What We're Watching
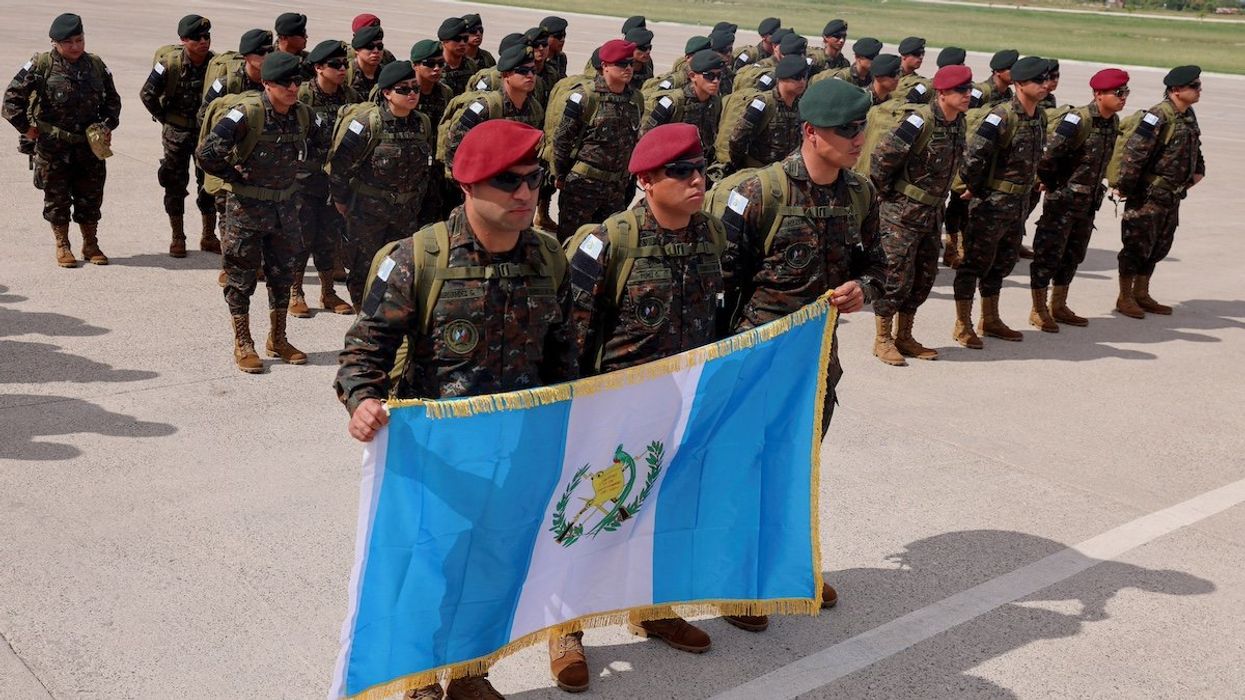
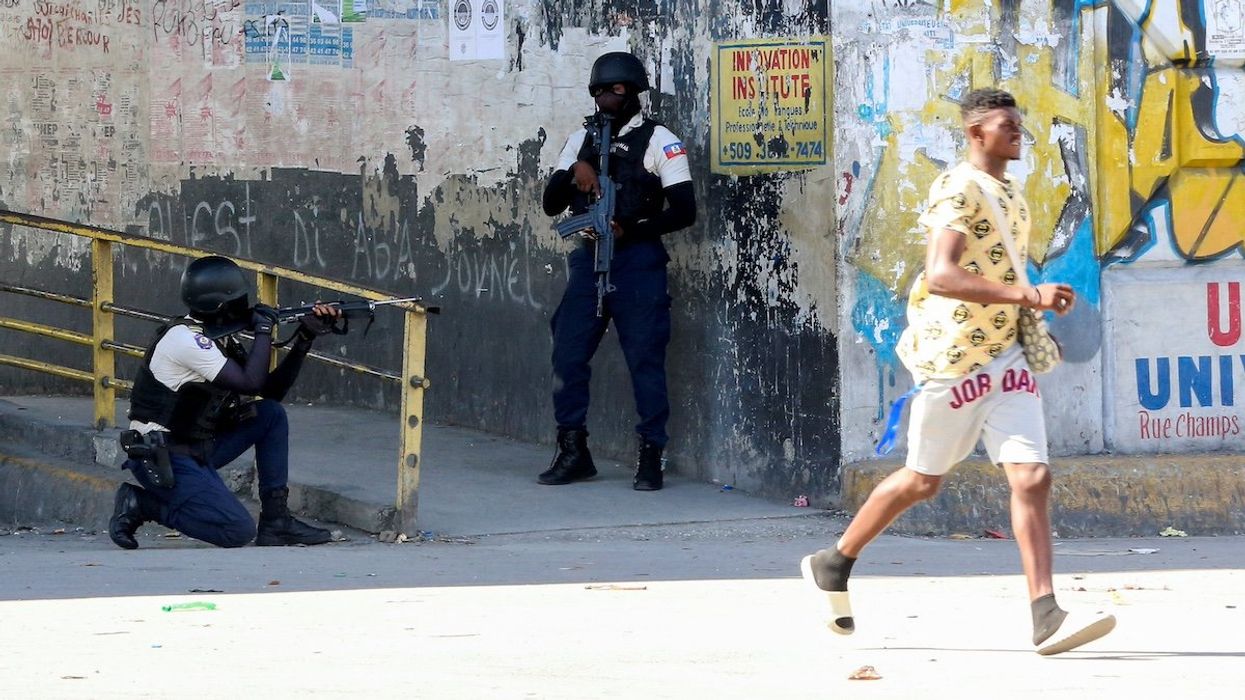
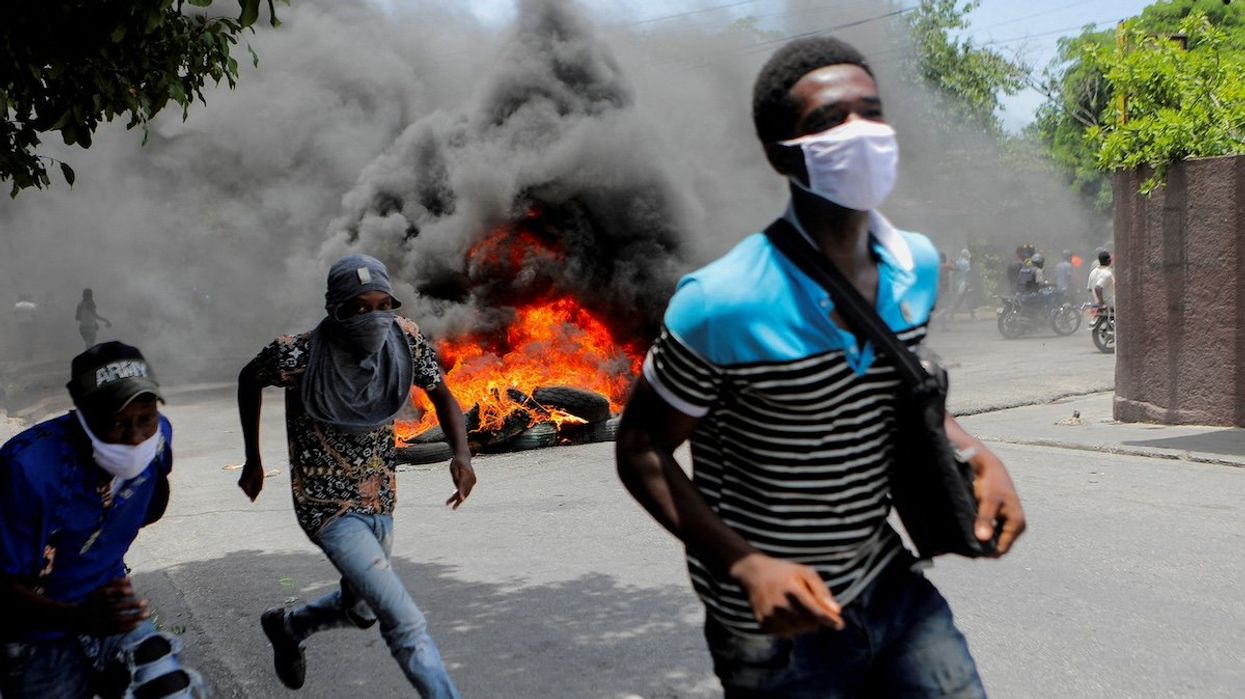
Guatemalan troops arrive in Haiti to combat gang violence
A total of 150 Guatemalan soldiers landed in Haiti on Friday and Saturday to join a United Nations-backed mission led by Kenya aimed at curbing rampant gang violence.
Jan 05, 2025