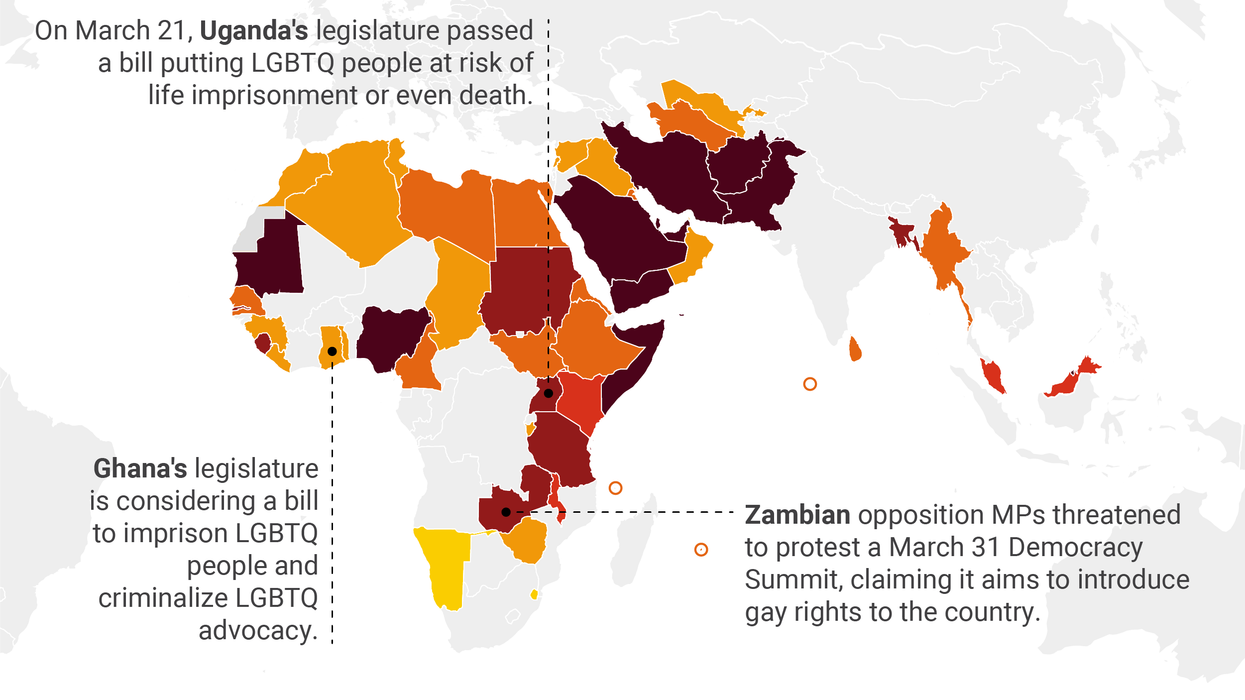
Hard Numbers
Ukrainian Olympian disqualified for political helmet, Falling cocoa prices hit Ghana, US troops to deploy to Nigeria, and Lufthansa goes on strike
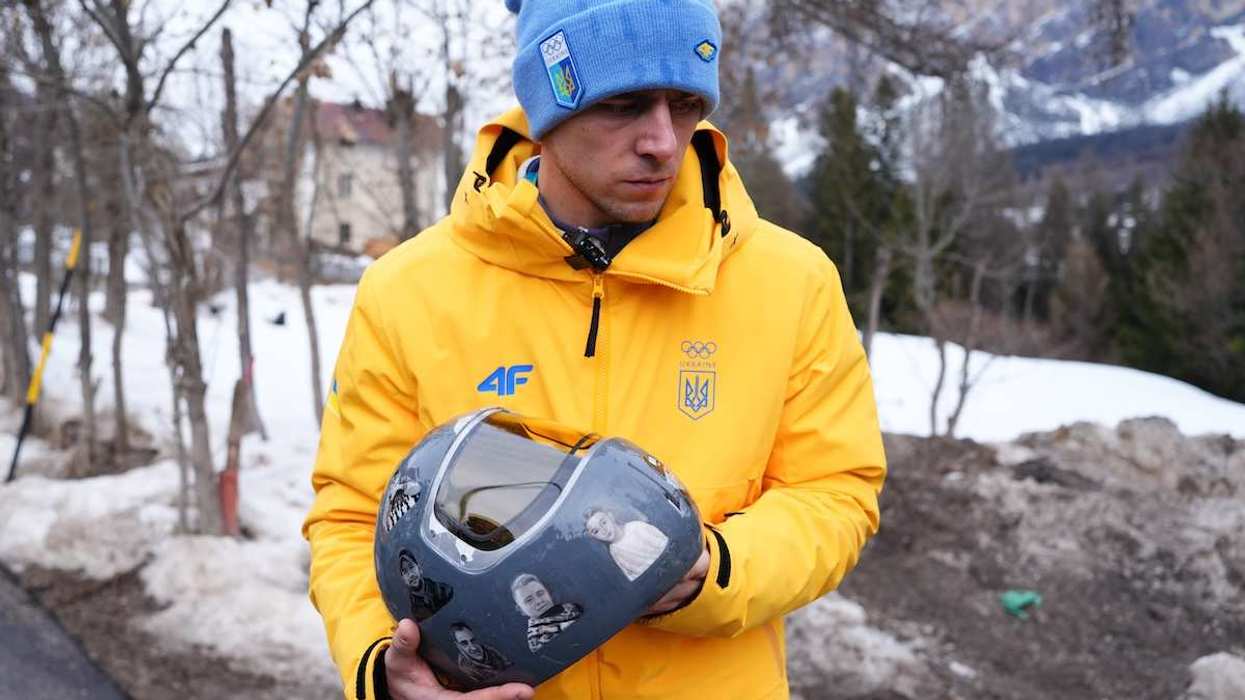
20: The number of fallen Ukrainian athletes and coaches depicted on a Ukrainian skeleton racer’s helmet at the Winter Olympics, which prompted the International Olympic Committee (IOC) to disqualify him on Thursday.
Feb 12, 2026