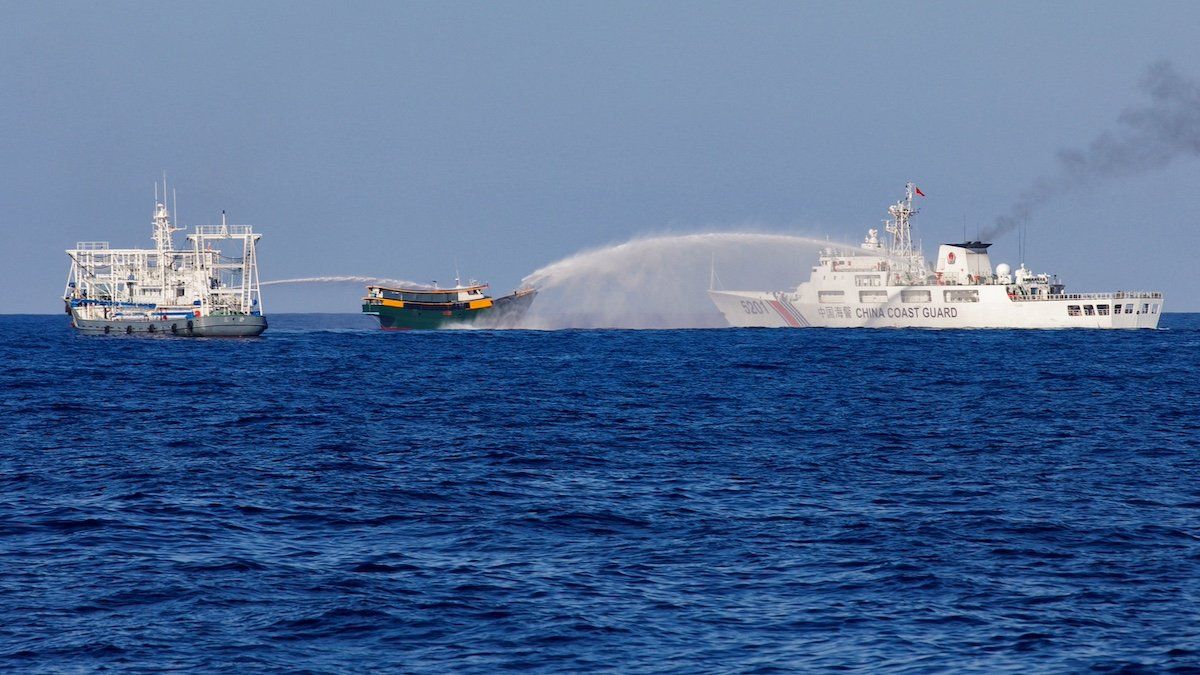
On Saturday, a Chinese coast guard vessel blocked two Philippine government ships near the country’s coast for over eight hours. The incident occurred at the boundary of the nine-dash line, a demarcation Beijing uses to assert its claims to the waters but which was dismissed by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague in 2016.
This latest dustup appears to be Beijing’s response to last week’s high-profile Washington summit between US President Joe Biden, Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida, and President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. of the Philippines. The three leaders expressed “serious concerns about the People’s Republic of China’s (PRC) dangerous and aggressive behavior in the South China Sea,” and Marcos Jr. stressed the trilateral relationship would “change the dynamic” in the region.
“Any attack on Philippine aircraft, vessels, or armed forces in the South China Sea will invoke our Mutual Defense Treaty,” Biden said.
Beijing has already engaged in risky blockings and using water-cannon attacks that have injured sailors. The Philippines has become increasingly vocal about its sovereignty claims, especially around strategic areas including Second Thomas Shoal, a point of recurring friction between Philippine forces and the Chinese Coast Guard. On Thursday, China’s foreign ministry accused Marcos of reneging on a bilateral understanding on the Second Thomas Shoal issue, setting the scene for Saturday’s standoff – and, no doubt, more to come in future.