GZERO North
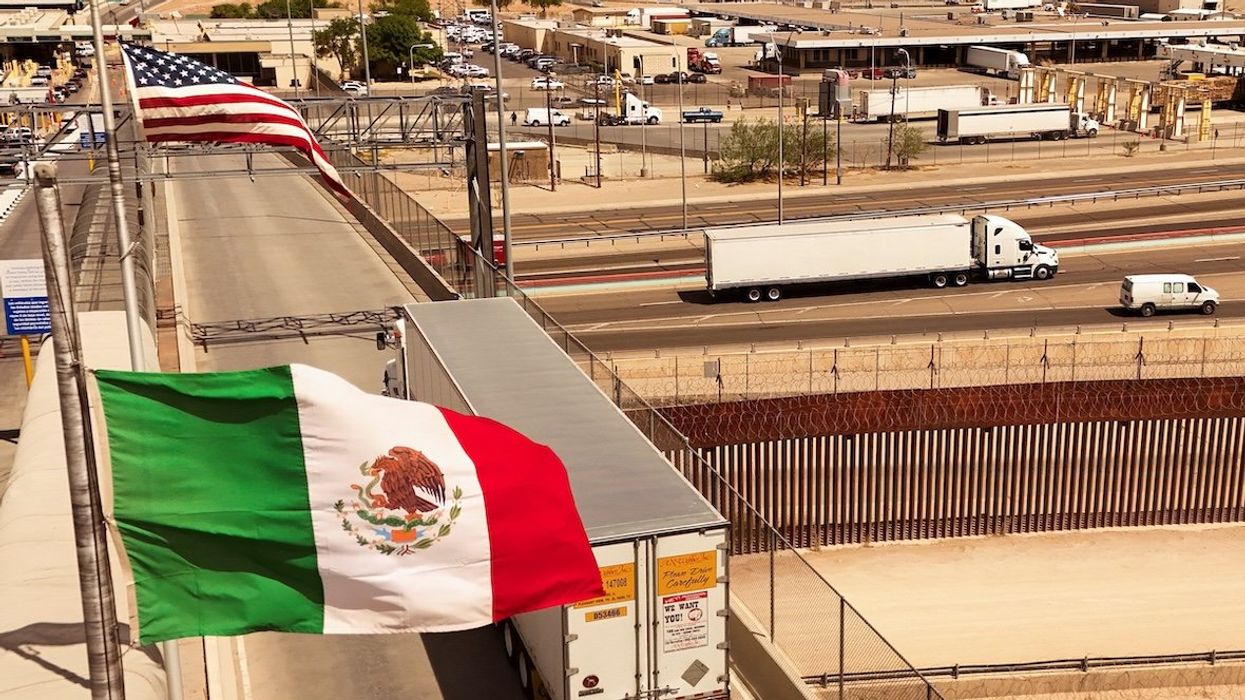
White House claims win on border security but stays mum on tariffs
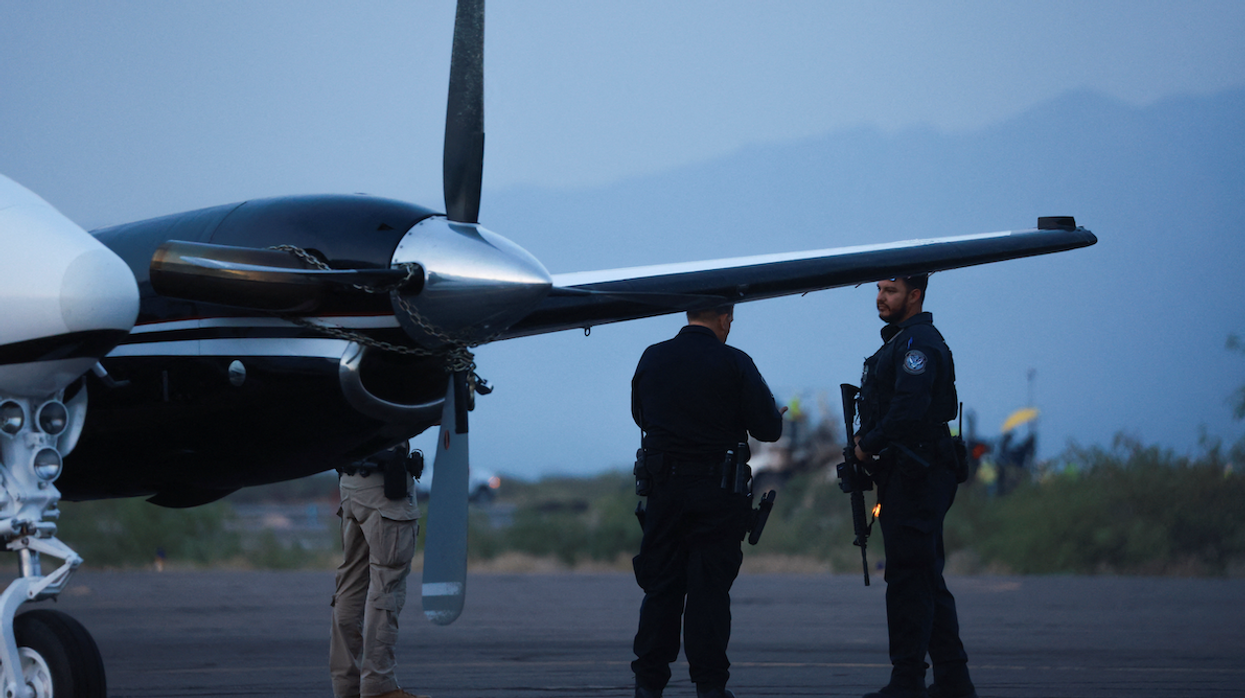
When Donald Trump first threatened to slap tariffs on Canada in December, he cited fentanyl and border security as two ostensible reasons for the duties, which followed soon after. Observers have pointed out that very little fentanyl has been found to cross the US-Canada border, but it didn’t seem to change any minds in the White House.
Apr 24, 2025