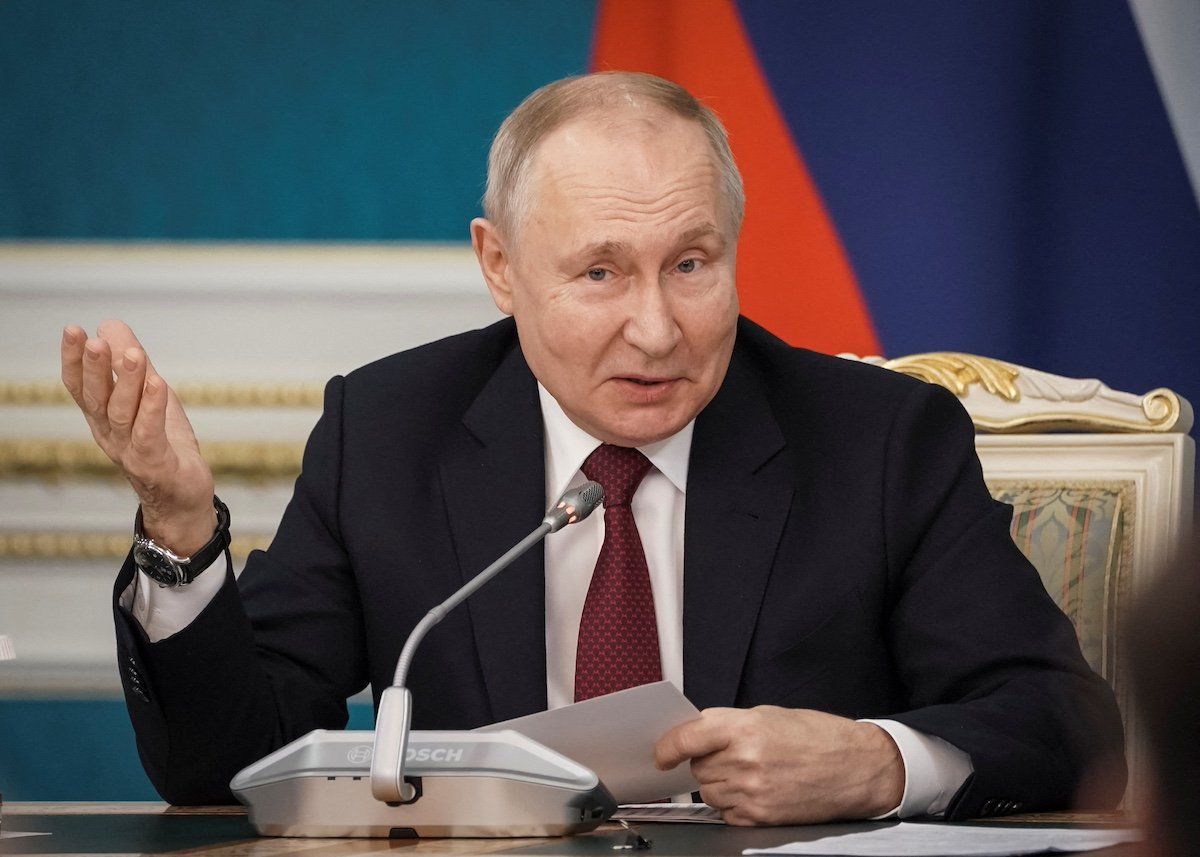
Despite moves to isolate Moscow economically and politically following its February 2022 invasion of Ukraine, the two-year anniversary of the war looms. Russian President Vladimir Putin maintains a firm grip on power, and Moscow continues to operate in unrestrained ways both at home and abroad.
On Tuesday, Putin approved new restrictions on media coverage ahead of Russia’s presidential elections next March. The Russian leader, who has already taken myriad steps to squash the free press in Russia, is expected to run for a fifth presidential term.
Much of the country’s independent media has gone into exile since Russia invaded Ukraine and the Kremlin accelerated its crackdown on free expression and dissent. Putin signed a law not long after the invasion that barred spreading “false” information on the military, effectively criminalizing criticism of the war. In Putin’s Russia, journalists who’ve provided accurate reporting have ended up imprisoned and in some cases killed.
Under the new rules, only journalists employed by registered media outlets can cover Central Election Commission sessions. The law also imposes restrictions on the coverage of commission activities at military bases and areas under martial law. The changes appear unlikely to drastically change an already undemocratic process that has helped Putin retain power for 24 years but are yet another sign that the 71-year-old Russian leader is taking steps to stay in the Kremlin.
Meanwhile, Russia continues to skirt US-led economic sanctions designed to cut off oil revenue that helps fuel Moscow’s war machine. Ukraine’s allies have capped Russian oil barrel sales at $60, but Western officials told the Financial Times that almost no oil from Russia is sold under that limit. Russia has found various ways to circumvent the cap, including via the help of a “shadow fleet” of oil tankers that employ deceptive tactics and have murky ownership.
Ukraine pushed to the back pages: As support for Ukraine slips in the US, there are concerns in Kyiv and Washington that Putin is benefiting from attention being diverted by the Oct. 7 attacks and Israel’s campaign to eradicate Hamas in Gaza.