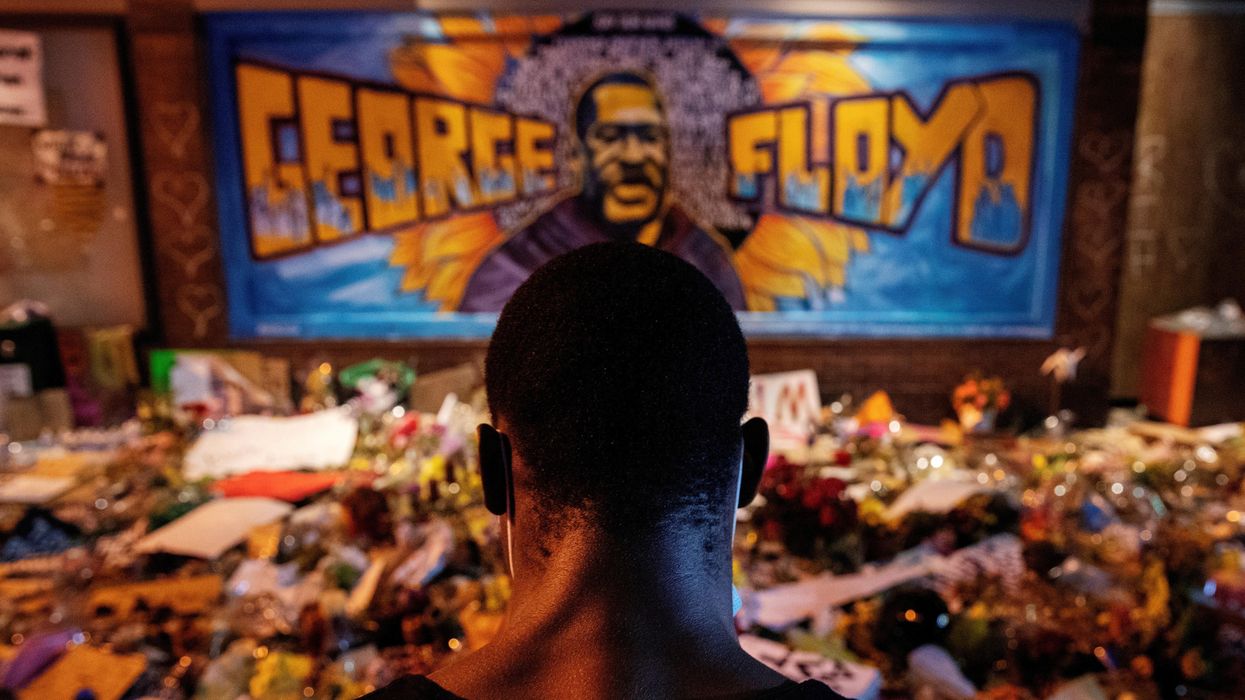GZERO North
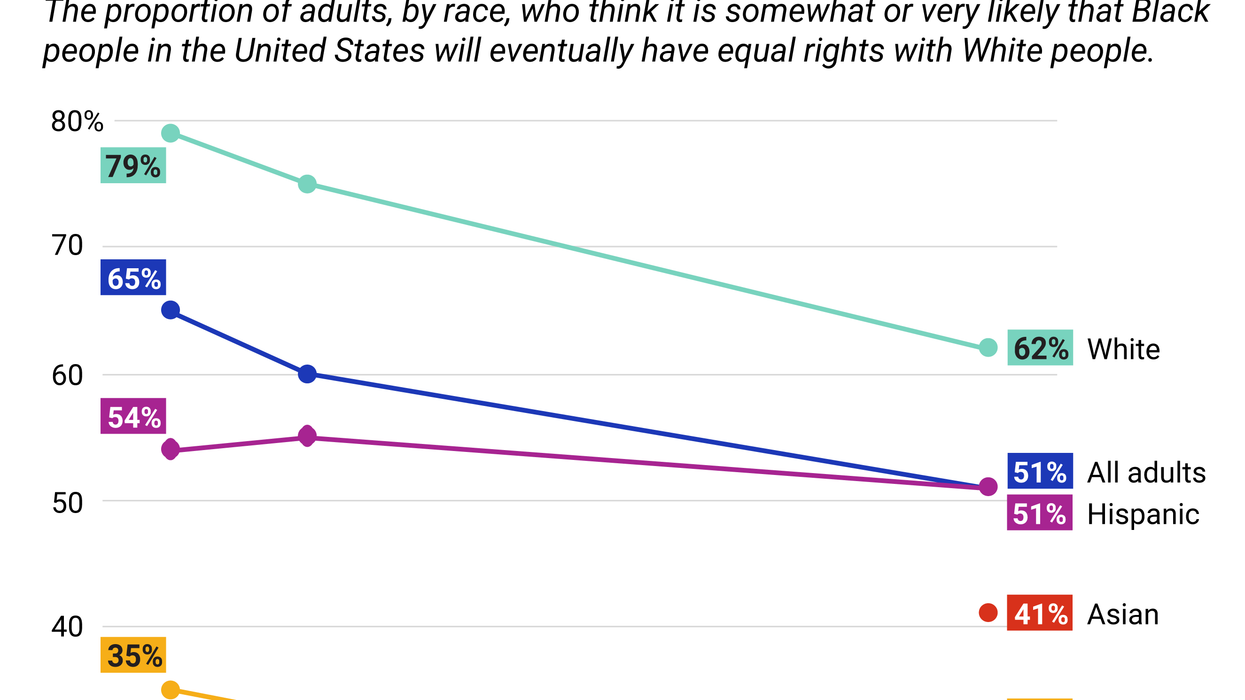
Graphic Truth: Five years on from George Floyd, pessimism sets in
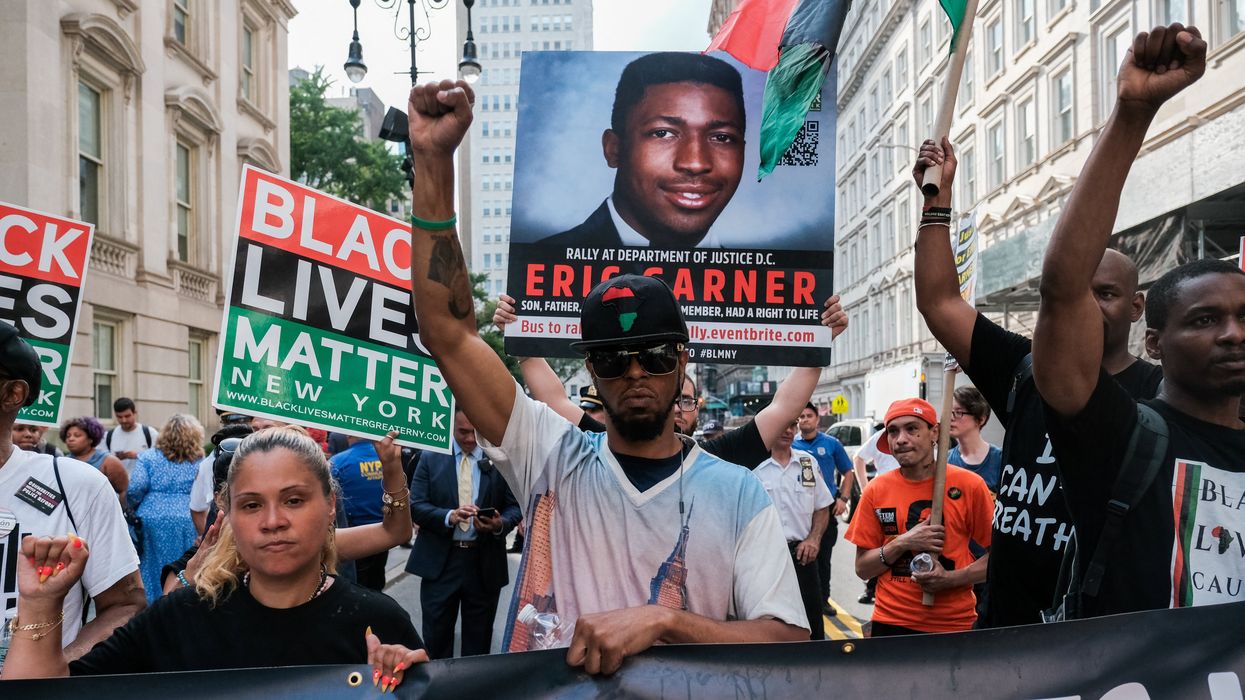
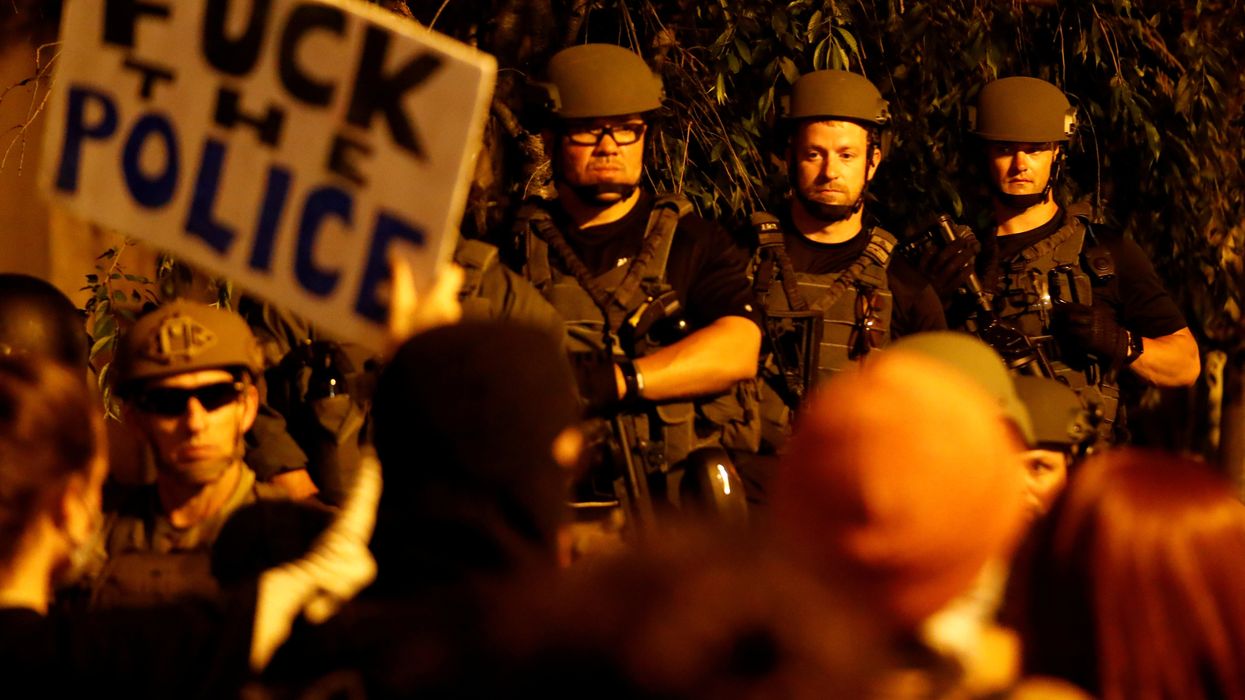
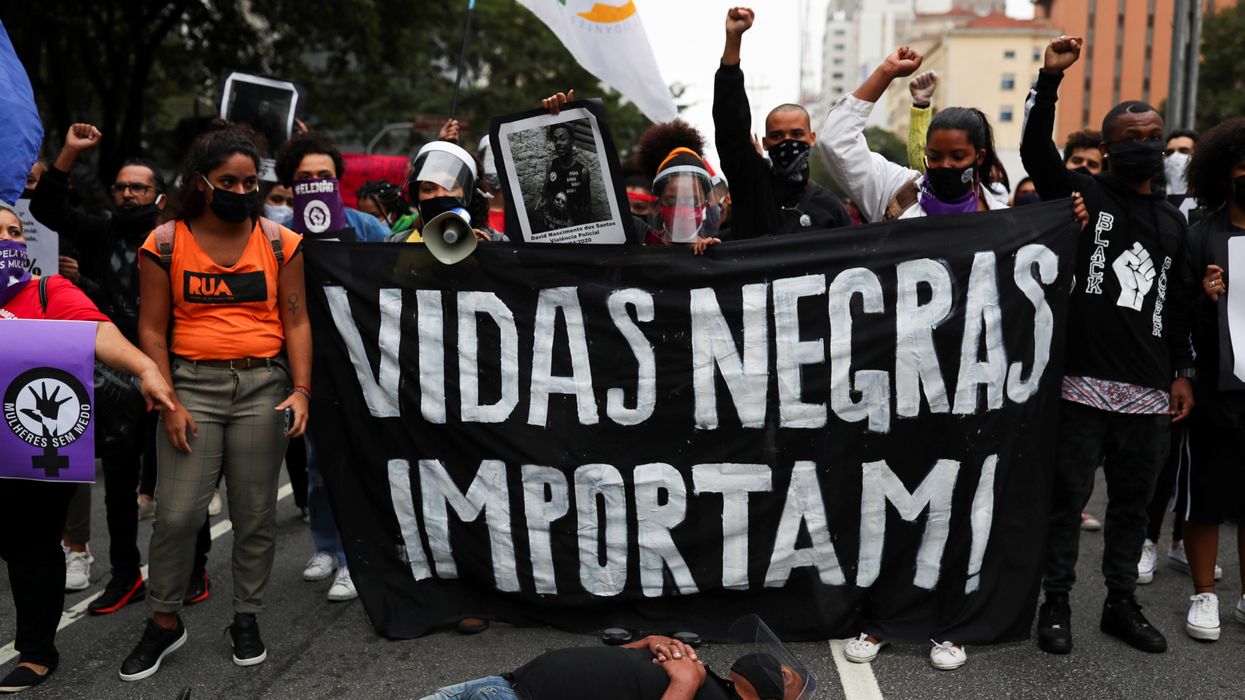
Five years ago this Sunday, a white police officer was filmed killing George Floyd, a Black man, in Minneapolis during an arrest. Hopes for addressing racial inequalities, though, have only dropped lower since.
May 22, 2025