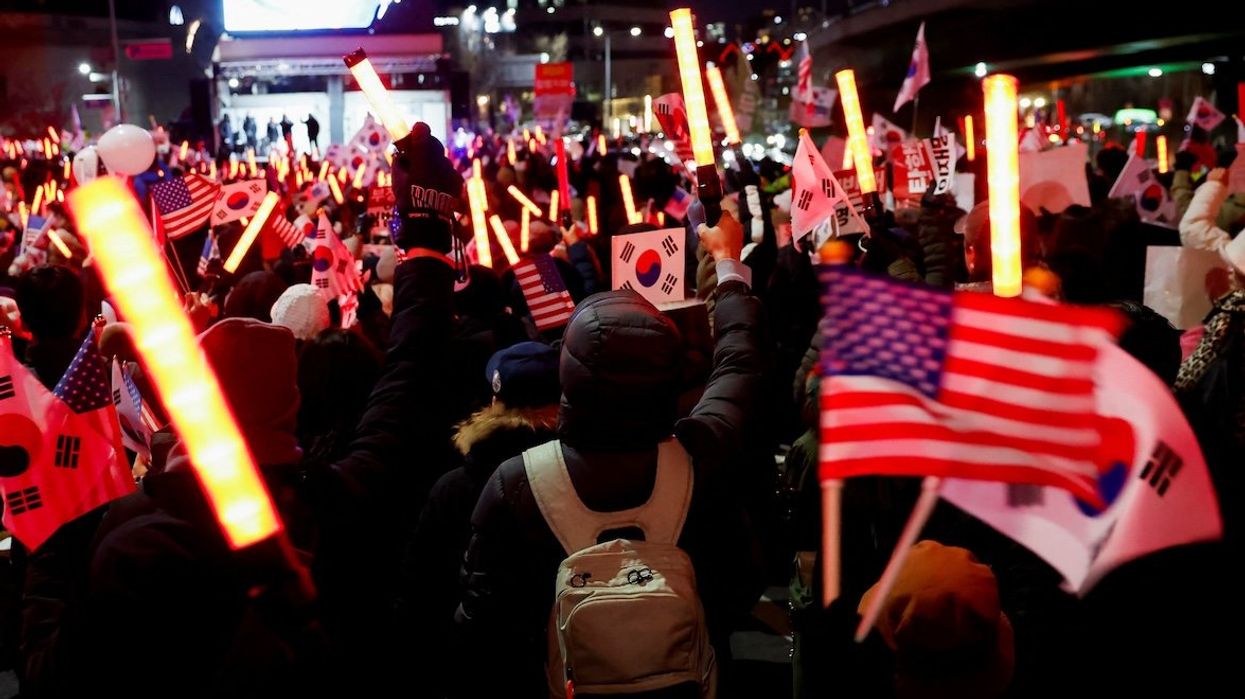
It’s a standoff. Officers from South Korea’s anti-corruption authority arrived at the residence of impeached President Yoon Suk Yeol’s on Friday morning to serve an arrest warrant over his attempt to impose martial law last month. Confronted by a crowd of Yoon supporters and a military unit, they were unable to execute the warrant.
Jan 03, 2025