What We're Watching
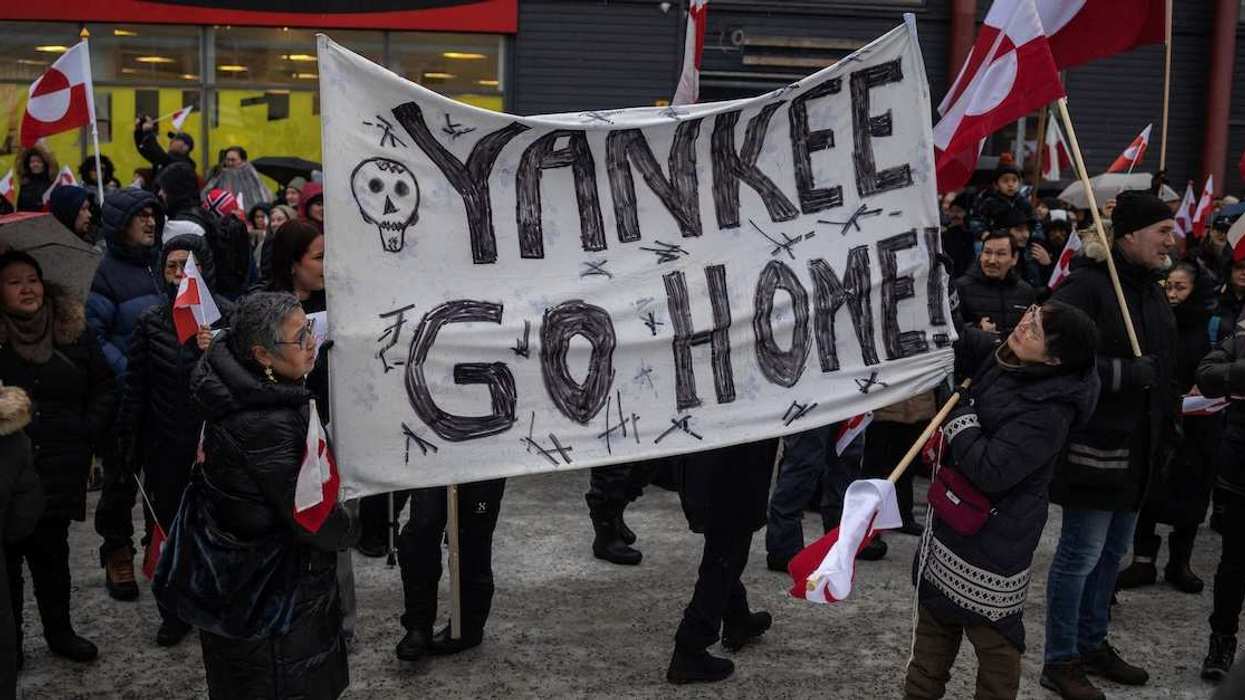
What We’re Watching: Trump says there’s a Greenland deal framework, Iran’s regime say protests have ended, Sheinbaum’s extraditions spark controversy at home
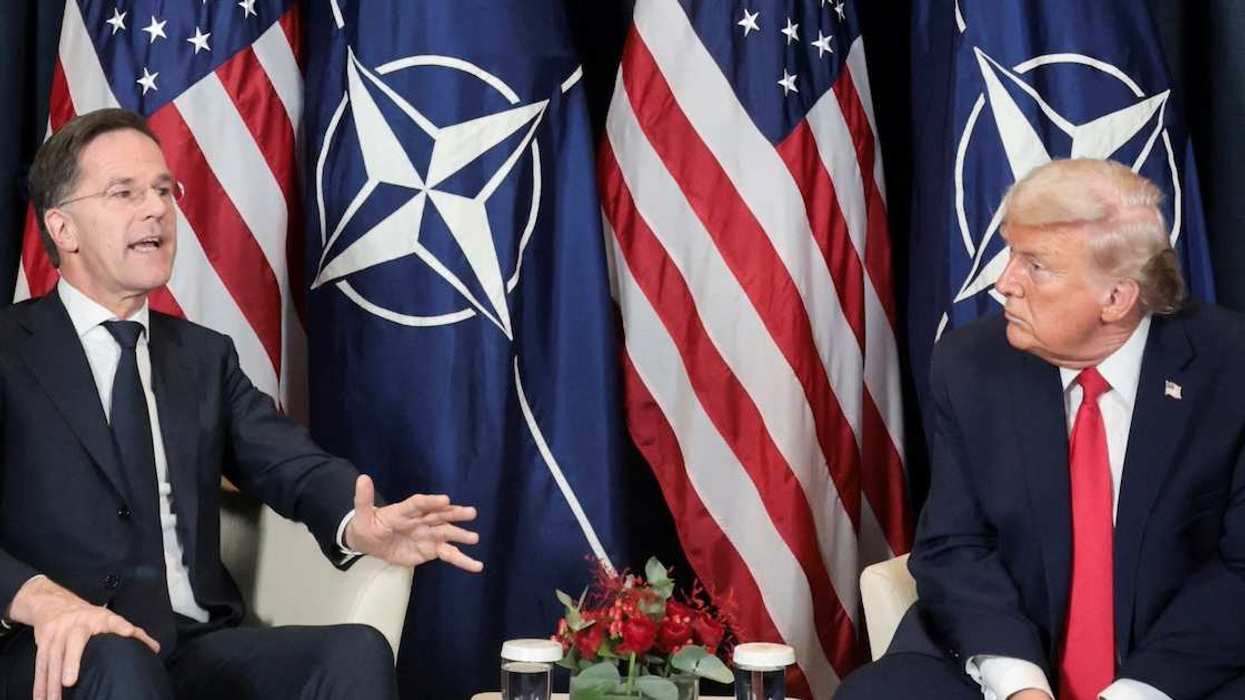
After saying numerous times that he would only accept a deal that puts Greenland under US control, President Donald Trump emerged from his meeting with NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte singing a different tune.
Jan 22, 2026